At its core, vacuum heat treatment provides superior material outcomes by eliminating the uncontrolled variable of atmospheric air. This prevents undesirable surface reactions like oxidation and decarburization, resulting in parts with enhanced mechanical properties, higher purity, and a clean, bright finish directly from the furnace.
The fundamental difference is one of control. Traditional methods treat materials in spite of the atmosphere, requiring corrective steps, while vacuum methods treat materials by mastering the atmosphere, enabling a level of precision and quality that is otherwise unattainable.
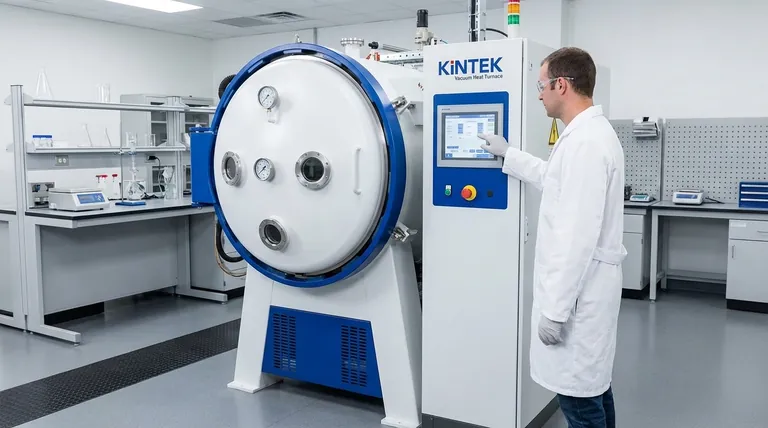

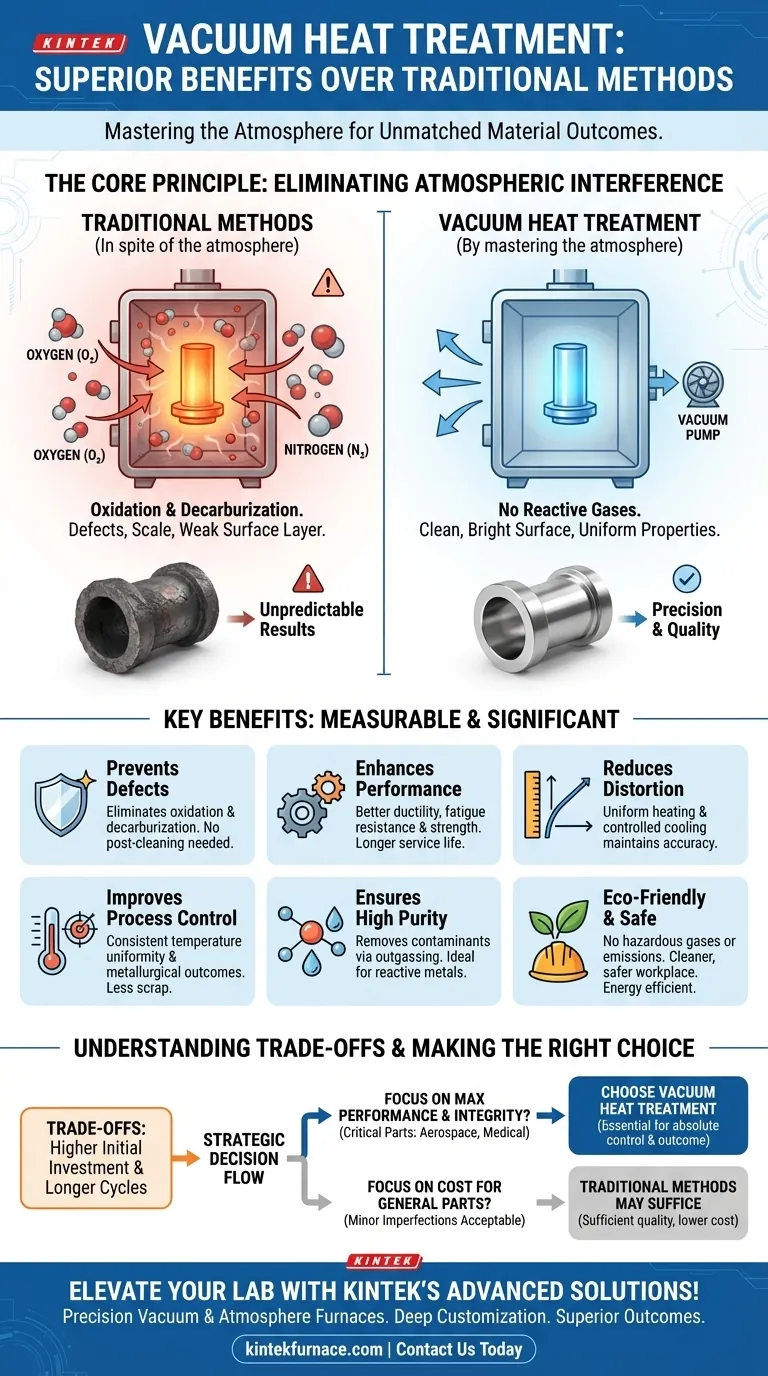
The Core Principle: Eliminating Atmospheric Interference
Heat treating in a conventional furnace means exposing a heated, highly reactive metal surface to an atmosphere composed of approximately 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen. This interaction is the source of most heat treatment defects.
The Problem with Traditional Atmospheres
In a traditional furnace, oxygen aggressively reacts with the hot metal surface, a process known as oxidation. This forms a layer of scale or discoloration.
This oxidation layer is not just cosmetic. It can degrade surface hardness, cause dimensional inaccuracies, and even create initiation points for cracks or fatigue failure.
Furthermore, the atmosphere can react with carbon within the steel, leading to decarburization. This loss of surface carbon results in a soft, weak outer layer that compromises the wear resistance and strength of the final component.
The Vacuum Solution
A vacuum furnace works by removing the atmosphere before applying heat. By operating in a near-perfect vacuum, there is virtually no oxygen or other reactive gases to interact with the part.
This complete control over the environment ensures that the material's surface chemistry remains unaltered throughout the process. The part that exits the furnace is the same, chemically, as the part that entered—only with its internal crystalline structure refined.
Superior Material Properties and Surface Integrity
Eliminating unwanted chemical reactions directly translates to a higher quality, better-performing final product. The benefits are measurable and significant.
Preventing Oxidation and Decarburization
Parts treated in a vacuum emerge clean, bright, and free of scale. This often eliminates the need for post-treatment cleaning operations like sandblasting or acid pickling, saving time and money.
More importantly, the surface retains its full carbon content and alloying elements, ensuring that the hardness, wear resistance, and strength achieved through heat treatment are uniform from the core to the surface.
Enhancing Mechanical Performance
A clean, non-oxidized surface is free from the microscopic defects that can plague conventionally treated parts. This preserves the material's inherent ductility and fatigue resistance.
The result is a component with a longer and more predictable service life, a critical factor for high-stress applications in industries like aerospace, medical, and high-performance automotive.
Reducing Distortion
Vacuum furnaces provide extremely uniform heating, as heat is primarily transferred through radiation in the absence of air currents. This, combined with controlled cooling (quenching) using inert gas, minimizes the thermal stresses that cause parts to warp or distort.
Unmatched Process Control and Repeatability
Beyond the metallurgical benefits, vacuum technology provides an exceptionally stable and repeatable manufacturing process.
Achieving Temperature Uniformity
The absence of convection currents in a vacuum ensures that all surfaces of a component—including complex geometries and internal bores—are heated at the same rate. This temperature uniformity is key to achieving consistent metallurgical transformations across the entire part.
Ensuring High Purity
A vacuum environment is inherently clean. It actively pulls contaminants, moisture, and absorbed gases off the surface of the parts, a process known as outgassing.
This results in a finished product with exceptionally high purity, which is essential for processing reactive metals like titanium or high-purity alloys used in electronics and medical implants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are clear, vacuum heat treatment is not the default solution for every application. It is a precision process with associated costs.
Higher Initial Investment and Cycle Costs
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment compared to traditional atmosphere furnaces. The process cycle itself can also be longer due to the time required to pump down the chamber to the required vacuum level.
When Simpler Methods Suffice
For general-purpose components where surface finish is not critical and slight decarburization is acceptable, conventional atmosphere-controlled or open-air furnace treatments can be more cost-effective. The key is to match the process to the part's performance requirements.
Operational and Environmental Advantages
Modern manufacturing decisions are also driven by efficiency, safety, and environmental impact, areas where vacuum technology excels.
Improving Energy Efficiency
Although cycle times can be longer, modern vacuum furnaces are highly insulated and lose very little heat to their surroundings. Unlike many traditional furnaces that must be idled at temperature over weekends to prevent thermal shock, a vacuum furnace can be completely shut down, saving significant energy.
Creating a Safer, Cleaner Workplace
Vacuum furnaces eliminate the need for flammable or explosive gases (like hydrogen or endothermic gas) often used in atmosphere furnaces. The process produces no emissions, no toxic byproducts, and no hazardous chemicals requiring disposal, leading to a much safer and more environmentally friendly operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heat treatment method requires aligning the process capabilities with your component's end-use requirements and value.
- If your primary focus is maximum material performance and surface integrity: Vacuum treatment is essential for critical components in aerospace, medical, or tool & die applications where failure is not an option.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability for high-value parts: The precision and stability of vacuum processing reduce scrap and rework, providing long-term value that can outweigh the initial cost.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general-purpose parts: Traditional atmosphere-controlled furnaces may provide sufficient quality for components where minor surface imperfections are acceptable.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum heat treatment is a strategic decision to prioritize absolute control over the metallurgical outcome of your most critical components.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Prevents Oxidation/Decarburization | Eliminates surface reactions, ensuring clean, bright finishes and uniform hardness without post-treatment cleaning. |
| Enhances Mechanical Properties | Improves ductility, fatigue resistance, and strength for longer service life in high-stress industries. |
| Reduces Distortion | Provides uniform heating and controlled cooling to minimize warping and maintain dimensional accuracy. |
| Ensures High Purity | Removes contaminants through outgassing, ideal for reactive metals and high-purity alloys. |
| Improves Process Control | Offers temperature uniformity and repeatability, reducing scrap and rework in manufacturing. |
| Environmental and Safety Benefits | Eliminates hazardous gases and emissions, creating a safer, cleaner workplace with better energy efficiency. |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with precision equipment like Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering superior material outcomes, enhanced process control, and cost savings. Don't settle for less—contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your heat treatment processes and drive innovation in your applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















