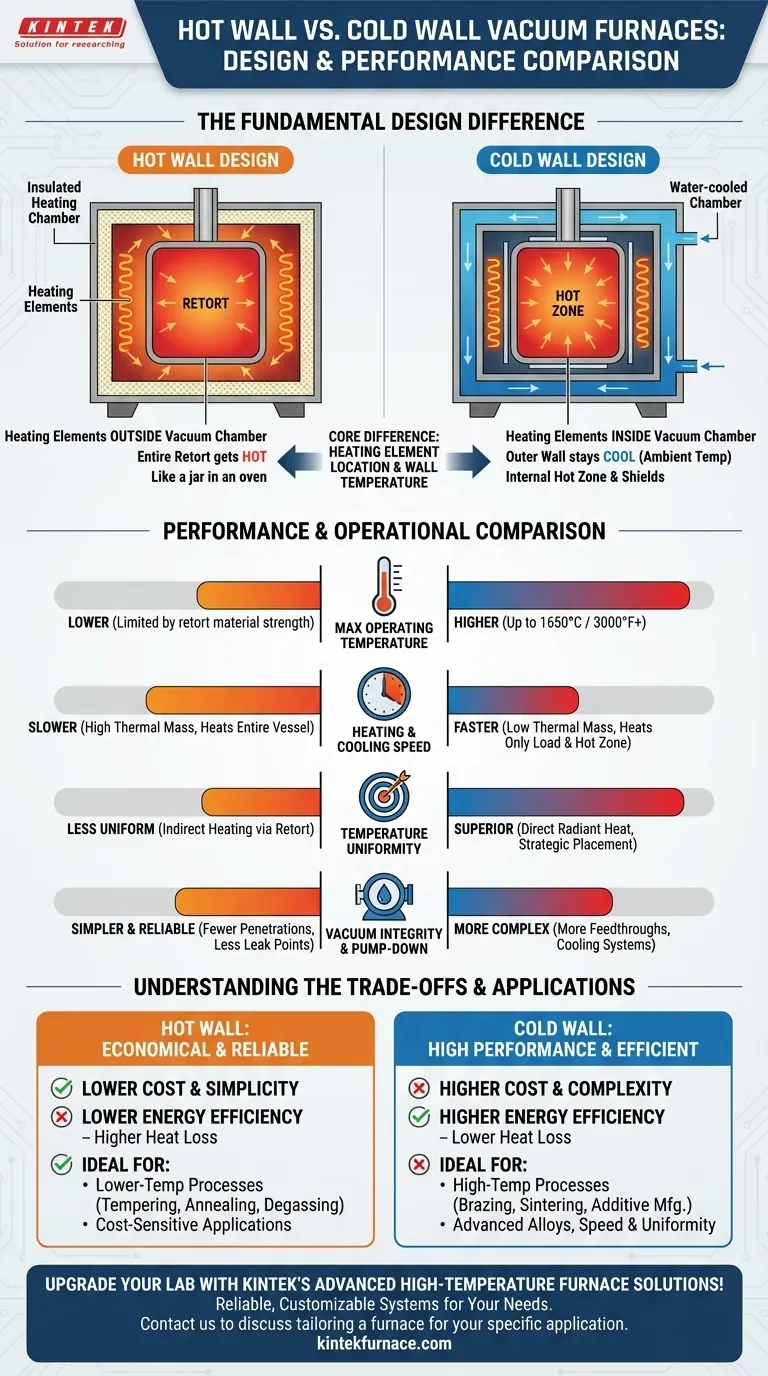
At its core, the difference between a hot wall and a cold wall vacuum furnace lies in the location of the heating system and the temperature of the vacuum chamber's main wall. In a hot wall design, the heating elements are outside the vacuum chamber, heating the entire vessel. In a cold wall design, the heating elements are inside the vacuum chamber, while the outer vessel wall is actively cooled and remains near ambient temperature.
The choice is a classic engineering trade-off. Cold wall furnaces offer superior performance—higher temperatures, faster cycles, and better uniformity—making them ideal for advanced applications. Hot wall furnaces are simpler and more economical, excelling in reliability for lower-temperature processes.

The Fundamental Design Difference
To understand the performance trade-offs, you must first visualize how each furnace is constructed. The core distinction is whether the primary vacuum vessel gets hot or stays cold.
How a Hot Wall Furnace Works
In a hot wall furnace, the vacuum chamber, often called a retort, is placed inside a larger, insulated heating chamber. The heating elements surround the outside of this retort.
Think of it like placing a sealed jar inside a conventional oven. The entire jar and its contents heat up together. This design is mechanically simple, as it requires fewer complex seals and penetrations into the vacuum zone.
How a Cold Wall Furnace Works
In a cold wall furnace, the heating elements and heat shielding are located inside the vacuum chamber. The outer wall of the chamber has integrated cooling channels, typically circulating water.
This design keeps the main structural vessel cool, strong, and stable, even when the interior is at extremely high temperatures. The heat is contained within a "hot zone" made of insulation or reflective metal shields.
Performance and Operational Comparison
The architectural difference directly leads to significant variations in performance, cost, and operational characteristics.
Maximum Operating Temperature
A cold wall furnace is the clear winner for high-temperature work. Because the structural vessel remains cool, it can easily support processes running up to 1650°C (3000°F) or even higher with specialized designs.
A hot wall furnace is limited by the material strength of the retort, which weakens as it gets hotter. This typically restricts its use to lower-temperature applications.
Heating and Cooling Speed
Cold wall furnaces provide significantly faster heating and cooling cycles. This is because they have lower thermal mass; the furnace only needs to heat the workload and the lightweight internal hot zone.
Hot wall furnaces must heat the entire heavy retort, which stores a massive amount of thermal energy and therefore heats and cools much more slowly.
Temperature Uniformity
A cold wall design offers superior temperature uniformity. Heating elements can be strategically placed around the workload inside the chamber, providing precise and direct radiant heat from all sides.
In a hot wall design, the workload is heated indirectly by the hot retort wall, which can lead to less uniform temperature distribution.
Vacuum Integrity and Pump-Down
A hot wall furnace often has an advantage in simplicity and vacuum reliability. Its design typically has fewer penetrations (ports, power feedthroughs), which means fewer potential leak points.
The hot surfaces also help "bake out" volatile contaminants during pump-down, which can sometimes lead to faster cycle times for reaching moderate vacuum levels.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither design is universally better; they are optimized for different goals. Understanding their inherent compromises is key to making an informed decision.
Cost and Complexity
Hot wall furnaces are generally less expensive and simpler to manufacture. The design avoids the complexity of internal heating elements and the plumbing required for a water-cooled vessel.
Cold wall furnaces are more complex and costly due to their internal hot zones, power feedthroughs, and extensive water-cooling systems.
Energy Efficiency and Heat Loss
Cold wall furnaces typically exhibit lower heat losses to the surrounding environment. The water-cooled outer shell effectively contains the energy within the furnace, and modern multi-layer insulation is extremely efficient.
A hot wall furnace, by its nature, radiates a significant amount of heat from the entire exterior of the furnace body, making it less energy-efficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your process requirements should dictate your choice. Base your decision on the primary performance driver for your specific task.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance, speed, and uniformity: A cold wall furnace is the definitive choice for demanding processes like brazing, sintering, additive manufacturing, and treating advanced alloys.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for lower-temperature processes: A hot wall furnace is an excellent, reliable workhorse for applications like tempering, annealing, and degassing where extreme temperatures are not required.
- If your primary focus is minimizing vacuum leaks and operational simplicity: The simpler construction of a hot wall furnace offers inherent reliability and easier maintenance for less demanding vacuum processes.
Ultimately, understanding these core design principles empowers you to select the right tool for your specific engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Wall Furnace | Cold Wall Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Element Location | Outside vacuum chamber | Inside vacuum chamber |
| Maximum Temperature | Lower (limited by retort material) | Higher (up to 1650°C or more) |
| Heating/Cooling Speed | Slower (high thermal mass) | Faster (low thermal mass) |
| Temperature Uniformity | Less uniform | Superior uniformity |
| Cost and Complexity | Lower cost, simpler | Higher cost, more complex |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower (more heat loss) | Higher (better insulation) |
| Ideal Applications | Lower-temperature processes (e.g., tempering, annealing) | High-temperature processes (e.g., brazing, sintering) |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable, customizable systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, boosting efficiency and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a furnace for your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















