In short, muffle furnaces are essential high-temperature tools used in a wide array of industries, including materials science, analytical chemistry, ceramics, metallurgy, and biomedical fields. Their common purpose is to heat materials in a highly controlled and contamination-free environment.
The unifying principle behind the muffle furnace's broad utility is not just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its design that isolates the material being heated from the direct flame or heating elements, ensuring purity and thermal uniformity.
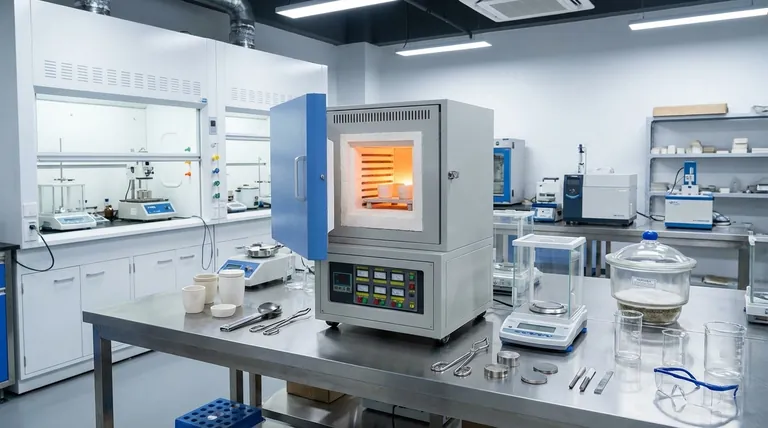

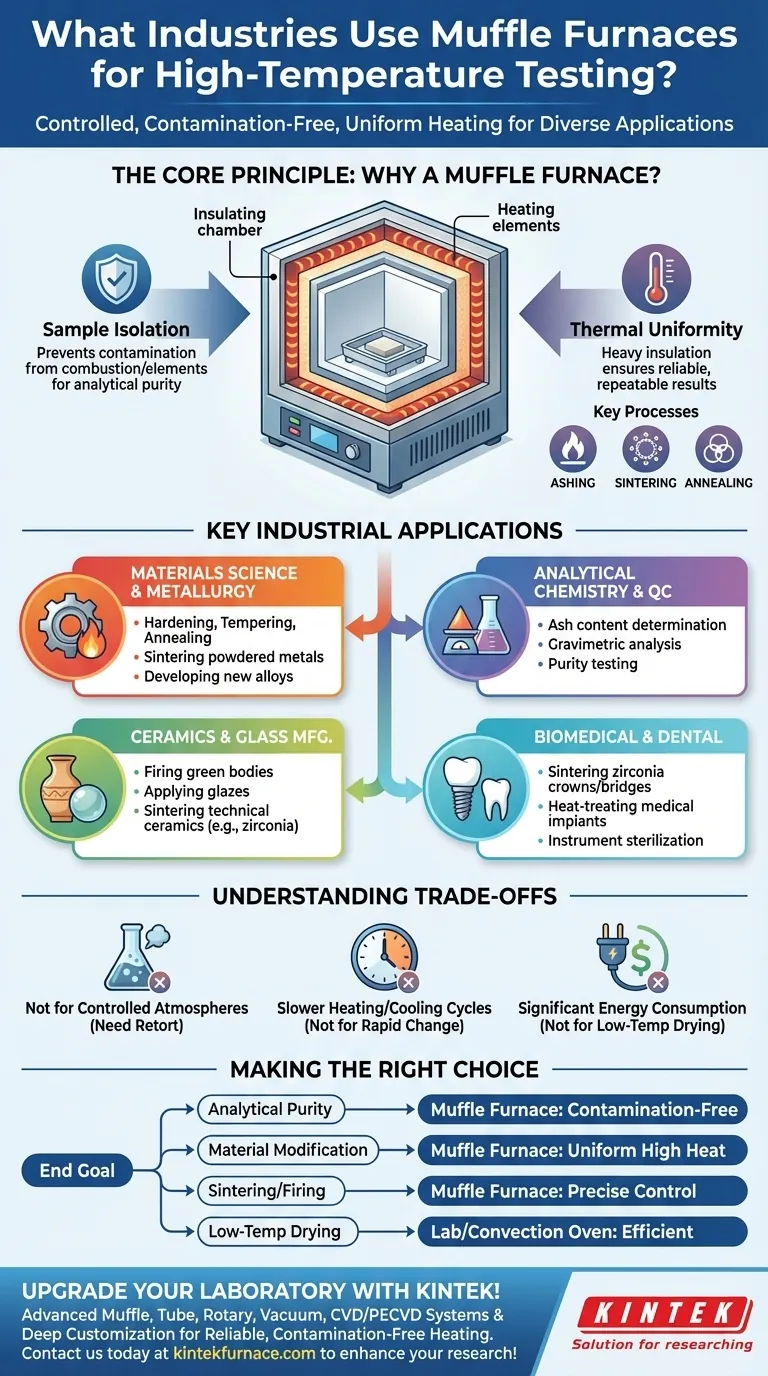
The Core Principle: Why a Muffle Furnace?
A standard oven heats things, but a muffle furnace does so with a specific set of advantages. Understanding these is key to seeing why so many different fields rely on it. The name itself comes from the "muffle"—an insulating inner chamber that separates the sample from the heating source.
Isolating the Sample from Contamination
The muffle chamber prevents combustion byproducts, like gases or soot from a fuel source, from contacting the sample. Even in electric furnaces, it protects the sample from flakes or radiation directly from the heating elements.
This isolation is critical for analytical purity, where any foreign material could skew test results.
Achieving High-Temperature Uniformity
These furnaces are engineered with heavy insulation and strategically placed heating elements to create a highly uniform temperature zone within the chamber.
This ensures that an entire sample or batch of products is subjected to the exact same thermal conditions, leading to reliable and repeatable results.
Enabling Specific Thermal Processes
The controlled, high-heat environment is perfect for inducing specific physical or chemical changes in materials.
Processes like ashing (burning off all organic material to measure what remains), sintering (fusing powders together), and annealing (softening metals) all depend on the precision of a muffle furnace.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
While the principles are the same, the specific applications vary significantly by industry.
Materials Science and Metallurgy
This sector uses muffle furnaces for fundamental heat treatment processes that define a material's final properties.
Applications include hardening, tempering, and annealing metals to alter their strength and ductility. They are also used for sintering powdered metals to create solid components and for developing new alloys.
Analytical Chemistry and Quality Control
Across nearly every manufacturing industry, labs use muffle furnaces for gravimetric analysis.
The most common application is ash content determination. A sample of plastic, rubber, paint, food, or coal is weighed, completely combusted in the furnace, and the remaining non-combustible ash is weighed again. This is a critical quality control test.
Ceramics and Glass Manufacturing
The production of advanced ceramics and specialized glass relies on precise heating cycles.
Muffle furnaces are used for firing green ceramic bodies to harden them, for applying glazes, and for sintering technical ceramics like zirconia, which are used in everything from dental crowns to industrial cutting tools.
Biomedical and Dental Fields
The need for biocompatible materials that can withstand stress makes muffle furnaces indispensable.
Dental labs use them extensively to sinter zirconia crowns and bridges, creating incredibly hard and durable restorations. They are also used in research to heat-treat metallic alloys for medical implants and to sterilize certain instruments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not the right tool for every heating task. Understanding its limitations is crucial for proper selection.
Not Ideal for Controlled Atmospheres
A standard muffle furnace operates with an air atmosphere. If your process requires an inert gas (like argon) or a reactive gas, you will need a specialized retort furnace, not a conventional muffle furnace.
Slower Heating and Cooling Cycles
The heavy insulation required to reach and maintain high temperatures means these furnaces heat up and cool down relatively slowly.
This can be a bottleneck in high-throughput environments. For applications requiring rapid temperature changes, other furnace types may be more suitable.
Significant Energy Consumption
Reaching temperatures of 1000°C or higher requires a substantial amount of energy. For lower-temperature applications (below 300°C), a simple lab oven is often a more efficient and cost-effective choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating equipment depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity (e.g., ash testing): A muffle furnace is non-negotiable for its contamination-free environment.
- If your primary focus is modifying material properties (e.g., hardening steel): A muffle furnace provides the uniform, high heat essential for repeatable heat treatment.
- If your primary focus is creating ceramic or sintered parts: The precise temperature control of a muffle furnace is critical for successful firing and densification.
- If your primary focus is simply drying a sample at low temperatures: A standard laboratory or convection oven is a more efficient and appropriate tool.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace is best understood as a precise instrument for material transformation and analysis, not just a simple source of heat.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Materials Science & Metallurgy | Hardening, tempering, annealing, sintering metals and alloys |
| Analytical Chemistry & Quality Control | Ash content determination, gravimetric analysis for purity |
| Ceramics & Glass Manufacturing | Firing, glazing, sintering technical ceramics |
| Biomedical & Dental Fields | Sintering zirconia crowns, heat-treating implants, sterilization |
Upgrade your laboratory with precision high-temperature solutions from KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for reliable, contamination-free heating. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research and production efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















