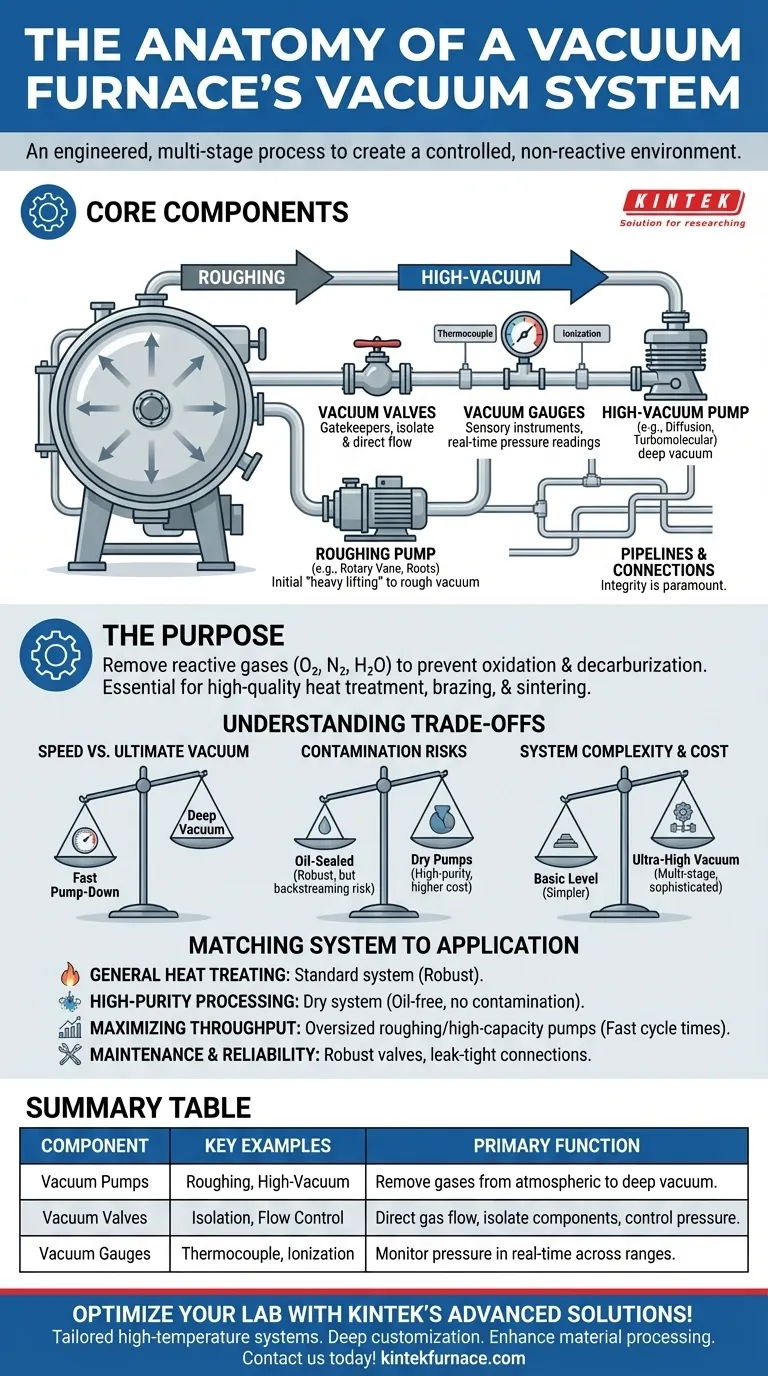
At its core, a vacuum furnace's vacuum system consists of the components required to remove atmosphere from a sealed chamber and measure the resulting pressure level. The primary elements are always a vacuum pump (or a series of pumps), vacuum valves to control flow, and a vacuum gauge to monitor the environment. The specific types and arrangement of these components are determined by the final vacuum level required for the process.
The critical takeaway is that a "vacuum system" is not just a single pump. It is an engineered, multi-stage process where different types of pumps and controls work in sequence to efficiently remove atmosphere from the furnace, moving from atmospheric pressure down to a deep vacuum.

The Purpose: Why a Vacuum System is Essential
A standard furnace heats materials in the presence of the surrounding air, which is rich in oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor. This can lead to unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation and decarburization, which degrade the material's surface and properties.
The sole purpose of the vacuum system is to remove these reactive gases from the furnace chamber before and during the heating process. This creates a clean, controlled, and non-reactive environment, which is essential for high-quality heat treatment, brazing, and sintering.
A Breakdown of Core Components
A vacuum system's architecture can range from simple to highly complex, but it is always built around three functional pillars: pumping, control, and measurement.
Vacuum Pumps: The Engine of the System
It is extremely rare for a single pump to handle the entire job. Different pumps operate efficiently at different pressure ranges, so they are used in sequence.
- Roughing Pumps (Primary Pumps): These pumps do the initial "heavy lifting," removing the bulk of the air from the chamber from atmospheric pressure down to a rough vacuum. Mechanical rotary vane pumps and Roots pumps are common examples.
- High-Vacuum Pumps (Secondary Pumps): Once the roughing pump has lowered the pressure sufficiently, a high-vacuum pump takes over to achieve the final, deep vacuum level. Common types include oil diffusion pumps and turbomolecular pumps, which can reach pressures as low as 7 x 10⁻³ Pa or even lower.
Vacuum Valves: Controlling the Flow
Valves are the gatekeepers of the vacuum system. They isolate components, direct the flow of gas, and allow the chamber to be returned to atmospheric pressure in a controlled manner.
Their functions include isolating the high-vacuum pump until the proper pressure is reached, switching between different pumps, and sealing the chamber from the pump system entirely to perform leak checks.
Vacuum Gauges: The System's Eyes and Ears
You cannot control what you cannot measure. Vacuum gauges are the sensory instruments that provide real-time pressure readings inside the furnace.
Like pumps, different gauges are used for different pressure ranges. A system will typically have a thermocouple gauge to measure the initial rough vacuum and a more sensitive ionization gauge to measure the final high vacuum level accurately.
Pipelines and Connections: The System's Skeleton
Connecting all of these components are a series of pipes, flanges, and seals. The integrity of these connections is paramount. A single small leak can prevent the system from ever reaching its target vacuum, compromising the entire process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing and designing a vacuum system involves balancing performance, cost, and process requirements. There is no single "best" configuration.
Speed vs. Ultimate Vacuum
Some pumps, like a large Roots pump, can remove gas very quickly but cannot achieve a deep vacuum. Others, like a diffusion pump, are slower but can reach extremely low pressures. The system design must balance the need for a fast pump-down time with the required ultimate vacuum level for the process.
Contamination Risks
The type of pump used can introduce contaminants. Oil-sealed pumps (like rotary vane and diffusion pumps) are cost-effective and robust but carry a small risk of "backstreaming," where oil vapor migrates from the pump back into the furnace chamber.
"Dry" pumps (like scroll or turbomolecular pumps) eliminate this risk, making them essential for high-purity applications like medical implants or electronics, but they come at a higher initial cost and can have different maintenance needs.
System Complexity and Cost
Achieving a deeper vacuum requires more stages and more sophisticated components. A system designed for a basic vacuum level will be far simpler and less expensive than a multi-stage, dry-pump system required for ultra-high vacuum applications. The complexity and cost must be justified by the needs of the material being processed.
Matching the System to the Application
When evaluating a vacuum furnace, consider how the system's design aligns with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating or brazing: A standard system with a mechanical roughing pump and a diffusion or turbomolecular pump will be robust and sufficient.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing for sensitive materials: A "dry" system with oil-free pumps is necessary to eliminate the risk of hydrocarbon contamination.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: A system with oversized roughing pumps and high-capacity secondary pumps will be required to achieve fast pump-down and cycle times.
- If your primary focus is maintenance and reliability: Prioritize robust valves and high-quality, leak-tight connections, as these are the most common points of failure in any vacuum system.
Ultimately, viewing the vacuum system not as a list of parts, but as an integrated solution for atmospheric control, is the key to mastering your vacuum furnace operations.
Summary Table:
| Component Type | Key Examples | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Pumps | Roughing (e.g., Rotary Vane), High-Vacuum (e.g., Turbomolecular) | Remove gases from atmospheric to deep vacuum levels |
| Vacuum Valves | Isolation, Flow Control Valves | Direct gas flow, isolate components, and control pressure |
| Vacuum Gauges | Thermocouple, Ionization Gauges | Monitor pressure in real-time across different ranges |
Optimize your lab's performance with KINTEK's advanced vacuum furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether for high-purity processing, fast throughput, or reliable maintenance. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum systems can enhance your material processing and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance



















