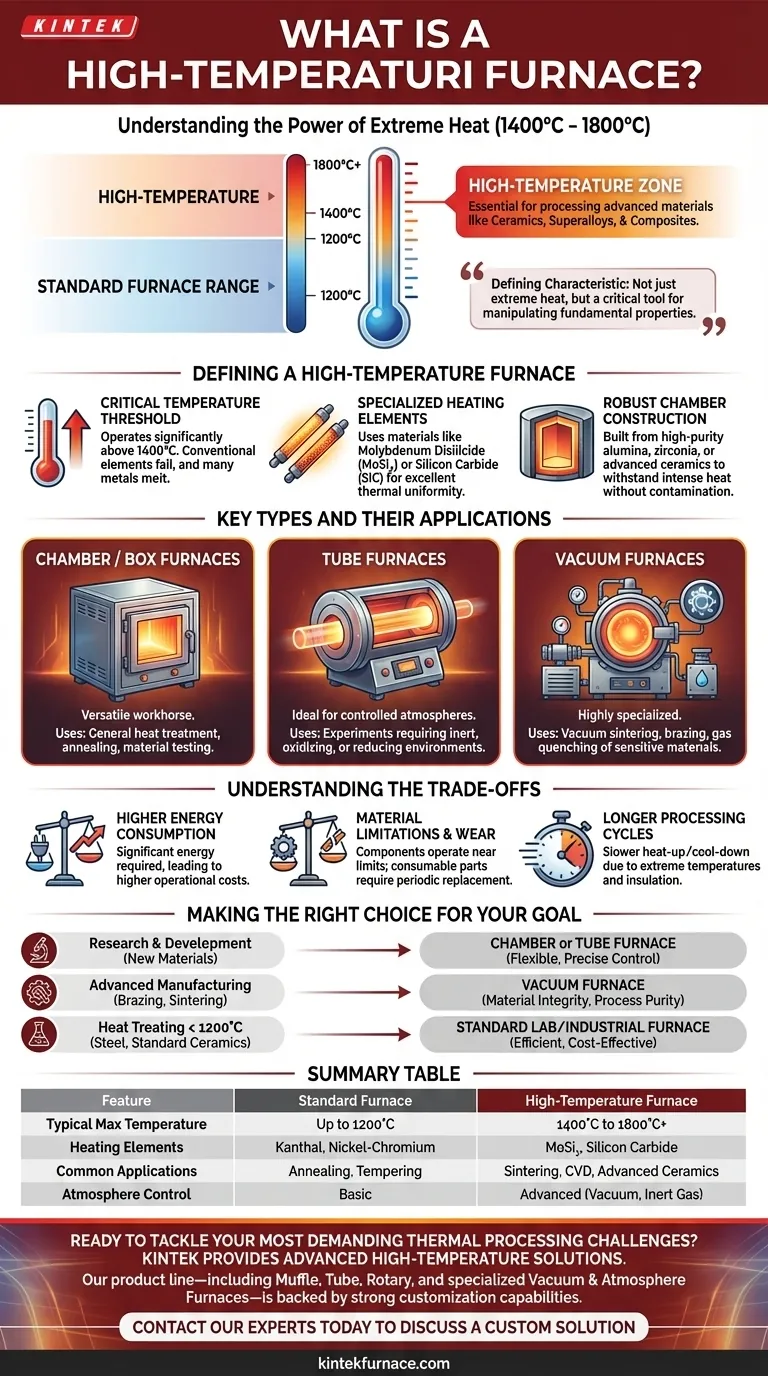
In essence, a high-temperature furnace is a specialized thermal processing unit designed to operate at temperatures significantly above standard laboratory or industrial ovens, typically in the range of 1400°C to 1800°C (2552°F to 3272°F). This capability is necessary for processing advanced materials that require extreme heat for their synthesis, shaping, or treatment.
The defining characteristic of a high-temperature furnace is not just its ability to generate extreme heat, but its role as a critical tool for manipulating the fundamental properties of advanced materials like ceramics, superalloys, and composites.

What Defines a High-Temperature Furnace?
Unlike conventional furnaces, which often top out around 1100°C to 1200°C, high-temperature furnaces are engineered from the ground up to safely and reliably manage extreme thermal stress.
The Critical Temperature Threshold
The primary distinction is the operational temperature range. A furnace operating above 1400°C is generally considered a high-temperature unit. This is a threshold where many common metals would melt and conventional heating elements would quickly fail.
Specialized Heating Elements and Uniformity
To achieve and sustain these temperatures, these furnaces use specialized heating elements, often made from materials like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) or Silicon Carbide (SiC).
These elements are typically positioned on multiple sides of the heating chamber to provide excellent thermal uniformity, ensuring that the material being processed is heated evenly.
Robust Chamber Construction
The internal chamber, which contains the material, must be built from extremely heat-resistant materials. Common choices include high-purity alumina, zirconia, or other advanced ceramics that can withstand the intense heat without degrading or contaminating the sample.
Key Types and Their Applications
High-temperature furnaces are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Their design is often tailored to a specific process or material.
Chamber or Box Furnaces
This is a common design featuring a front-loading door and a rectangular chamber. It is a versatile workhorse for general-purpose heat treatment, annealing, and material testing in a research or small-scale production environment.
Tube Furnaces
A high-temperature tube furnace features a cylindrical chamber, typically made of quartz or ceramic. Materials are placed inside this tube for processing.
This design is ideal for experiments requiring a controlled atmosphere, as gases can be flowed through the tube to create an inert, oxidizing, or reducing environment.
Vacuum Furnaces
This highly specialized variant is designed to heat materials in a vacuum or a tightly controlled, high-pressure gas environment.
It is essential for processes like vacuum sintering, brazing, and gas quenching of sensitive materials, including titanium alloys, high-temperature superalloys, and certain magnetic materials, preventing oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, these furnaces come with specific operational considerations that are critical to understand.
Higher Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures of 1400°C or more requires a significant amount of electrical energy compared to standard furnaces. This results in higher operational costs.
Material Limitations and Wear
The components themselves, from heating elements to chamber insulation, are operating near their absolute limits. They are consumable parts that will degrade over time and require periodic replacement.
Longer Processing Cycles
Due to the extreme temperatures and the mass of the insulating materials, high-temperature furnaces often have much slower heat-up and cool-down rates. This can impact throughput in a production setting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on the material you are working with and the process you need to perform.
- If your primary focus is research and development on new materials: A versatile box or tube furnace with precise temperature control offers the flexibility needed for experimentation.
- If your primary focus is advanced manufacturing like brazing or sintering: A specialized high-temperature vacuum furnace is non-negotiable to ensure material integrity and process purity.
- If your work involves heat treating standard steels or ceramics below 1200°C: A conventional lab or industrial furnace is more efficient, cost-effective, and likely a better fit.
Ultimately, choosing a furnace is about precisely matching the tool's capabilities to your specific thermal processing requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Furnace | High-Temperature Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Max Temperature | Up to 1200°C | 1400°C to 1800°C+ |
| Heating Elements | Kanthal, Nickel-Chromium | MoSi₂, Silicon Carbide |
| Common Applications | Annealing, tempering | Sintering, CVD, advanced ceramics processing |
| Atmosphere Control | Basic | Advanced (Vacuum, Inert Gas) |
Ready to tackle your most demanding thermal processing challenges?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions for diverse laboratories. Whether your work involves advanced ceramics, superalloys, or composites, our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and specialized Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can engineer a solution for your specific goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















