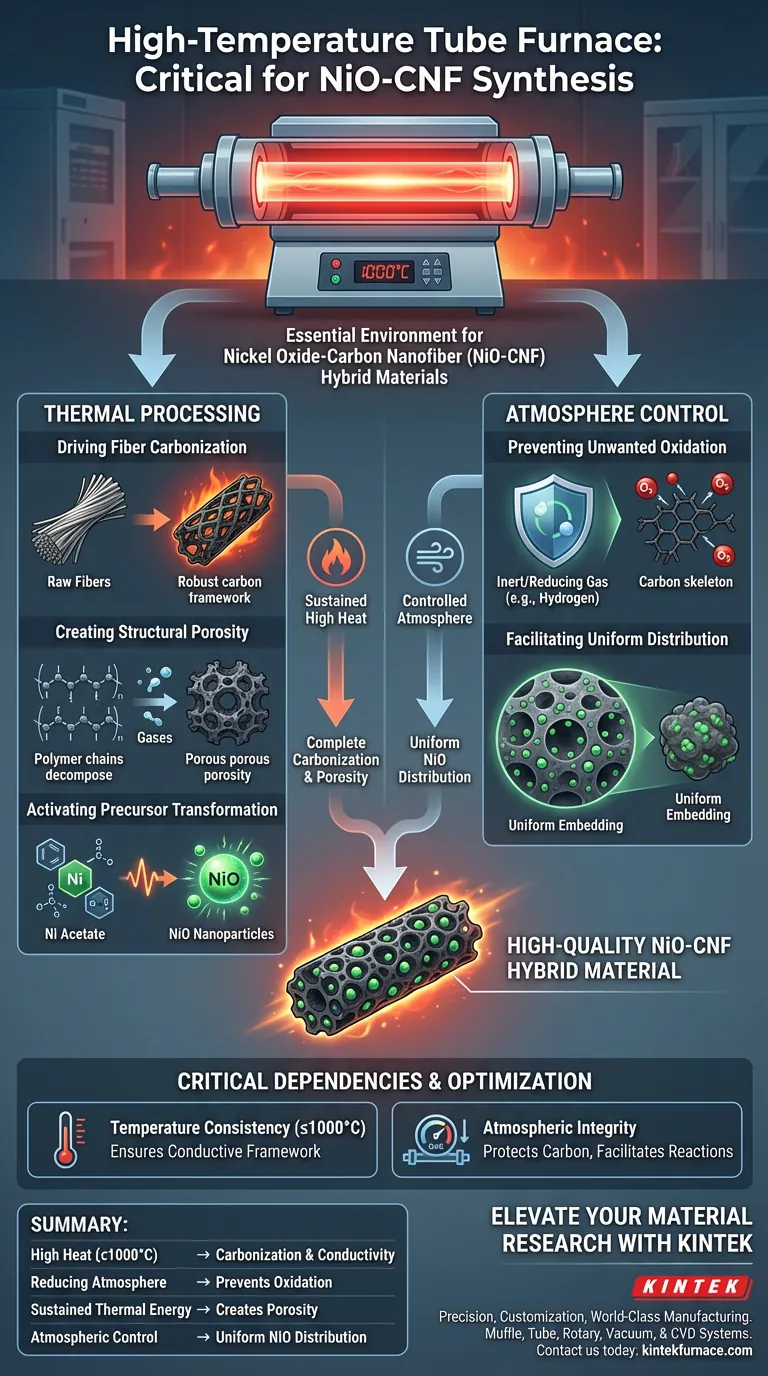
A High-Temperature Tube Furnace creates the essential environment for synthesizing Nickel Oxide-Carbon Nanofiber (NiO-CNF) hybrid materials by providing constant high heat alongside a strictly controlled atmosphere. This equipment maintains temperatures up to 1000°C within a reducing or inert environment (such as hydrogen), driving the simultaneous carbonization of the fiber matrix and the chemical conversion of precursors into active nanoparticles.
The High-Temperature Tube Furnace is not merely a heat source; it acts as a precise reactor that synchronizes the creation of a conductive carbon skeleton with the synthesis and uniform embedding of Nickel Oxide (NiO) nanoparticles.

The Role of Thermal Processing
Driving Fiber Carbonization
The furnace provides constant high temperatures that are critical for the carbonization process. Under this sustained heat, the raw fibers are converted into a robust, conductive carbon framework that serves as the structural backbone of the hybrid material.
Creating Structural Porosity
The thermal energy drives the decomposition of the sacrificial polymer components within the material. This decomposition is essential because it excavates the pore structures where the active nanoparticles will eventually reside.
Activating Precursor Transformation
The heat works in tandem with the chemical precursors. Specifically, it provides the energy required for nickel acetate precursors to undergo the chemical changes necessary to become nickel oxide (NiO) nanoparticles.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
Preventing Unwanted Oxidation
A standard open-air environment would destroy the material at these temperatures. The tube furnace provides a controlled reducing or inert atmosphere, often utilizing hydrogen, to protect the developing carbon structure from burning away.
Facilitating Uniform Distribution
The controlled atmosphere ensures the chemical reactions proceed at a regulated pace. This regulation allows the newly formed NiO nanoparticles to be uniformly distributed throughout the pores created by the polymer decomposition, rather than clumping on the surface.
Critical Process Dependencies
Temperature Consistency
The process relies on the furnace's ability to hold a constant temperature (up to 1000°C). Fluctuations in heat can lead to incomplete carbonization or inconsistent pore formation, compromising the material's conductivity.
Atmospheric Integrity
The quality of the final material is directly tied to the purity of the furnace environment. If the reducing or inert atmosphere is compromised, the chemical transformation of the nickel acetate may fail, or the carbon framework may degrade.
Optimizing Material Synthesis
To achieve high-quality NiO-CNF hybrids, you must tune the furnace conditions to match your specific material goals:
- If your primary focus is maximum conductivity: Ensure the furnace maintains a consistent high temperature to guarantee the complete carbonization of the carbon framework.
- If your primary focus is particle dispersion: Prioritize the stability of the inert or reducing atmosphere to facilitate the uniform distribution of NiO nanoparticles within the pore structures.
The success of NiO-CNF formation hinges on the rigorous control of both thermal stability and atmospheric composition.
Summary Table:
| Process Condition | Function in NiO-CNF Synthesis | Impact on Material Quality |
|---|---|---|
| High Heat (≤1000°C) | Drives carbonization & precursor transformation | Determines structural backbone & conductivity |
| Reducing/Inert Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation & protects carbon skeleton | Ensures integrity of the conductive framework |
| Sustained Thermal Energy | Decomposes sacrificial polymers | Creates essential porosity for nanoparticle embedding |
| Atmospheric Control | Regulates chemical reaction rates | Facilitates uniform distribution of NiO nanoparticles |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when synthesizing high-performance NiO-CNF hybrids. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific laboratory requirements.
Whether you need rigorous atmosphere control for carbonization or uniform heat distribution for nanoparticle dispersion, our high-temperature furnaces provide the stability your research demands.
Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace needs and optimize your synthesis workflow with KINTEK.
Visual Guide
References
- Juhyeong Kim, Yoonkook Son. Lotus Root Type Nickel Oxide-Carbon Nanofibers: A Hybrid Supercapacitor Electrode Material. DOI: 10.3390/app14072977
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are some thermal processes that tube furnaces are used for? Achieve Precise Heat Treatment with Uniformity
- What is the function of autoclaves and tube reactors in hydrometallurgical leaching? Unlock Refractory Ore Potential
- What critical process conditions does a horizontal diffusion furnace provide? Master Silicide Formation Today
- How does the working temperature range affect the choice of a vertical tube furnace? Optimize Your Lab's Performance and Budget
- What critical process conditions does a tube atmosphere furnace provide for Sr2CuWO6? Control Atmosphere & Temperature
- What role does a tube annealing furnace play in CdSeTe passivation? Optimize Thin Film Carrier Lifetime
- How does a tube furnace facilitate the carbonization of ZIFs while preventing oxidation? Expert Insights
- What is the range of heating zone lengths in a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Optimize Your Thermal Processing



















