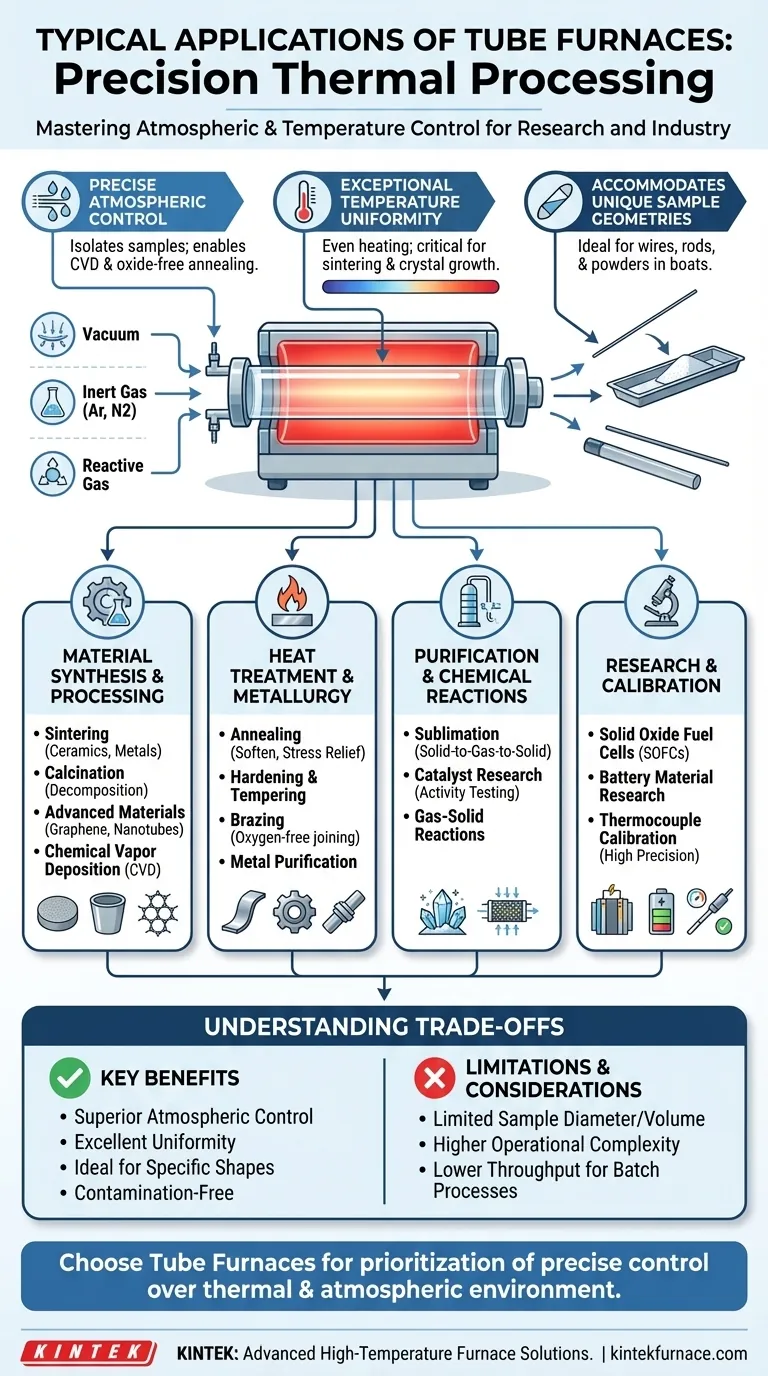
Tube furnaces are the workhorses of controlled thermal processing, used for an exceptionally wide range of applications in both research and industry. Their primary functions revolve around material synthesis, heat treatment, purification, and testing under highly specific conditions. Common applications include annealing metals, sintering powders, growing crystals, purifying compounds via sublimation, and testing catalysts or fuel cells.
The true value of a tube furnace is not simply its ability to reach high temperatures, but its capacity for precise atmospheric control. Its sealed, cylindrical chamber is uniquely suited for processes requiring a vacuum, an inert gas, or a reactive gas environment, making it indispensable where contamination or oxidation must be eliminated.

The Core Capabilities: Why a Tube Furnace?
A tube furnace is chosen over other furnace types, like a box furnace, when the process environment is as critical as the temperature itself. Its design delivers three key advantages.
Achieving Precise Atmospheric Control
The defining feature of a tube furnace is its ability to isolate a sample from the ambient air. By sealing the ends of the process tube, you can pull a vacuum or introduce a continuous flow of specific gases.
This is essential for applications like annealing, where an inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) prevents metals from oxidizing at high temperatures. It is also the foundation of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), where precursor gases are introduced to react and deposit a thin film onto a substrate.
Ensuring Exceptional Temperature Uniformity
The cylindrical geometry of a tube furnace naturally promotes even heating around the sample. This uniformity is critical for processes like sintering, where inconsistent temperatures would result in a material with non-uniform density and strength.
Many modern tube furnaces are available in multi-zone configurations. These allow for a highly uniform flat zone in the center or the creation of a specific temperature gradient along the tube, a requirement for certain crystal growth and chemical transport experiments.
Accommodating Unique Sample Geometries
The shape of a tube furnace makes it ideal for processing samples with a high aspect ratio, such as wires, rods, or strips that can be easily pushed through the tube.
It is also perfectly suited for processing powders or small components contained within a "boat," a long, narrow ceramic crucible. This configuration allows for efficient heating and easy interaction with process gases.
A Breakdown of Key Application Areas
The unique capabilities of tube furnaces make them integral to numerous fields, from fundamental research to industrial production.
Material Synthesis and Processing
This is a primary use case. Applications include sintering ceramic or metal powders into a dense solid, calcination to thermally decompose materials, and synthesis of advanced materials like graphene, carbon nanotubes, and polymer composites.
Heat Treatment and Metallurgy
In metallurgy, tube furnaces are used for a variety of heat treatments. These include annealing to soften metals and relieve internal stresses, hardening and tempering to achieve specific mechanical properties, and brazing components together in an oxygen-free environment.
Purification and Chemical Reactions
The controlled atmosphere is ideal for purification. Sublimation is a common technique where a solid is heated under vacuum, turns directly into a gas, and then re-deposits as a pure solid in a cooler part of the tube.
They are also used for catalyst research, where specific reactant gases are passed over a catalyst bed at a controlled temperature and flow rate to measure activity and longevity.
Research and Calibration
In a laboratory setting, tube furnaces are essential for foundational research on materials like solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) and next-generation batteries.
They are also a standard for the high-precision calibration of thermocouples, where the sensor is placed in the furnace's highly stable and uniform temperature zone to verify its accuracy against a known standard.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, a tube furnace is not the universal solution for all heating applications. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
The Limitation of Sample Size
The most obvious limitation is the diameter of the process tube. Tube furnaces are inherently unsuitable for heating large, bulky, or irregularly shaped objects. For these applications, a box furnace or muffle furnace provides the necessary volume.
Complexity and Throughput
Effectively running a process with a controlled atmosphere requires managing gas lines, flow controllers, vacuum pumps, and airtight seals. This adds a layer of operational complexity compared to a simple box furnace that heats in air. For batch processing, the usable volume can also be a bottleneck for industrial-scale throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct thermal equipment depends entirely on your process requirements for temperature, atmosphere, and sample geometry.
- If your primary focus is advanced material synthesis (like CVD or graphene): A tube furnace is essential for the required atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is heat treatment of small parts or powders (like annealing): A tube furnace offers superior results by preventing oxidation and ensuring uniform properties.
- If your primary focus is processing large, bulky, or irregularly shaped items: A box furnace or chamber furnace is the more practical and efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is simple drying, ashing, or debinding in air: A less complex and more cost-effective muffle or box furnace will suffice.
Ultimately, choosing a tube furnace is a decision to prioritize precise control over your sample's thermal and atmospheric environment.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis | Sintering, Calcination, CVD | Precise atmospheric control, uniform heating |
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, Hardening, Tempering | Oxidation prevention, temperature uniformity |
| Purification | Sublimation, Catalyst Research | Contamination-free environments |
| Research & Calibration | SOFC Testing, Thermocouple Calibration | High stability and accuracy |
Ready to elevate your thermal processing with precision and reliability?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, our product line—including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is designed for diverse laboratory applications. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure our furnaces precisely meet your experimental requirements, whether for material synthesis, heat treatment, or purification.
Don't let process limitations hold you back—contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can optimize your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















