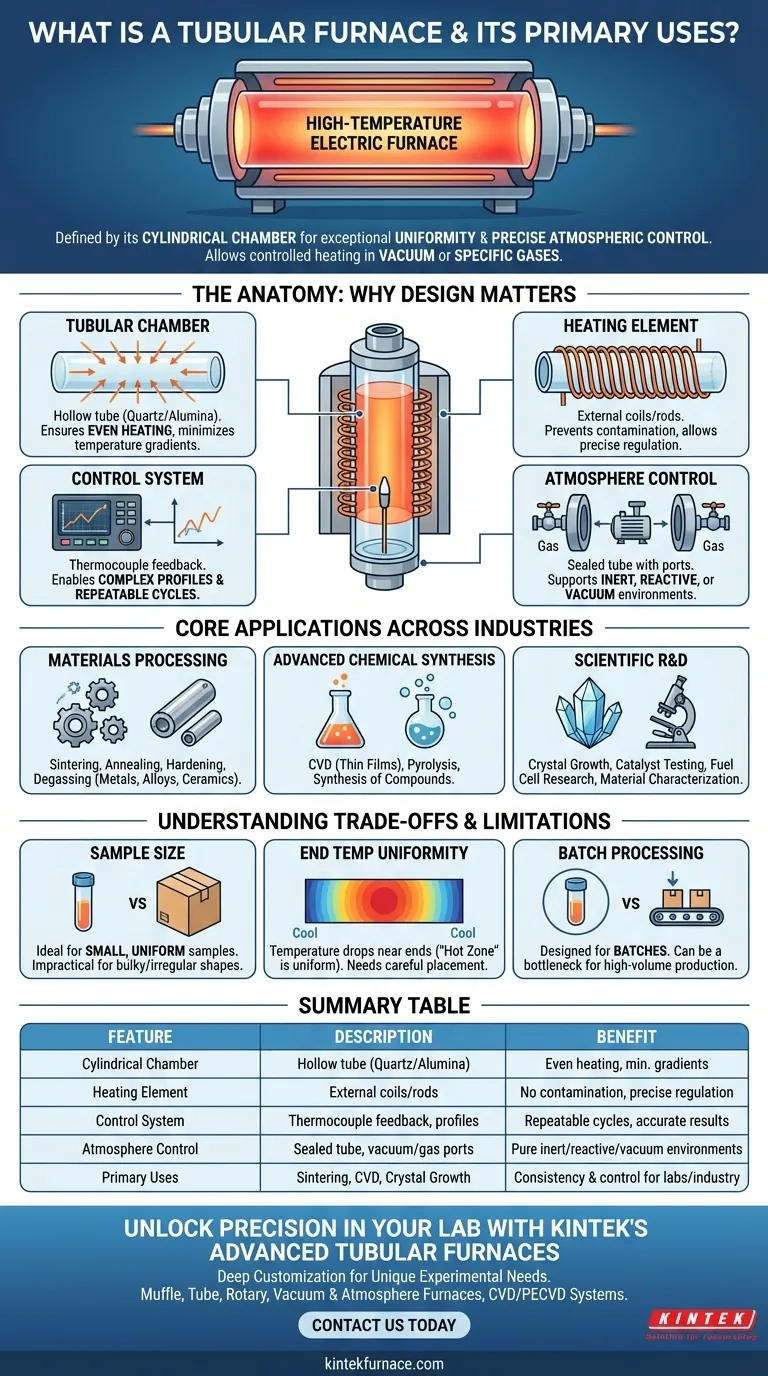
At its core, a tubular furnace is a high-temperature electric furnace defined by its cylindrical heating chamber. This design is not arbitrary; it is specifically engineered for processes that demand exceptional temperature uniformity and precise atmospheric control. The tube acts as a self-contained environment, allowing for the controlled heating of materials in a vacuum or the presence of specific gases, making it indispensable in advanced research and industrial applications.
The defining advantage of a tubular furnace is not simply its ability to reach high temperatures, but its cylindrical design. This shape provides unparalleled heating uniformity and enables precise control over the internal atmosphere, making it the ideal instrument for processes where consistency and environmental purity are non-negotiable.
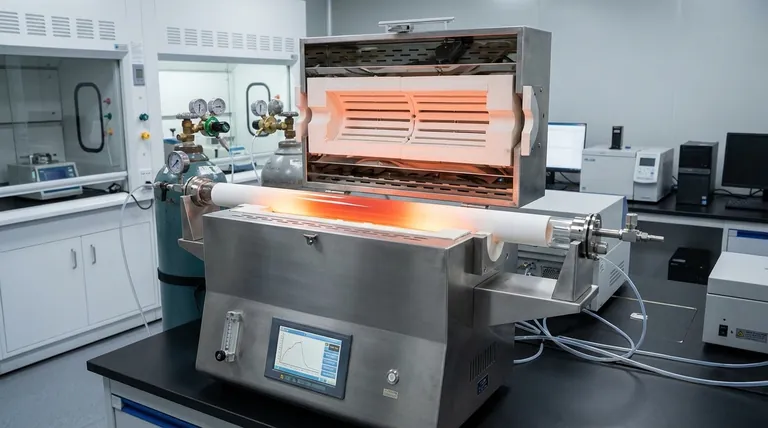

The Anatomy of a Tubular Furnace: Why the Design Matters
To understand the applications of a tubular furnace, you must first appreciate how its fundamental components work together to create a highly controlled thermal environment.
The Tubular Chamber: The Heart of Uniformity
The central chamber is a hollow tube, typically made from robust materials like quartz, alumina, or another ceramic. Its cylindrical geometry ensures that the sample is heated evenly from all sides, minimizing hot spots and temperature gradients.
This uniformity is critical for processes where even slight temperature variations can alter the outcome, such as growing a perfect crystal or evenly annealing a metal component.
The Heating Element: The Engine of Temperature
Heating elements, such as coils of wire or silicon carbide rods, are positioned around the exterior of the ceramic tube. This external placement allows for powerful and evenly distributed radiant heat.
This design separates the heating mechanism from the sample environment, preventing contamination and allowing the internal atmosphere to be tightly controlled.
The Control System: The Brain of Precision
A sophisticated temperature control system is the third critical component. It uses a thermocouple placed near the sample to provide real-time feedback, allowing the system to precisely regulate power to the heating elements.
This enables operators to execute complex heating profiles, such as slow ramps to a target temperature, extended holds (soaking), and controlled cooling cycles, ensuring repeatability across experiments.
Atmosphere Control: The Environmental Advantage
The sealed nature of the tube is arguably its most powerful feature. End caps can be fitted with ports that allow a vacuum pump to remove the air or introduce a specific gas.
This enables processes that must occur in an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon), a reactive one (like hydrogen), or a complete vacuum, which is impossible in an open-air box furnace.
Core Applications Across Industries
The unique capabilities of a tubular furnace make it essential for a wide range of high-stakes applications in both scientific labs and industrial production.
Materials Processing and Heat Treatment
This is a primary function of tubular furnaces. Applications include sintering (fusing powdered materials together), annealing (softening materials and relieving internal stresses), hardening, and degassing metals, alloys, and ceramics.
The uniform heating ensures that the material's properties are consistent throughout the entire component.
Advanced Chemical Synthesis
Many chemical reactions require specific temperatures and atmospheres. Tubular furnaces are used for chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to create thin films, pyrolysis to thermally decompose materials without oxygen, and the general synthesis of inorganic or organic compounds.
Scientific Research and Development
In R&D, these furnaces are workhorses. They are used for growing high-purity crystals, testing the performance of catalysts, characterizing the thermal properties of novel materials, and researching fuel cells.
Their versatility allows researchers to test a wide range of variables with a high degree of control and repeatability.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a tubular furnace is a specialized tool with inherent trade-offs. Understanding these is key to knowing when to use it and when to choose an alternative.
Sample Size and Geometry Constraints
The primary limitation is the tube's diameter and length. This design is ideal for small, uniform samples but is impractical for processing very large or irregularly shaped objects.
For bulky components, a box or muffle furnace provides a more accommodating chamber, albeit often with less temperature uniformity.
Temperature Uniformity at the Ends
While the central "hot zone" of a tube is highly uniform, the temperature naturally drops off near the ends of the tube. This can be mitigated with longer tubes or multi-zone furnaces that have independent heating elements for the ends.
For some applications, like crystal growth, this temperature gradient can even be a desirable feature, but for others, it requires careful sample placement.
Batch Processing Throughput
Most standard tubular furnaces are designed for batch processing, where one sample or a small group of samples is processed at a time. This is perfect for labs but can be a bottleneck in high-volume industrial production unless more complex, continuous furnace systems are employed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal equipment depends entirely on the requirements of your process. Use these points as a guide.
- If your primary focus is material purity or synthesis in a specific atmosphere: The sealed environment of a tubular furnace is your most critical advantage.
- If your primary focus is processing large or irregularly shaped components: A box furnace offers a more practical chamber geometry for bulkier items.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum temperature uniformity across a sample: A multi-zone tubular furnace, which can independently heat the center and ends, provides the most precise control.
- If your primary focus is research and development on small samples: The versatility of a tubular furnace for handling different atmospheres and precise temperature profiles makes it an indispensable tool.
By understanding its design-driven capabilities, you can confidently determine if a tubular furnace is the optimal tool for your specific thermal processing goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical Chamber | Hollow tube made of quartz or alumina | Ensures even heating and minimizes temperature gradients |
| Heating Element | External coils or rods | Prevents contamination and allows precise temperature regulation |
| Control System | Thermocouple feedback with programmable profiles | Enables repeatable heating cycles and accurate results |
| Atmosphere Control | Sealed tube with vacuum/gas ports | Supports inert, reactive, or vacuum environments for purity |
| Primary Uses | Sintering, annealing, CVD, pyrolysis, crystal growth | Ideal for labs and industries requiring consistency and control |
Unlock Precision in Your Lab with KINTEK's Advanced Tubular Furnaces
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in materials science, chemical synthesis, or R&D, our tubular furnaces deliver unparalleled temperature uniformity and atmosphere control to enhance your results.
Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific needs and boost your lab's efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















