At the heart of any cement plant, the rotary kiln's cylinder is the massive, rotating steel tube that serves as the primary reactor for transforming raw materials into cement clinker. It is far more than a simple container; it is an engineered environment designed to contain extreme heat, facilitate chemical reactions, and convey material in a precisely controlled manner.
The cylinder's core function is not merely to hold material, but to act as an integrated system for conveyance, heat exchange, and chemical reaction. Its design, from its incline to its protective lining, is a masterclass in process engineering tailored for a single purpose: the efficient production of high-quality clinker.
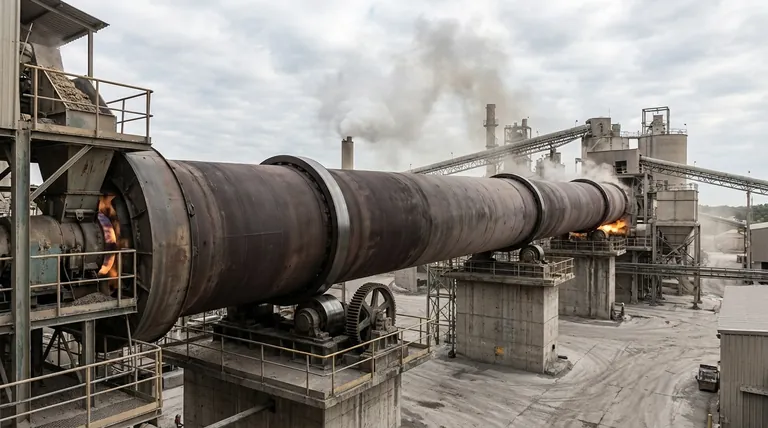

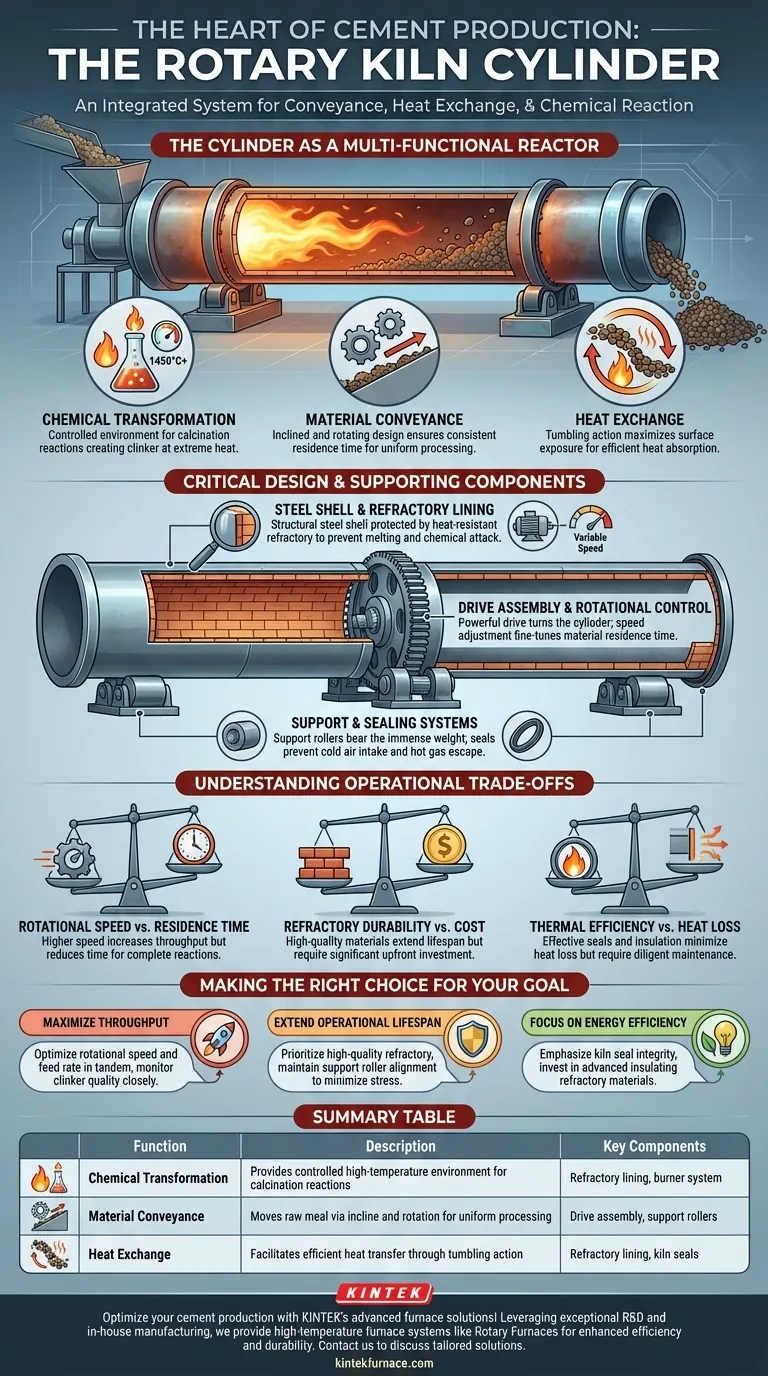
The Cylinder as a Multi-Functional Reactor
Often called the "heart of the cement factory," the cylinder is where the critical transformation of raw meal into clinker occurs. Its design allows it to perform several functions simultaneously.
A Vessel for Chemical Transformation
The primary purpose of the cylinder is to provide a controlled environment for the high-temperature chemical reactions, or calcination, that create clinker. It contains the raw material as it is heated to temperatures often exceeding 1450°C (2640°F).
This extreme environment is what drives the chemical synthesis necessary to produce the compounds that give cement its strength.
A System for Material Conveyance
The cylinder is installed at a slight incline, typically 1-4 degrees from horizontal. This incline, combined with the slow, constant rotation, causes the material to tumble and flow from the upper feed end to the lower discharge end.
This movement is not accidental. It ensures a consistent residence time in the kiln, exposing all material to the required heat for the necessary duration and promoting uniform processing.
An Engine for Heat Exchange
The cylinder facilitates the transfer of heat from the burner flame to the material bed. As the cylinder rotates, it lifts and tumbles the material, creating a cascading effect that exposes new surfaces to the radiant heat from the flame and hot gases.
This tumbling action maximizes heat transfer efficiency, ensuring the material absorbs the energy needed for the endothermic chemical reactions to proceed.
Critical Design and Supporting Components
The cylinder does not operate in isolation. Its effectiveness depends on its robust construction and a series of critical subsystems that enable its function.
The Steel Shell and Refractory Lining
The outer body of the cylinder is a welded steel shell, providing the structural integrity to span hundreds of feet and support its own weight plus the weight of the material inside.
Because steel would melt at operating temperatures, the shell is protected by an internal refractory lining. This layer of specialized, heat-resistant brick insulates the shell, prevents it from overheating, and protects it from chemical attack by the hot material.
The Drive Assembly and Rotational Control
The cylinder is turned by a powerful drive assembly, which can be a gear, chain, or direct drive system depending on the kiln's size and power requirements.
These drives often feature variable-speed motors. Adjusting the rotational speed is a primary method for controlling material residence time, allowing operators to fine-tune the process for different conditions or raw material characteristics.
The Support and Sealing Systems
The immense weight of the cylinder is distributed across several support roller stations along its length. These rollers allow the kiln to rotate smoothly and maintain its alignment.
At both the feed and discharge ends, kiln seals are used to prevent cold air from leaking into the kiln and hot gases from escaping. Since the kiln operates under negative pressure, effective seals are critical for maintaining thermal efficiency and a stable combustion process.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Managing a rotary kiln cylinder involves balancing competing operational priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is key to efficient and reliable cement production.
Rotational Speed vs. Residence Time
Increasing the kiln's rotational speed increases throughput but reduces the time the material spends in the kiln. This can lead to incomplete reactions and lower-quality clinker if not managed carefully with feed rate and flame temperature.
Refractory Durability vs. Cost
High-performance refractory bricks can significantly extend the kiln's service life between shutdowns, but they represent a major capital investment. Using cheaper materials can lower upfront costs but may lead to more frequent and expensive maintenance cycles. The failure of a refractory lining during operation can be catastrophic.
Thermal Efficiency vs. Heat Loss
A thick, high-quality refractory lining and tight kiln seals are essential for minimizing heat loss and reducing fuel consumption. However, these systems require diligent maintenance. Any degradation directly translates to wasted energy and higher operating costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Optimizing cylinder performance depends entirely on your primary operational objective. Your strategy for maintenance, control, and investment should align with that goal.
- If your primary focus is maximizing production throughput: Concentrate on optimizing rotational speed and feed rate in tandem, while using process control systems to closely monitor clinker quality in real-time.
- If your primary focus is extending operational lifespan: Prioritize the selection of high-quality refractory materials and conduct meticulous maintenance on the support roller alignment to minimize mechanical stress on the steel shell.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Emphasize the integrity of the kiln seals and invest in advanced refractory materials with superior insulating properties to minimize radiant heat loss.
Ultimately, the cylinder functions as the engineered core of the entire cement manufacturing process, where mechanical design and chemical engineering converge.
Summary Table:
| Function | Description | Key Components |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Transformation | Provides controlled high-temperature environment for calcination reactions | Refractory lining, burner system |
| Material Conveyance | Moves raw meal via incline and rotation for uniform processing | Drive assembly, support rollers |
| Heat Exchange | Facilitates efficient heat transfer through tumbling action | Refractory lining, kiln seals |
Optimize your cement production with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Rotary Furnaces, designed to enhance efficiency and durability in processes like clinker production. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique operational needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can boost your productivity and reduce costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource



















