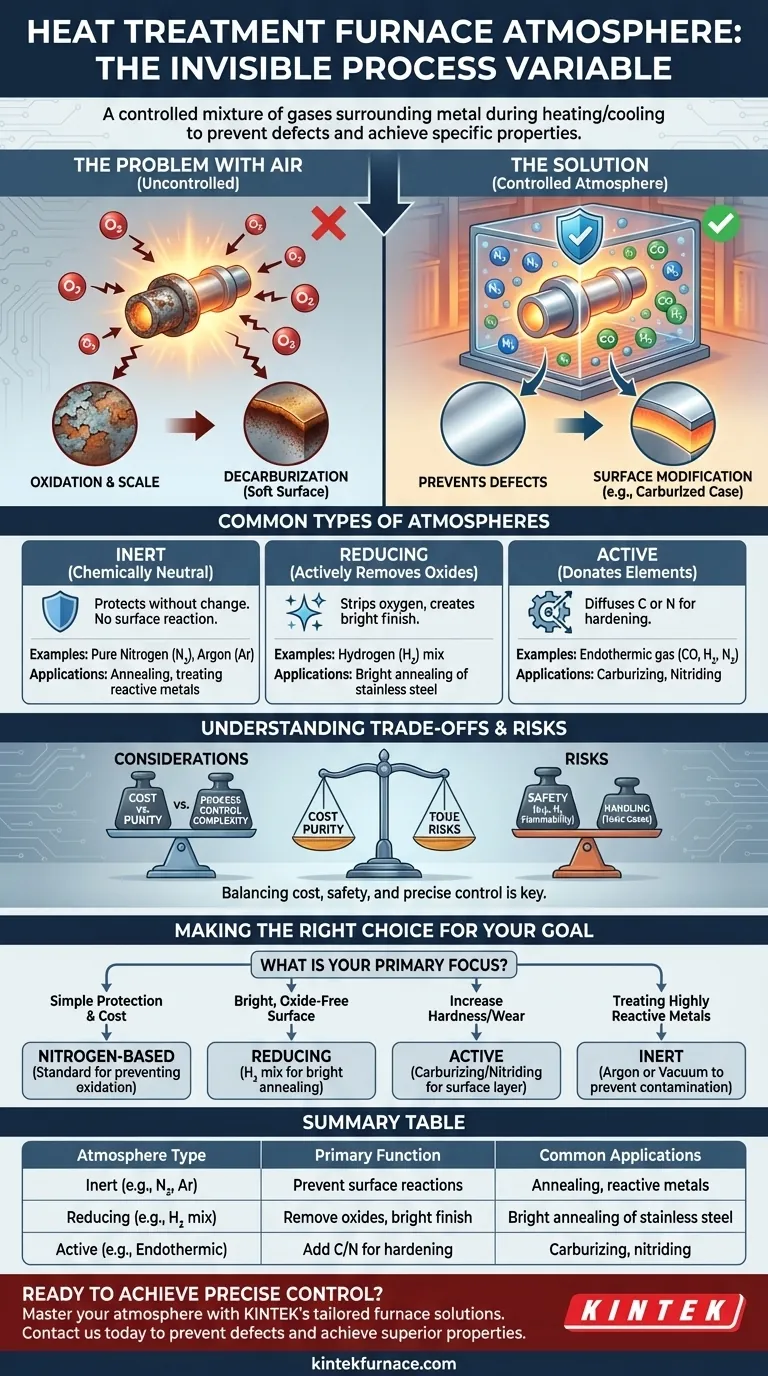
In heat treatment, the furnace "atmosphere" is the specific, controlled mixture of gases that surrounds a metal part during the heating and cooling cycle. This is done to prevent harmful reactions with air, primarily oxidation (rusting), and in many cases, to intentionally alter the surface chemistry of the metal to achieve desired properties like hardness.
The atmosphere in a heat treatment furnace is not merely a protective shield; it is an active and critical process variable. Choosing the correct atmosphere is essential for preventing defects and achieving specific surface properties, directly impacting the final performance and integrity of the metal component.

Why a Controlled Atmosphere is Non-Negotiable
Heating metal to high temperatures in ambient air is almost always detrimental. A controlled atmosphere solves several fundamental problems that arise from exposing hot metal to oxygen and other elements in the air.
The Problem with Air
When you heat metal, its reactivity increases dramatically. The oxygen in the air will rapidly bond with the metal's surface, creating a layer of oxide scale.
This scale is undesirable as it damages the surface finish, alters the part's final dimensions, and must be removed through costly secondary operations like sandblasting or acid pickling.
Preventing Surface Defects
The primary function of a furnace atmosphere is to displace the oxygen. By filling the furnace chamber with a non-oxidizing gas mixture, you prevent scale from forming.
This also prevents decarburization, a critical issue in steels where carbon can be leached out of the surface, leaving it soft and unable to be properly hardened.
Enabling Surface Modification
Beyond simple protection, active atmospheres are used to intentionally diffuse elements into the surface of a part.
This is the basis for case-hardening processes like carburizing (adding carbon) and nitriding (adding nitrogen), which create a hard, wear-resistant outer layer while maintaining a softer, tougher core.
Common Types of Furnace Atmospheres
Furnace atmospheres are generally categorized by their chemical behavior at high temperatures.
Inert Atmospheres
These atmospheres are chemically neutral and serve only to protect the metal from reacting. They are used when the goal is to heat and cool the part with absolutely no change to its surface chemistry.
Common examples include pure Nitrogen (N2) and Argon (Ar). Argon is more perfectly inert but significantly more expensive, so it is reserved for highly reactive metals like titanium.
Reducing Atmospheres
Reducing atmospheres actively remove oxygen. They will strip oxygen atoms from any oxides present on the part's surface, resulting in a clean, bright finish.
Hydrogen (H2) is a powerful reducing agent. Atmospheres rich in hydrogen are used for processes like bright annealing of stainless steel. A common mixture is nitrogen and hydrogen, generated from dissociated ammonia.
Active (Reactive) Atmospheres
These atmospheres are designed to donate elements to the steel's surface.
Endothermic gas is a classic example used for carburizing. It is generated by reacting natural gas and air to produce a mixture of nitrogen, hydrogen, and—most importantly—carbon monoxide (CO), which provides the carbon for hardening the steel.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Choosing an atmosphere involves balancing cost, safety, and process requirements. There is no single "best" atmosphere for all applications.
Cost vs. Purity
High-purity gases like argon provide the best protection but come at a premium. Nitrogen is a cost-effective workhorse for many applications, but it can react with certain metals at very high temperatures.
Safety and Handling
Hydrogen is an exceptional reducing gas but is also highly flammable and poses an explosion risk. Its use requires specialized furnace designs and extensive safety protocols. Ammonia, used for nitriding, is toxic and corrosive.
Process Control Complexity
Active atmospheres like those for carburizing require extremely precise control of gas composition, temperature, and time. If the "carbon potential" of the gas is too high, it can cause sooting on the part's surface. If it's too low, it can cause the exact decarburization you were trying to prevent.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal atmosphere is determined entirely by the material you are treating and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is simple protection and cost-effectiveness: A nitrogen-based atmosphere is the standard choice for preventing oxidation in general-purpose annealing or stress relieving.
- If your primary focus is achieving a bright, oxide-free surface: A reducing atmosphere containing hydrogen is necessary for processes like bright annealing of copper or stainless steel.
- If your primary focus is increasing surface hardness and wear resistance: An active carburizing or nitriding atmosphere is required to diffuse carbon or nitrogen into the steel's surface.
- If your primary focus is treating highly reactive metals like titanium: An inert gas like argon or a complete vacuum is the only way to prevent contamination.
Ultimately, mastering the furnace atmosphere transforms heat treatment from simple heating into a precise engineering process.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Primary Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Inert (e.g., N₂, Ar) | Prevent surface reactions | Annealing, treating reactive metals |
| Reducing (e.g., H₂ mix) | Remove oxides, produce bright finish | Bright annealing of stainless steel |
| Active (e.g., Endothermic gas) | Add carbon/nitrogen for hardening | Carburizing, nitriding for wear resistance |
Ready to Achieve Precise Control Over Your Heat Treatment Processes?
The right furnace atmosphere is not just a setting—it's the difference between a flawed part and a high-performance component. At KINTEK, we understand that every application has unique requirements. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs.
Contact us today (#ContactForm) to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can help you master your atmosphere control, prevent defects, and achieve superior material properties.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling



















