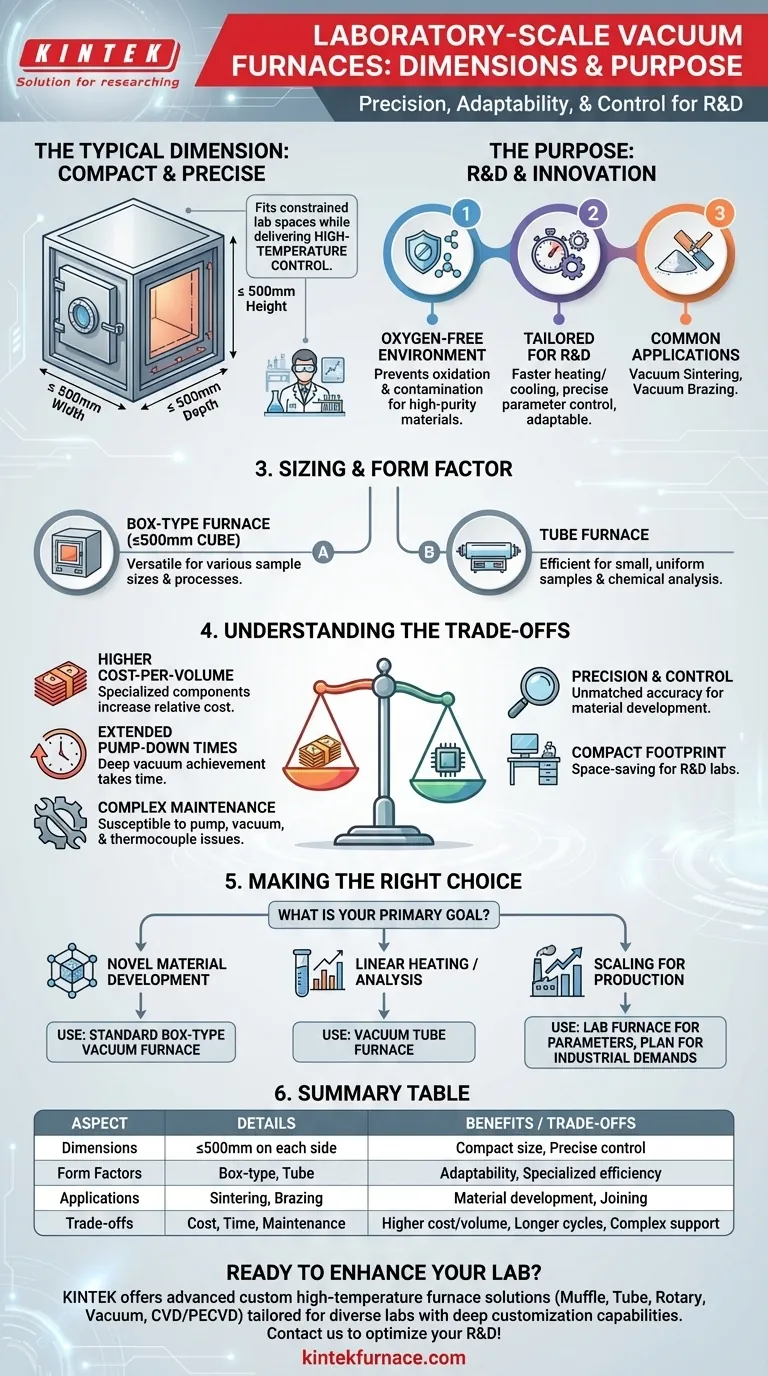
In short, a typical laboratory-scale vacuum furnace features internal chamber dimensions of 500x500x500mm or less. This compact size is a deliberate design choice to fit within constrained lab spaces while delivering the precise, controlled, high-temperature processing required for research and development.
The compact footprint of a laboratory vacuum furnace is not just about saving space. It reflects a design philosophy centered on precision, adaptability, and control over material properties, which introduces a distinct set of operational trade-offs compared to larger industrial systems.
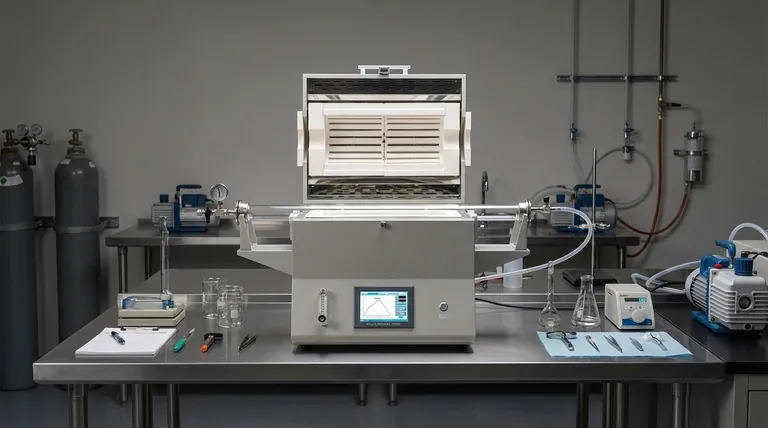

The Purpose of a Laboratory Vacuum Furnace
Understanding why these furnaces are built this way is key to using them effectively. Their design prioritizes experimental control over production volume.
Precision in an Oxygen-Free Environment
A vacuum furnace's primary function is to create a high-temperature processing environment that is free of oxygen and other reactive gases.
This prevents oxidation and contamination, allowing for the creation of materials with exceptional purity and specific properties that would be impossible to achieve in a conventional furnace.
Tailored for Research and Development
Unlike their industrial counterparts designed for mass production, lab-scale furnaces are built for adaptability.
Their compact size allows for faster heating and cooling cycles (relative to chamber mass) and more precise control over parameters, which is essential for testing new materials, validating processes, and conducting fundamental research.
Common Research Applications
These furnaces are platforms for a variety of high-temperature processes.
Common applications include high-temperature vacuum sintering, used to bond powdered materials together, and high-temperature vacuum brazing, which joins components with a filler metal.
Sizing and Form Factor
The "500mm cube" is a common benchmark, but the physical design can vary based on the specific research application.
The "≤500mm Cube" Standard
The typical internal chamber dimension of ≤500mm on each side is a direct response to the physical constraints of most research laboratories.
This allows the unit, including its necessary pumps and control systems, to occupy a manageable footprint.
Functionality in a Compact Form
Despite their small size, these furnaces are not "lite" versions of industrial systems. They retain all core functionalities, including sophisticated vacuum pumps, precise temperature controllers, and robust safety interlocks.
Alternative Form Factors: The Tube Furnace
For certain applications, such as element analysis or processing small, uniform samples, a vacuum tube furnace offers a more efficient alternative.
This design provides a cylindrical heating zone for highly controlled experiments in disciplines like chemistry and physics.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
The precision and compact nature of lab-scale vacuum furnaces come with specific operational complexities that every user must anticipate.
Higher Relative Equipment Costs
Specialized components required for high-vacuum and high-temperature performance mean that lab-scale furnaces often have a higher cost-per-volume than larger industrial units.
Extended Pump-Down Times
Achieving a deep vacuum is a time-consuming process. The pump-down cycle, where air is evacuated from the chamber, can add significant time to each experiment, impacting overall throughput.
Complex Maintenance and Troubleshooting
The stringent demands of a vacuum environment make these systems susceptible to specific failures. Maintenance is not trivial.
Common issues include pump failures, inconsistent vacuum levels due to leaks, and thermocouple failures caused by high vapor pressures from certain materials. Troubleshooting requires a systematic approach, checking each stage of the pumping system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on your experimental or process objective.
- If your primary focus is novel material development: A standard box-type vacuum furnace offers the greatest versatility for testing different sample sizes and process parameters.
- If your primary focus is linear sample heating or chemical analysis: A vacuum tube furnace provides a more specialized and efficient platform for your work.
- If your primary focus is scaling a process for production: Use the lab furnace to define parameters, but be prepared for the different operational and maintenance demands of larger industrial equipment.
Ultimately, a laboratory vacuum furnace is a powerful tool for innovation, designed to prioritize precision above all else.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Typical Internal Chamber Dimensions | ≤500mm on each side (e.g., 500x500x500mm) |
| Common Form Factors | Box-type, Tube furnace |
| Key Applications | High-temperature vacuum sintering, brazing, material development |
| Primary Benefits | Compact size, precise temperature control, oxygen-free environment |
| Trade-offs | Higher cost-per-volume, longer pump-down times, complex maintenance |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a custom vacuum furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your research and development processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role do tube furnaces play in semiconductor and battery production? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the primary function of high-purity quartz sealed tubes? Master Sb-Te Alloy Synthesis with Precision Isolation
- What materials are used for the tubes in a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Choose the Right Tube for Your Lab
- What is the primary function of a vacuum-sealed quartz tube in MnBi2Te4 growth? Ensure High-Purity Crystal Synthesis
- Why is a high-precision vacuum tube furnace essential for CVD graphene? Master Growth Control & Purity



















