At its core, a muffle furnace can be customized across nearly every aspect of its design, from its fundamental physical structure to its data output and atmospheric controls. Available options allow you to specify the furnace's size and orientation, the materials used for its heating elements, its level of process automation, and the specific accessories needed for material handling and safety.
The key is to understand that customization goes far beyond simple add-ons. It is about fundamentally tailoring the furnace's construction, atmosphere, and control systems to meet the precise demands of your specific scientific process or production workflow.

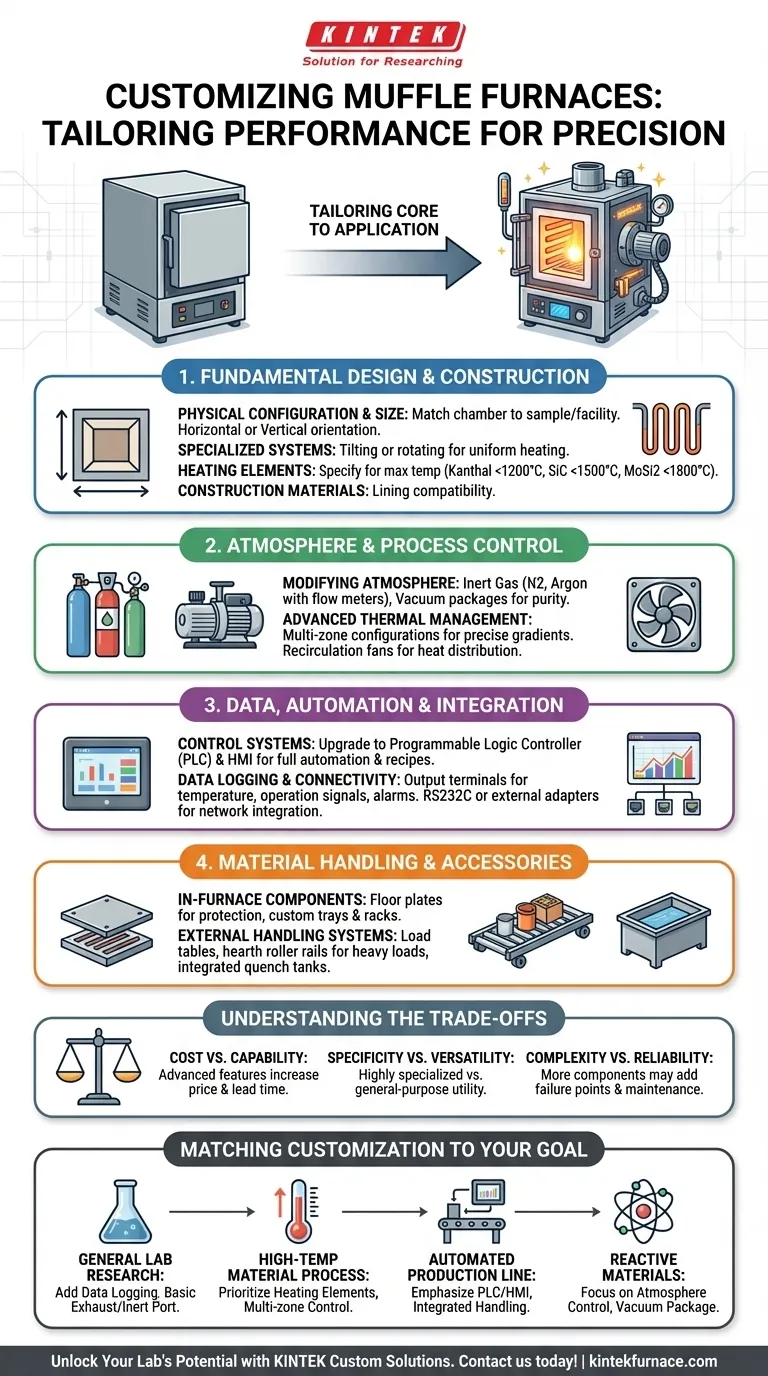
Breaking Down the Customization Categories
A standard muffle furnace offers programmable heating in a reliable, sturdy box. Customization is the process of modifying that box to perform a highly specific task with greater efficiency, safety, and control. These modifications fall into four main categories.
1. Fundamental Design and Construction
This is the most basic level of customization, defining the furnace's physical footprint, orientation, and thermal capabilities.
Physical Configuration and Size
The internal chamber dimensions and overall size of the furnace can almost always be specified to match your sample size or facility constraints. You can also define the furnace's basic orientation as a horizontal (front-loading) or vertical (top-loading) unit.
For more specialized processes, advanced mechanical systems like tilting or rotating furnaces can be designed to ensure materials are heated uniformly.
Construction Materials and Heating Elements
The maximum achievable temperature is determined by the heating elements. You can specify elements like Kanthal (up to 1200°C), Silicon Carbide (SiC, up to 1500°C), or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2, up to 1800°C) based on your thermal requirements.
The furnace's internal lining and other construction materials can also be selected for compatibility with your specific process.
2. Atmosphere and Process Control
For many applications, controlling the environment inside the furnace is just as important as controlling the temperature.
Modifying the Internal Atmosphere
Simple exhaust systems can be added to vent fumes. For more advanced control, you can specify a furnace built for inert gas atmospheres, which includes sealed gas inlets, outlets, and N2 or Argon loading devices with flow meters.
For the highest level of atmospheric purity, full vacuum packages are available, turning the unit into a vacuum furnace with dedicated ports and pumps.
Advanced Thermal Management
While standard furnaces offer high temperature uniformity, multi-zone configurations provide even more precise control over the thermal gradient within the chamber.
Recirculation fans can also be added to improve heat distribution through convection, which is especially useful at lower temperatures.
3. Data, Automation, and Integration
Modern labs and industrial facilities require furnaces to be more than just standalone ovens; they must integrate into larger systems.
Control Systems and Automation
Standard programmable controllers can be upgraded to sophisticated Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) and Human-Machine Interface (HMI) systems. This allows for full automation of complex heating cycles, safety interlocks, and process recipes.
Data Logging and Connectivity
To monitor and record process data, a variety of output terminals can be added. These include temperature output terminals, operation signal terminals, and alarm or event output terminals.
For connecting to external computers or networks, you can add an RS232C terminal or a more modern external communication adapter. This is essential for formal data acquisition and quality control.
4. Material Handling and Accessories
These options focus on the practical aspects of getting materials in and out of the furnace safely and protecting the equipment.
In-Furnace Components
Furnace floor plates (hearth plates) are a common addition to protect the furnace's insulation from spills and mechanical wear. Custom sample trays and racks can also be designed to hold your specific parts or crucibles.
External Handling Systems
In a production environment, efficiency and safety are paramount. Options like load tables, hearth roller rails for heavy loads, and integrated quench tanks for rapid cooling can be engineered into a complete system.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Customization provides immense capability, but it's critical to weigh the associated costs and complexities.
Cost vs. Capability
Every modification adds cost. Fundamental design changes, like adding a vacuum system or PLC controls, will significantly increase the price and lead time compared to adding a simple data port.
Specificity vs. Versatility
A highly specialized furnace, perfectly designed for one unique process, may be inefficient or unusable for other general-purpose tasks. You may be trading future flexibility for present-day performance.
Complexity vs. Reliability
Advanced features like multi-zone control, automation, and recirculation fans introduce more components. While they enhance performance, they also add potential points of failure and may require more sophisticated maintenance and operator training.
Matching Customization to Your Goal
Use your primary objective to guide your customization choices.
- If your primary focus is general lab research or QA: Start with a standard furnace and add data logging capabilities (temperature output, RS232C) and a basic exhaust or inert gas port for versatility.
- If your primary focus is a specific high-temperature material process: Prioritize the heating elements (SiC, MoSi2), chamber insulation, and consider a multi-zone controller for precise thermal uniformity.
- If your primary focus is an automated production line: Emphasize PLC/HMI control, robust data acquisition, and integrated material handling systems like roller hearths and load tables.
- If your primary focus is working with reactive or sensitive materials: Your entire design must revolve around atmosphere control, specifying a fully sealed chamber with either an inert gas or a complete vacuum package.
By clearly defining your core need, you can specify a furnace that is the right tool for your job.
Summary Table:
| Customization Category | Key Options |
|---|---|
| Design & Construction | Size, orientation (horizontal/vertical), heating elements (Kanthal, SiC, MoSi2), tilting/rotating systems |
| Atmosphere & Process Control | Exhaust systems, inert gas atmospheres, vacuum packages, multi-zone configurations, recirculation fans |
| Data, Automation & Integration | PLC/HMI systems, data logging terminals (temperature, operation, alarm), RS232C, external communication adapters |
| Material Handling & Accessories | Floor plates, sample trays/racks, load tables, hearth roller rails, quench tanks |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Laboratory with KINTEK's Custom High-Temperature Furnaces
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need tailored designs for specific processes, enhanced automation, or specialized accessories, we deliver reliable, efficient solutions that boost productivity and ensure precise results.
Ready to optimize your setup? Contact us today for a personalized consultation and discover how our expertise can transform your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are precision stirring and drying equipment necessary for photocatalytic materials? Master Microstructure Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in analyzing the combustion residues? Optimize Your Composite Char Analysis
- What is the primary use of a muffle furnace in the assembly of side-heated resistive gas sensors? Expert Annealing Guide
- Why is a muffle furnace used to determine the ash content of biochar? Master Your Material Purity Analysis
- How does a stainless steel reactor function within a muffle furnace for PET to graphene? Master Carbon Synthesis



















