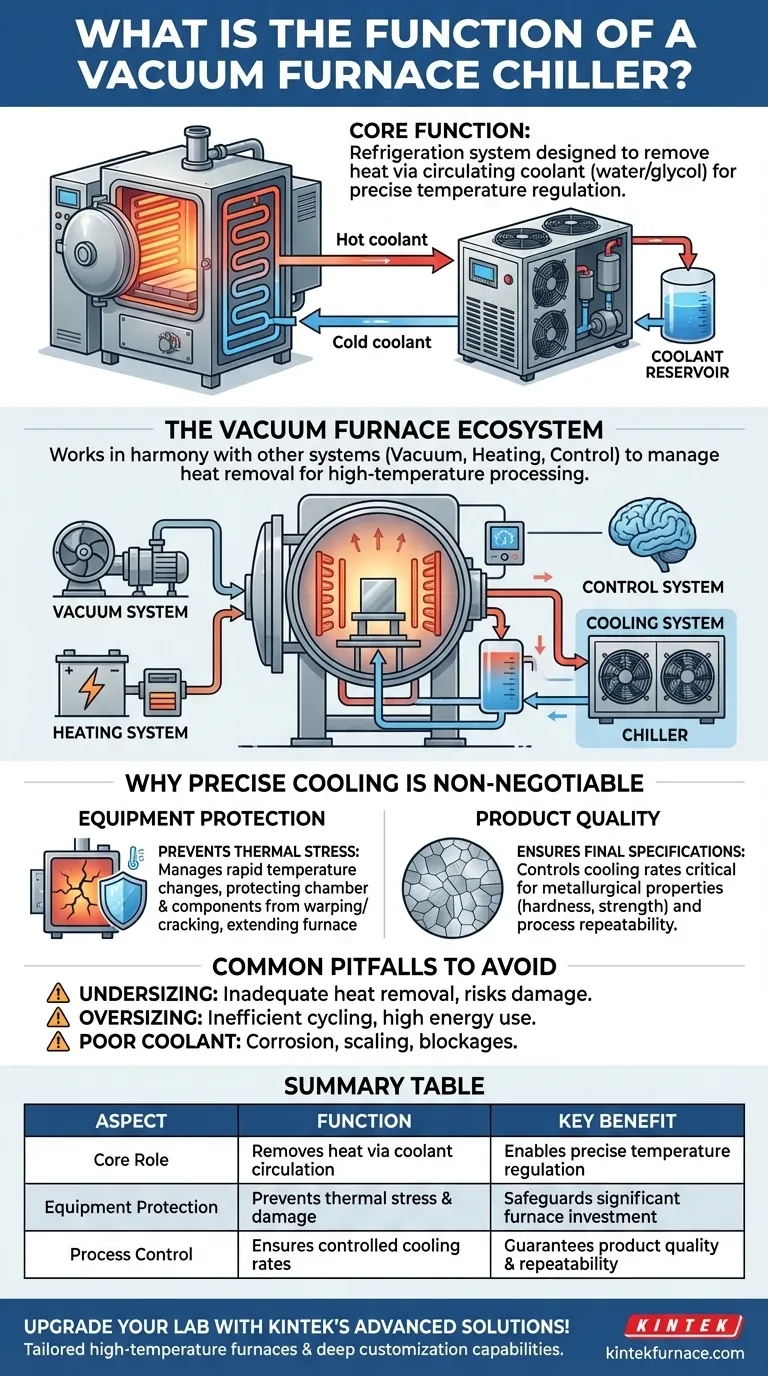
At its core, a vacuum furnace chiller is a refrigeration system designed specifically to remove heat from a vacuum furnace. It enables precise temperature regulation by actively circulating a coolant, like water or a water-glycol mix, through the furnace's cooling circuits. This process is critical for controlling both the high-temperature operational phases and the rapid cooling cycles required in modern material processing.
The chiller's true function is not just cooling; it is a critical asset protection device. It safeguards the significant investment of the furnace itself by preventing damage from thermal stress while ensuring the final product meets exact metallurgical specifications through controlled cooling rates.

The Role of a Chiller in the Vacuum Furnace Ecosystem
To understand the chiller's importance, you must first understand the environment it supports. The chiller is one of several interdependent systems that must work in perfect harmony.
The Vacuum Furnace Environment
A vacuum furnace is a highly specialized piece of equipment used for heat-treating, brazing, and sintering materials at high temperatures.
Its primary advantage is the vacuum environment, which removes air and other gases. This prevents oxidation and contamination, which is essential when processing reactive metals and high-performance alloys.
Key Systems of a Vacuum Furnace
A furnace is more than just a hot box. It is a complex system of components, including:
- Vacuum Chamber: The sealed vessel where the process takes place.
- Heating System: Elements, often made of graphite or molybdenum, that generate the required heat.
- Vacuum System: A series of pumps responsible for creating and maintaining the vacuum.
- Control System: The brain that regulates temperature, time, and pressure according to a programmed recipe.
- Cooling System: The network of passages and fans that manage heat removal, supported directly by the chiller.
The Chiller's Core Task: Controlled Heat Removal
The chiller's mechanical function is straightforward. It chills a reservoir of fluid and then pumps that fluid to the furnace.
This coolant circulates through channels in the furnace walls, power cables, and other components, absorbing waste heat. The now-warm fluid returns to the chiller, where the heat is ejected, and the cycle repeats.
Why Precise Cooling is Non-Negotiable
The value of a vacuum furnace lies in its precision. Uncontrolled cooling would undermine the entire process and risk catastrophic equipment failure. The chiller is the component that guarantees this control.
Protecting the Furnace Investment
Rapid temperature changes create immense thermal stress on the furnace's structural components. Without a chiller managing the cooling process, this stress can cause warping, cracking, and premature failure of the vacuum chamber and heating elements.
By ensuring a stable and controlled temperature drop, the chiller significantly extends the operational lifespan of the furnace, protecting a multi-million dollar asset from unnecessary wear and tear.
Ensuring Final Product Quality
For many metallurgical processes, the cooling rate is just as important as the heating temperature. The speed at which a metal part cools determines its final microstructure, which dictates properties like hardness, strength, and durability.
The chiller provides the ability to execute rapid, yet precisely controlled, cooling cycles. This ensures that every part meets the required engineering specifications, batch after batch.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While essential, integrating a chiller is not without its challenges. Misunderstanding its role can lead to costly mistakes.
The Danger of Undersizing
Specifying a chiller that is too small for the furnace's heat load is a common error. An undersized chiller will be unable to remove heat fast enough, jeopardizing both the product's metallurgical properties and the furnace's structural integrity.
The Inefficiency of Oversizing
Conversely, an excessively large chiller will cycle on and off too frequently, leading to inefficient operation and increased energy consumption. Proper sizing requires a careful analysis of the furnace's maximum heat load.
Ignoring Coolant Quality
The fluid circulating between the chiller and the furnace is the lifeblood of the system. Poor water quality or incorrect glycol concentration can lead to corrosion, scaling, and blockages in the cooling channels, crippling the system's effectiveness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your perspective on the chiller's function will depend on your primary responsibility.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: View the chiller as your primary defense against thermal stress and the premature failure of critical furnace components.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: The chiller is the tool that guarantees consistent cooling profiles, ensuring uniform results from one batch to the next.
- If your primary focus is final product quality: The chiller provides the precise control over the cooling phase necessary to achieve the exact metallurgical properties your parts require.
Ultimately, the vacuum furnace chiller is the essential safeguard that enables repeatable, high-quality production while protecting the integrity of the furnace itself.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Function |
|---|---|
| Core Role | Removes heat from vacuum furnace via coolant circulation |
| Equipment Protection | Prevents thermal stress, extends furnace lifespan |
| Process Control | Enables precise cooling rates for consistent product quality |
| Key Benefits | Safeguards investment, ensures metallurgical specifications |
Upgrade your lab's precision and efficiency with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs, delivering reliable performance and enhanced productivity. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can protect your equipment and optimize your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What additional processes can a vacuum heat treatment furnace carry out? Unlock Advanced Material Processing
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures
- How do vacuum furnaces contribute to long-term cost savings? Reduce Costs with Efficiency and Quality
- What technological features enhance the efficiency of vacuum furnaces? Boost Performance with Advanced Control & Energy Savings
- How are parts loaded into a vacuum furnace? Ensure Precision and Efficiency in Your Process



















