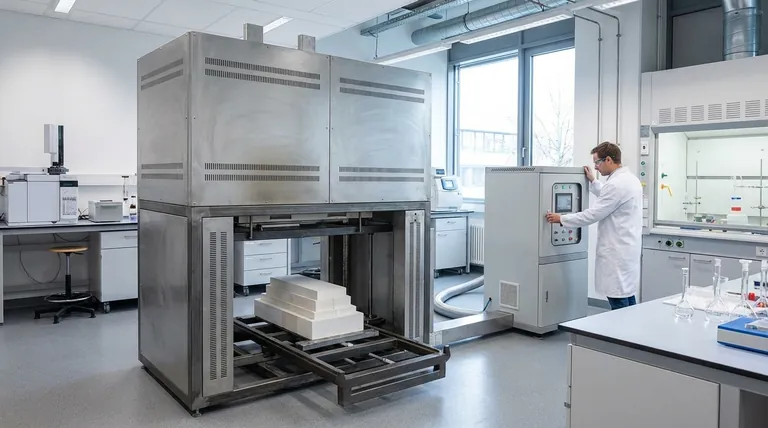
At its core, a laboratory furnace is a high-temperature thermal processing device designed to create an extremely precise and uniform heating environment. Unlike a simple oven, its primary function is to subject materials to specific temperature profiles for critical scientific and industrial processes, including material synthesis, heat treatment, curing, and drying.
The true importance of a laboratory furnace lies not just in its ability to generate heat, but in its capacity to do so with exceptional control and uniformity. This precision is the foundation for creating, testing, and refining materials with predictable and repeatable results.

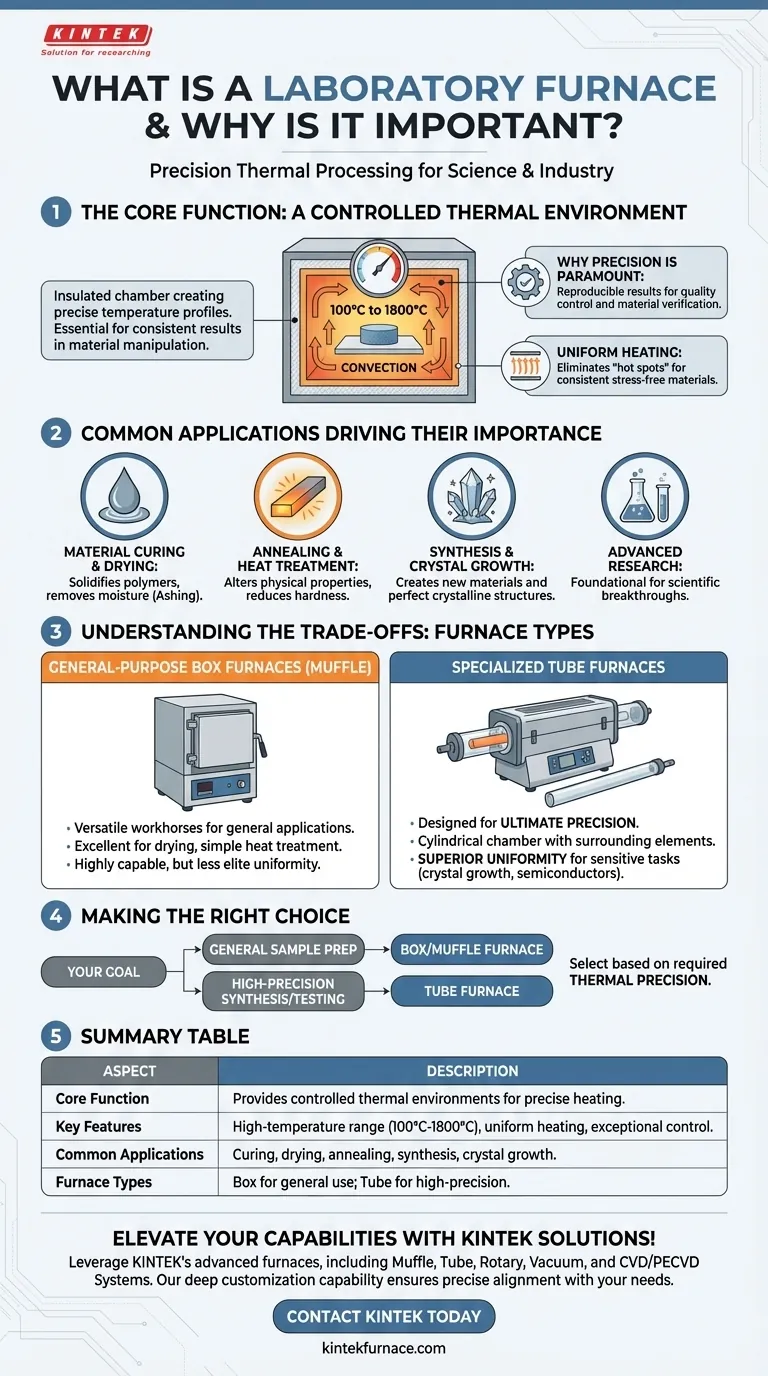
The Core Function: A Controlled Thermal Environment
A laboratory furnace’s value is defined by its ability to manipulate material properties through the precise application of heat. This control is what separates it from a standard heating appliance.
What is a Laboratory Furnace?
A laboratory furnace is an insulated chamber heated to temperatures often ranging from 100°C to over 1,800°C. Most models use convection to circulate hot air or an inert gas, ensuring the sample is heated evenly from all sides.
This controlled environment is essential for processes where slight temperature deviations could ruin an experiment or compromise the integrity of a final product.
Why Precision is Paramount
In scientific research and advanced manufacturing, results must be reproducible. A furnace's ability to hold a set temperature with minimal fluctuation ensures that an experiment performed today will yield the same thermal results as one performed next month.
This precision is critical for quality control, allowing technicians to verify that a material meets specific performance standards after treatment.
The Principle of Uniform Heating
Temperature uniformity means that there are no significant "hot spots" or "cold spots" within the furnace's heating chamber. Every part of the sample is exposed to the exact same temperature.
This is vital for processes like annealing metals or growing crystals, where inconsistent heating would create stress points or imperfections in the material's structure.
Common Applications Driving Their Importance
The need for controlled heating environments makes furnaces indispensable across a wide range of fields. These applications highlight their role in both foundational research and industrial production.
Material Curing and Drying
Furnaces are used to cure polymers, adhesives, and composites, a process that solidifies the material and strengthens its chemical bonds. They are also used for drying samples to remove all moisture content before analysis, a process known as ashing.
Annealing and Heat Treatment
In metallurgy, furnaces perform heat treatment to alter a material's physical and mechanical properties. Annealing, for example, involves heating metal and then cooling it slowly to reduce hardness and increase ductility.
Synthesis and Crystal Growth
Advanced scientific applications rely on the extreme stability of a laboratory furnace. They are used to synthesize new materials or for crystal growth, where a stable, uniform temperature is absolutely necessary for forming a perfect crystalline structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Furnace Types
Not all furnaces are created equal. The design of the furnace is directly tied to its intended application, representing a trade-off between versatility and specialized performance.
General-Purpose Box Furnaces
Often called muffle furnaces, these have a box-shaped chamber and are the workhorses of many labs. They are excellent for general-purpose applications like drying, simple heat treatments, and ashing.
While highly capable, they may not offer the elite level of temperature uniformity required for the most sensitive processes.
Specialized Tube Furnaces
A tube furnace is designed for ultimate precision. It features a cylindrical chamber where samples are placed inside a separate work tube, often made of ceramic or quartz.
The heating elements surround the tube, creating an exceptionally uniform thermal environment. This design is superior for applications like crystal growth, semiconductor manufacturing, and advanced materials synthesis where any temperature variance is unacceptable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace is crucial for achieving your desired outcome. The decision hinges entirely on the level of thermal precision your process requires.
- If your primary focus is general sample preparation, drying, or basic heat treatment: A standard box or muffle furnace provides the necessary performance and versatility.
- If your primary focus is high-precision material synthesis, crystal growth, or sensitive testing: A tube furnace is required for its superior temperature uniformity and control.
Ultimately, understanding which furnace to use is fundamental to ensuring the integrity and success of your work.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Provides controlled thermal environments for precise heating in labs. |
| Key Features | High-temperature range (100°C to 1,800°C), uniform heating, and exceptional control. |
| Common Applications | Material curing, drying, annealing, synthesis, and crystal growth. |
| Furnace Types | Box/muffle furnaces for general use; tube furnaces for high-precision tasks. |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—tailored to meet the unique needs of research labs and industrial facilities. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature furnace solutions can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production



















