In simple terms, a heating element is a specialized component designed to convert electrical energy directly into heat. Its primary function is to generate this heat through a controlled process called resistive heating, which is then used for countless applications, from cooking food in an oven to warming a room with a space heater.
A heating element operates on a fundamental principle: when electricity flows through a material with high electrical resistance, the resulting "friction" at an atomic level generates heat. The entire device is engineered to produce and manage this effect safely and efficiently.
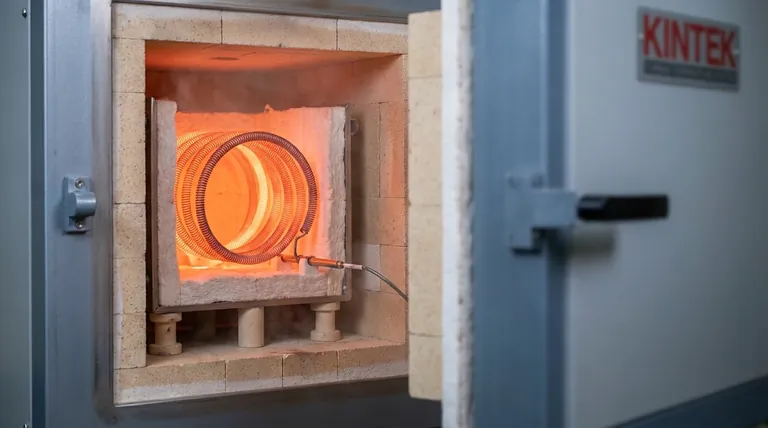

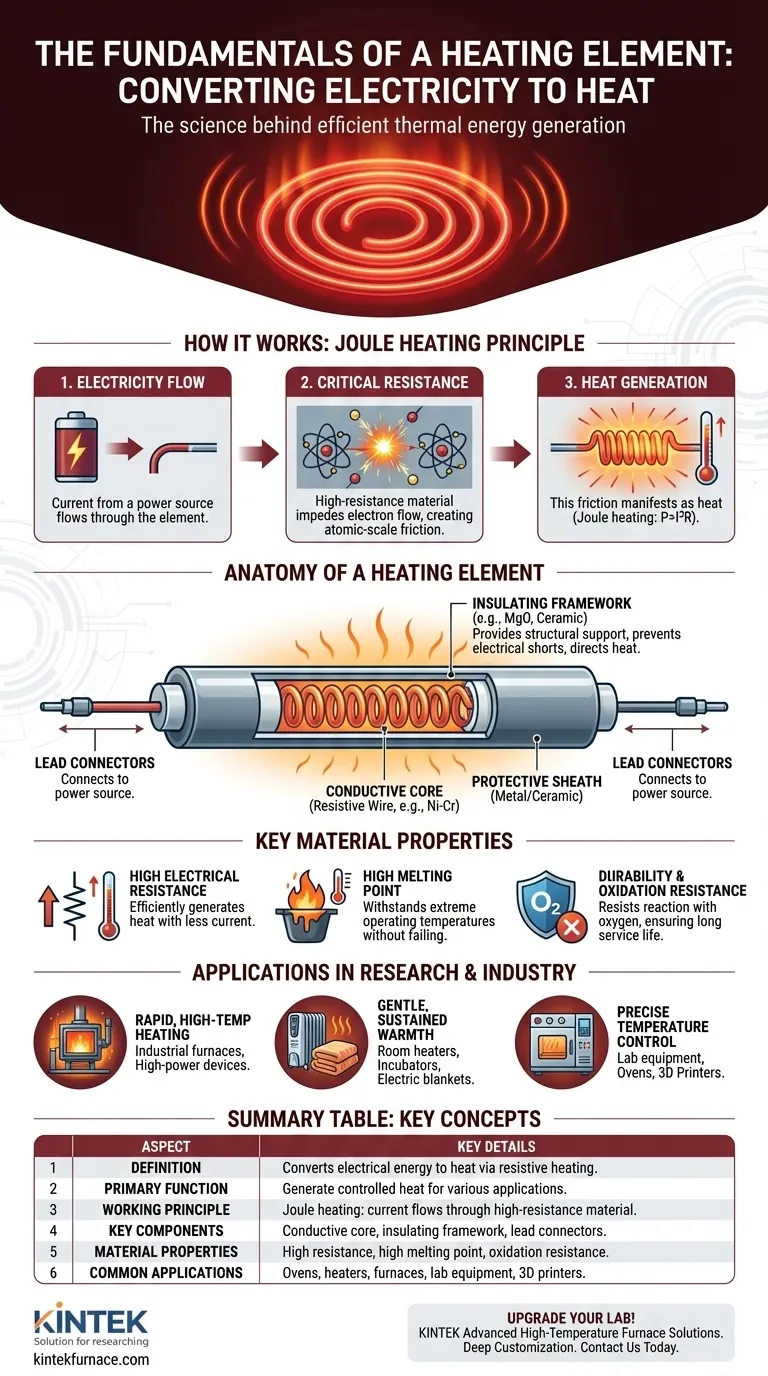
How Heating Elements Work: The Principle of Joule Heating
The conversion of electricity to heat is not magic; it is a predictable physical phenomenon known as Joule heating or resistive heating. The process can be broken down into three simple steps.
The Flow of Electricity
First, an electric current is passed from a power source through the heating element. This is simply a controlled flow of electrons through the element's core material.
The Critical Role of Resistance
The core of a heating element is made from a material with high electrical resistance. Unlike a copper wire, which is designed to let electricity flow easily, a resistive material deliberately impedes the flow of electrons.
As electrons are forced through this material, they collide with the atoms within it. This creates a sort of atomic-scale friction.
The Result: Heat Generation
This friction and the constant collisions manifest as heat, causing the element to get hot. The amount of heat produced is directly related to the amount of current and, most importantly, the material's resistance, a relationship described by Joule's first law (P = I²R).
Anatomy of a Heating Element
A functional heating element is more than just the wire that gets hot. It is an engineered assembly with several key parts designed to work together safely.
The Conductive Core
This is the heart of the device. It's the resistive wire or ribbon (often a nickel-chromium alloy) that is specifically chosen for its ability to generate heat efficiently and withstand high temperatures without degrading.
The Insulating Framework
The hot conductive core cannot be exposed directly. It is housed within or supported by an insulating material. This framework provides structural integrity and, critically, prevents the electrical current from shorting out and ensures the heat is directed where it is needed.
Lead Connectors
These are the terminals or wires that safely connect the resistive core to the external electrical circuit, allowing power to flow into the element.
Understanding the Key Material Properties
The choice of material for the conductive core is not arbitrary. To function correctly and have a long service life, the material must possess a specific set of properties.
High Electrical Resistance
This is the most important property. A higher resistance allows the element to generate significant heat with less electrical current, making the process more efficient and controllable.
High Melting Point
A heating element is designed to get very hot, often glowing red or white-hot. The material must have a very high melting point to withstand these operating temperatures without failing.
Durability and Oxidation Resistance
At high temperatures, many materials react with oxygen in the air, a process called oxidation. This causes them to become brittle and fail. Materials used in heating elements are chosen for their ability to resist oxidation, ensuring they last for thousands of hours of use.
Applying This to Your Goal
The design of a heating element is always tied to its final application. Understanding this principle helps clarify its role in any device.
- If the primary focus is rapid, high-temperature heating: The element is designed for high power output, using materials with very high resistance and heat tolerance, as seen in toasters and industrial furnaces.
- If the primary focus is gentle, sustained warmth: The element is designed for lower, consistent power output to provide safe and steady heat over long periods, like in an electric blanket or a room heater.
- If the primary focus is precise temperature control: The element is integrated into a system with temperature sensors and controllers that switch it on and off to maintain a specific temperature, which is essential in lab equipment, ovens, and 3D printers.
Ultimately, the heating element is a fundamental component that reliably transforms electricity into the thermal energy that powers our modern world.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Component converting electrical energy to heat through resistive heating |
| Primary Function | Generate controlled heat for applications like cooking, heating, and industrial processes |
| Working Principle | Joule heating: current flows through high-resistance material, producing heat |
| Key Components | Conductive core, insulating framework, lead connectors |
| Material Properties | High electrical resistance, high melting point, oxidation resistance |
| Common Applications | Ovens, space heaters, industrial furnaces, lab equipment, 3D printers |
Upgrade your laboratory or industrial processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with strong deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our heating technologies can enhance efficiency and performance for your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance



















