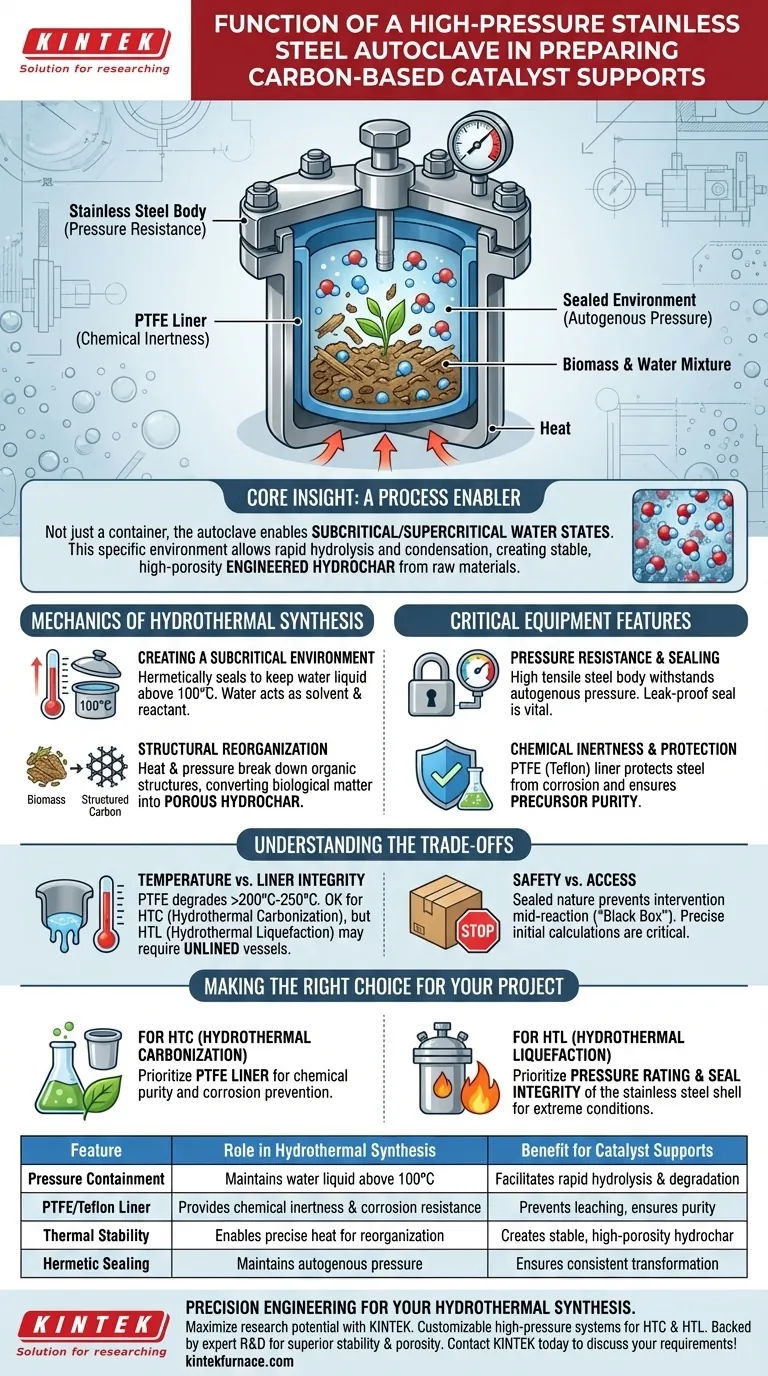
A high-pressure stainless steel autoclave acts as the essential containment vessel that enables the transformation of biomass into engineered carbon supports. By creating a sealed, pressurized environment, it allows water to remain in a liquid state at temperatures well above its boiling point, forcing the chemical degradation and structural reorganization of raw materials like rape straw into porous hydrochar.
Core Insight The autoclave is not merely a container; it is a process enabler that facilitates subcritical or supercritical water states. This specific environment creates a reaction medium where biomass allows for rapid hydrolysis and condensation, producing stable, high-porosity carbon structures that are impossible to synthesize under standard atmospheric conditions.

The Mechanics of Hydrothermal Synthesis
Creating a Subcritical Environment
To prepare carbon-based supports via hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) or liquefaction (HTL), water must act as both a solvent and a reactant.
The autoclave’s primary function is to hermetically seal the reaction mixture. This prevents water from boiling off at $100^{\circ}\text{C}$, allowing the temperature to rise significantly while keeping the water in a liquid phase.
Structural Reorganization of Biomass
Under these extreme conditions, the physical and chemical properties of the biomass change.
The heat and pressure facilitate the breakdown of complex organic structures (such as those found in rape straw). The material undergoes reorganization, converting from raw biological matter into engineered hydrochar.
This resulting material possesses the high porosity and stability required to serve as an effective support for loading active metals in catalytic applications.
Critical Equipment Features
Pressure Resistance and Sealing
The stainless steel body is selected for its high tensile strength. It must withstand the internal pressure generated by the heating of the solvent (often called autogenous pressure).
A failure in sealing would result in the loss of the solvent and a failure to reach the necessary supercritical or subcritical state. Therefore, the vessel’s ability to maintain a leak-proof seal under thermal stress is its most vital mechanical function.
Chemical Inertness and Protection
While stainless steel provides structural strength, the internal environment is often chemically aggressive.
To protect the vessel and ensure the purity of the carbon support, a liner made of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE/Teflon) is frequently used. This liner prevents acid or alkali corrosion of the steel body and ensures that no metallic impurities leach into the carbon support during synthesis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Limits vs. Liner Integrity
While the stainless steel shell can handle immense heat, the PTFE liner introduces a thermal ceiling.
Standard Teflon linings generally degrade above $200^{\circ}\text{C}$ to $250^{\circ}\text{C}$. For Hydrothermal Carbonization (HTC), which typically occurs at lower temperatures, this is acceptable.
However, for Hydrothermal Liquefaction (HTL) requiring higher temperatures, the liner may become a limiting factor, requiring unlined vessels or alternative high-performance alloys.
Safety vs. Access
The sealed nature of the autoclave is a double-edged sword. It creates the necessary reaction conditions but prevents any intervention once the process begins.
You cannot adjust precursors or remove byproducts mid-reaction. The process is strictly a "black box" until the vessel cools and is depressurized, making precise initial calculations of water-to-solid ratios critical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
The specific configuration of your autoclave should depend on the severity of the reaction conditions you require.
- If your primary focus is Hydrothermal Carbonization (HTC): Prioritize a vessel with a high-quality PTFE liner to ensure chemical purity and prevent corrosion from acidic byproducts.
- If your primary focus is Hydrothermal Liquefaction (HTL): Prioritize the pressure rating and seal integrity of the stainless steel shell, as the extreme conditions may exceed the limits of standard polymer liners.
The autoclave provides the brute force required to reshape organic chaos into structured, catalytic utility.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Hydrothermal Synthesis | Benefit for Catalyst Supports |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Containment | Maintains water in liquid phase above 100°C | Facilitates rapid hydrolysis and biomass degradation |
| PTFE/Teflon Liner | Provides chemical inertness and corrosion resistance | Prevents metallic leaching and ensures precursor purity |
| Thermal Stability | Enables precise heat for structural reorganization | Creates stable, high-porosity hydrochar structures |
| Hermetic Sealing | Maintains autogenous pressure during reaction | Ensures consistent transformation of organic raw materials |
Precision Engineering for Your Hydrothermal Synthesis
Maximize the potential of your material research with KINTEK. Whether you are focusing on Hydrothermal Carbonization (HTC) or Liquefaction (HTL), our high-pressure systems are designed to withstand the most demanding subcritical and supercritical environments.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, CVD systems, and other lab high-temp furnaces, all customizable for unique needs. We provide the structural integrity and chemical protection your catalysts require to achieve superior stability and porosity.
Ready to upgrade your lab's capabilities? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom autoclave and furnace requirements with our specialists!
Visual Guide
References
- Kapil Khandelwal, Ajay K. Dalai. Catalytic Supercritical Water Gasification of Canola Straw with Promoted and Supported Nickel-Based Catalysts. DOI: 10.3390/molecules29040911
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Stainless Steel Quick Release Vacuum Chain Three Section Clamp
People Also Ask
- Why is repeated flipping and remelting necessary in vacuum arc melting? Ensure HEA Chemical Homogeneity
- How do thermal imagers and hybrid AI models facilitate leak detection? 92% Accuracy in Industrial Furnaces
- How do vacuum furnaces contribute to new material preparation? Unlock Purity and Precision in Synthesis
- What role does a vacuum drying oven play in Ru-Mo2C@CN post-treatment? Preserve Morphology & Catalytic Activity
- Why is an electric heating oven required for laser cladding pre-treatment? Ensure High-Density AlxCoCrCuyFeNi Coatings
- What are the differences between hot wall and cold wall vacuum furnace designs? Compare for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the working principle of a vacuum carburizing furnace? Achieve Superior Surface Hardening for Steel Parts
- How do continuous vacuum furnaces contribute to metal annealing and hardening? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Purity



















