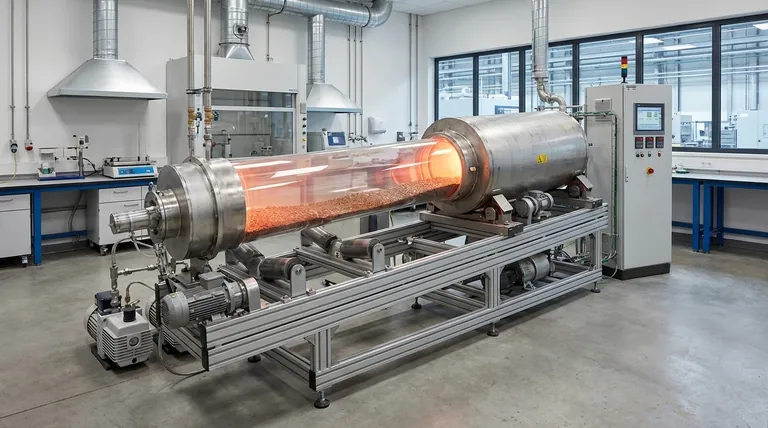
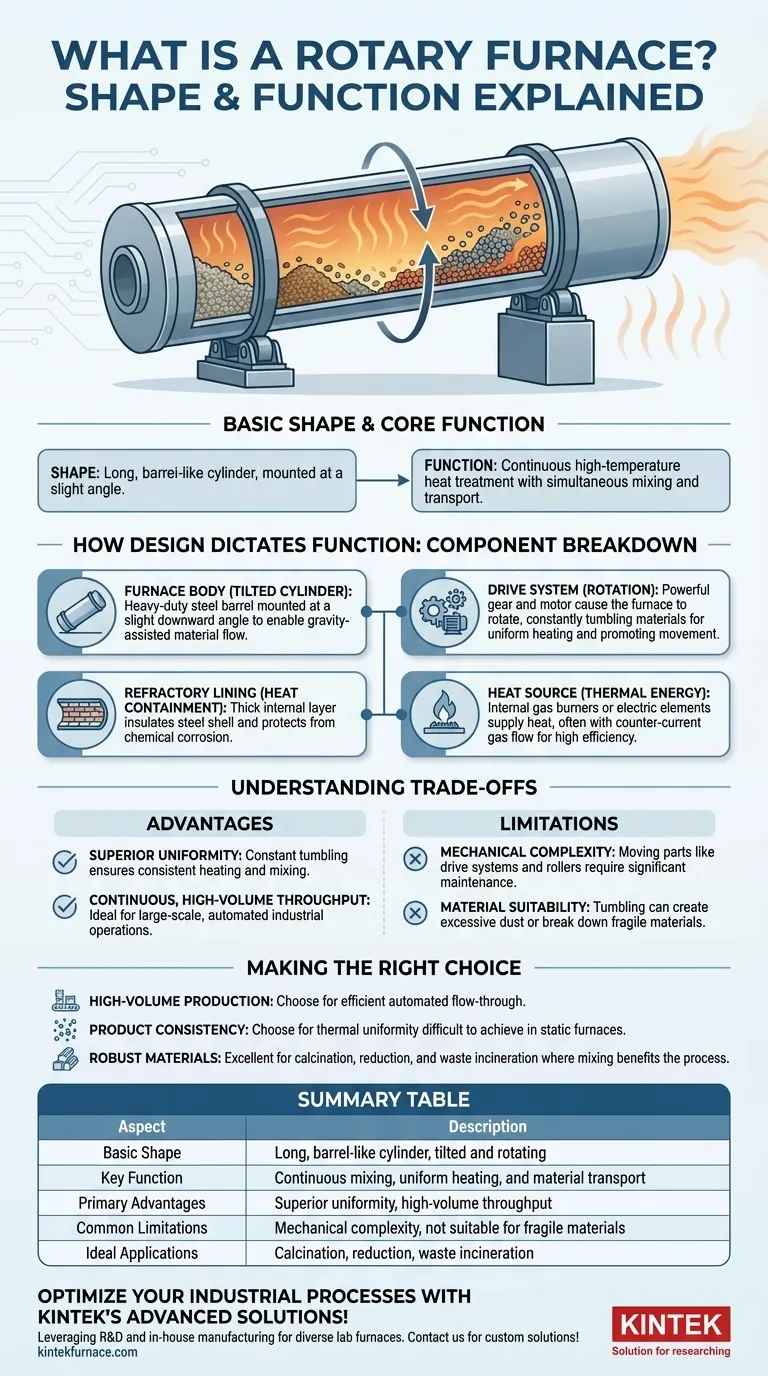
At its core, a rotary furnace is an industrial pyroprocessing device designed for continuous, high-temperature heat treatment. Its basic shape is a long, barrel-like cylinder or tube that is mounted at a slight angle and rotates around its longitudinal axis. This design allows materials to be heated while simultaneously being mixed and transported from one end to the other.
The defining characteristic of a rotary furnace is its shape and motion. The tilted, rotating cylinder is not just a container; it is an engineered system designed to ensure materials are continuously mixed, uniformly heated, and efficiently moved through a process.

How the Design Dictates Function
A rotary furnace’s effectiveness comes from the direct relationship between its components and its operational purpose. Understanding these parts reveals why it is a go-to solution for many industrial processes.
The Furnace Body: A Tilted Cylinder
The main body of the furnace is a long, cylindrical barrel constructed from heavy-duty steel plate. Its length can vary dramatically, sometimes reaching up to hundreds of meters depending on the specific application.
Crucially, the entire barrel is mounted at a slight downward angle. This tilt is fundamental to its operation.
The Drive System: Enabling Rotation
A powerful drive gear and motor system causes the entire furnace body to rotate at a controlled, often variable, speed. This rotation is central to the furnace's function.
First, it constantly tumbles and mixes the material inside. This ensures that all particles are uniformly exposed to the heat source, preventing hot spots and promoting a consistent reaction or transformation.
Second, the combination of rotation and the furnace's tilt causes the material to gradually move from the higher feed end to the lower discharge end, enabling a continuous process flow.
The Refractory Lining: Containing the Heat
The inside of the steel barrel is lined with a thick layer of refractory material, such as specialized bricks, castable cement, or other moldable substances.
This lining serves two critical purposes: it insulates the steel shell from the extreme internal temperatures, and it protects the structure from chemical corrosion caused by the process materials.
The Heat Source: Delivering Thermal Energy
Heat is supplied by an internal source, typically powerful gas burners or electric heating elements positioned within the furnace.
Hot gases often flow in a counter-current direction—opposite to the flow of the material. This design is highly efficient, as the hottest gases treat the most processed material near the discharge end, while the cooler, exiting gases preheat the raw material entering at the feed end.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary furnace design is not a universal solution. Its advantages are balanced by specific operational constraints.
Advantage: Superior Uniformity
The primary benefit of a rotary furnace is the exceptionally uniform heating and mixing it provides. The constant tumbling action is unparalleled for ensuring that every part of the material load receives the same treatment, leading to high product consistency.
Advantage: Continuous, High-Volume Throughput
The automated, gravity-assisted flow of material makes rotary furnaces ideal for large-scale, continuous industrial operations. They can process vast quantities of material with minimal manual intervention.
Limitation: Mechanical Complexity
A rotary furnace is a large, heavy, moving piece of equipment. The drive systems, support rollers, and seals required to operate the rotating barrel are complex, require significant maintenance, and can be points of failure.
Limitation: Material Suitability
The tumbling action can be a disadvantage for certain materials. It can create excessive dust with fine powders or break down fragile, agglomerated materials. The process must be matched to a material that can withstand the mechanical stress of rotation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use a rotary furnace hinges on balancing the need for uniformity and throughput against the nature of your material and operational capacity.
- If your primary focus is high-volume continuous production: The automated flow-through design of a rotary furnace makes it one of the most efficient options available.
- If your primary focus is product consistency: The constant mixing and tumbling action provides a level of thermal uniformity that is difficult to achieve in static furnaces.
- If you are processing robust materials that benefit from mixing: A rotary furnace is an excellent choice for processes like calcination, reduction, or waste incineration where tumbling improves reaction efficiency.
Ultimately, the rotary furnace is a prime example of form following function, with its cylindrical shape and rotational movement perfectly engineered to solve the challenge of uniform, continuous heating.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Basic Shape | Long, barrel-like cylinder, tilted and rotating |
| Key Function | Continuous mixing, uniform heating, and material transport |
| Primary Advantages | Superior uniformity, high-volume throughput |
| Common Limitations | Mechanical complexity, not suitable for fragile materials |
| Ideal Applications | Calcination, reduction, waste incineration |
Optimize your industrial processes with KINTEK's advanced rotary furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Rotary, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs



















