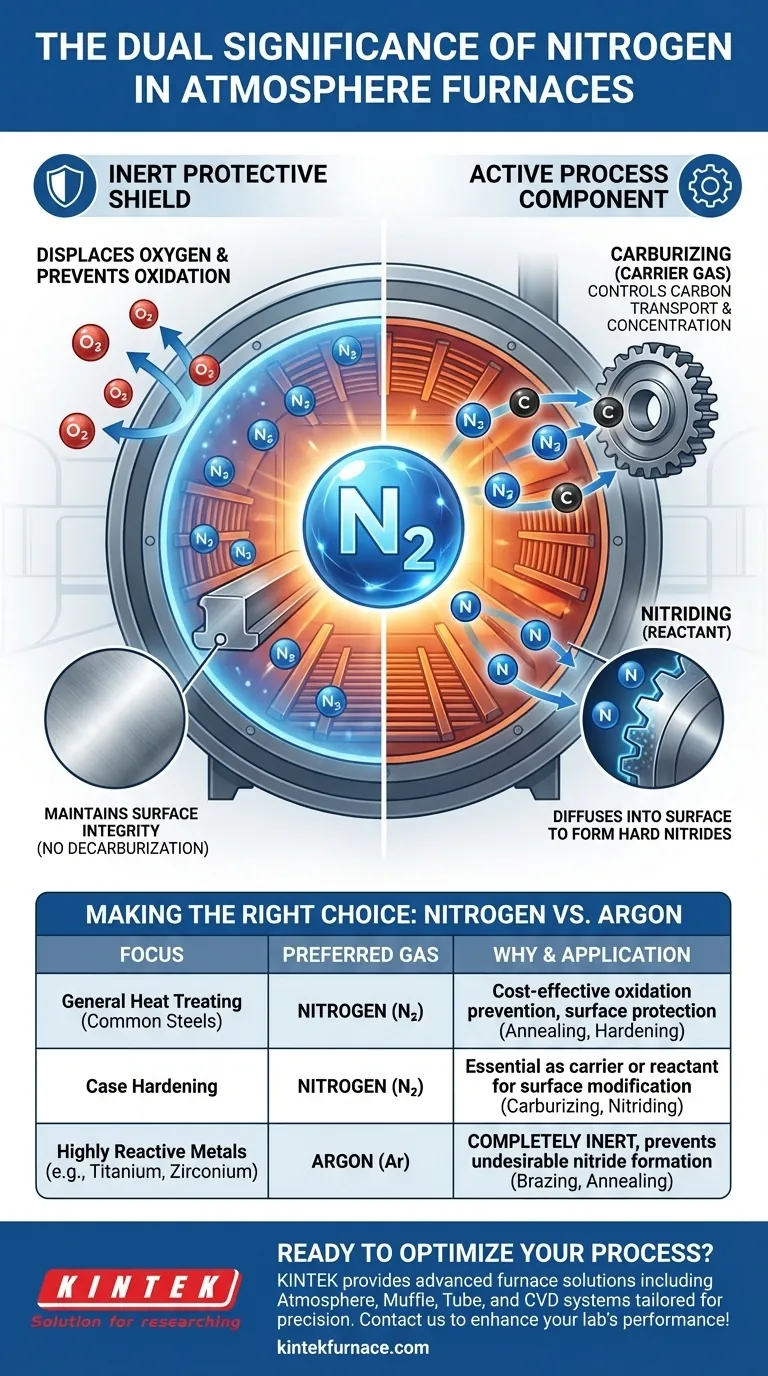
In atmosphere furnaces, nitrogen serves as both a protective shield and an active ingredient. Its primary significance is preventing destructive reactions like oxidation by displacing oxygen from the furnace environment. However, it also plays a direct, functional role as a key chemical component in surface-hardening treatments like nitriding and as a carrier gas in carburizing.
Nitrogen's core value lies in its duality. While most commonly used as a cost-effective inert gas to protect parts from oxidation, it is also intentionally used as a reactive element to fundamentally alter the surface properties of steel for advanced applications.

The Primary Role: An Inert Protective Shield
At the high temperatures required for heat treatment, metals like steel become highly reactive with the oxygen present in normal air. Nitrogen is used to create an inert atmosphere, displacing this oxygen and preventing unwanted chemical reactions.
Preventing Oxidation
The most immediate and common purpose of a nitrogen atmosphere is to prevent oxidation. When heated in the presence of oxygen, steel rapidly forms a layer of iron oxide, commonly known as scale.
This scale is undesirable as it damages the surface finish, can interfere with subsequent processing steps, and represents a loss of material. A nitrogen atmosphere effectively blankets the parts, shielding them from oxygen.
Ensuring Surface Integrity
Beyond just preventing visible scale, an inert nitrogen atmosphere protects the metallurgical integrity of the part's surface. It prevents decarburization, a process where carbon diffuses out of the steel's surface, leaving it soft and weak.
By maintaining a clean, bright, and chemically unchanged surface, nitrogen ensures the component retains its specified mechanical properties after heat treatment.
The Secondary Role: An Active Process Component
While often used for its non-reactive properties, nitrogen is also a critical active ingredient in several key surface modification processes. In these applications, it is not inert but is intended to react with the steel.
Carrier Gas in Carburizing
In carburizing, the goal is to diffuse carbon into the surface of steel to create a hard, wear-resistant case. This process requires a carbon-rich atmosphere, typically using gases like methane or propane.
Nitrogen is used as the "carrier gas" or "diluent," making up the majority of the furnace atmosphere. It controls the concentration of the active carbon-rich gas and transports it uniformly to the component's surface.
The Key Reactant in Nitriding
In nitriding processes, nitrogen is the primary active element. The goal is to diffuse nitrogen atoms—not just atmospheric nitrogen gas (N₂)—into the surface of the steel.
These nitrogen atoms react with iron and other alloying elements to form extremely hard nitride compounds. This creates a case-hardened surface with exceptional wear resistance, fatigue strength, and corrosion resistance. Here, nitrogen is not preventing a reaction; it is the reaction.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Nitrogen vs. Other Gases
While nitrogen is the most common atmosphere gas due to its effectiveness and low cost, it is not universally applicable. Understanding its limitations is key to process control.
When to Use Nitrogen
For the vast majority of heat treatment processes involving carbon and alloy steels—such as annealing, hardening, and carburizing—nitrogen is the ideal choice. It provides excellent protection at a much lower cost than other inert gases.
When to Choose Argon
Some materials, like titanium, zirconium, and certain grades of stainless steel, are so reactive that they can form undesirable nitrides even in a standard nitrogen atmosphere.
For these highly sensitive materials, a more truly inert gas like argon is required. Although significantly more expensive, argon will not react with the metal under any heat treatment conditions, guaranteeing a completely inert environment for processes like brazing or annealing reactive alloys.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct atmosphere is fundamental to achieving the desired metallurgical outcome. Your choice depends entirely on the material being processed and your intended result.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating of common steels: Nitrogen is your most cost-effective choice for preventing oxidation and decarburization.
- If your primary focus is case hardening: Nitrogen is essential, serving as a carrier gas for carburizing or as the active hardening agent in nitriding.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals (e.g., titanium, specialty stainless): You must use a more inert gas like argon to avoid the formation of unwanted surface compounds.
Mastering the use of nitrogen—as both a protector and a reactant—is fundamental to controlling the outcome of any advanced heat treatment process.
Summary Table:
| Role of Nitrogen | Key Functions | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Protective Shield | Prevents oxidation and decarburization, maintains surface integrity | Annealing, hardening of carbon and alloy steels |
| Active Component | Acts as carrier gas in carburizing, reactant in nitriding for surface hardening | Nitriding, carburizing processes for wear and fatigue resistance |
| Trade-offs | Cost-effective for most steels; use argon for highly reactive metals like titanium | Processing titanium, zirconium, or specialty stainless steels |
Ready to optimize your heat treatment processes with the right furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces tailored to your needs. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is designed for precision and efficiency. With strong deep customization capabilities, we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you're working with common steels or reactive alloys. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's performance and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab



















