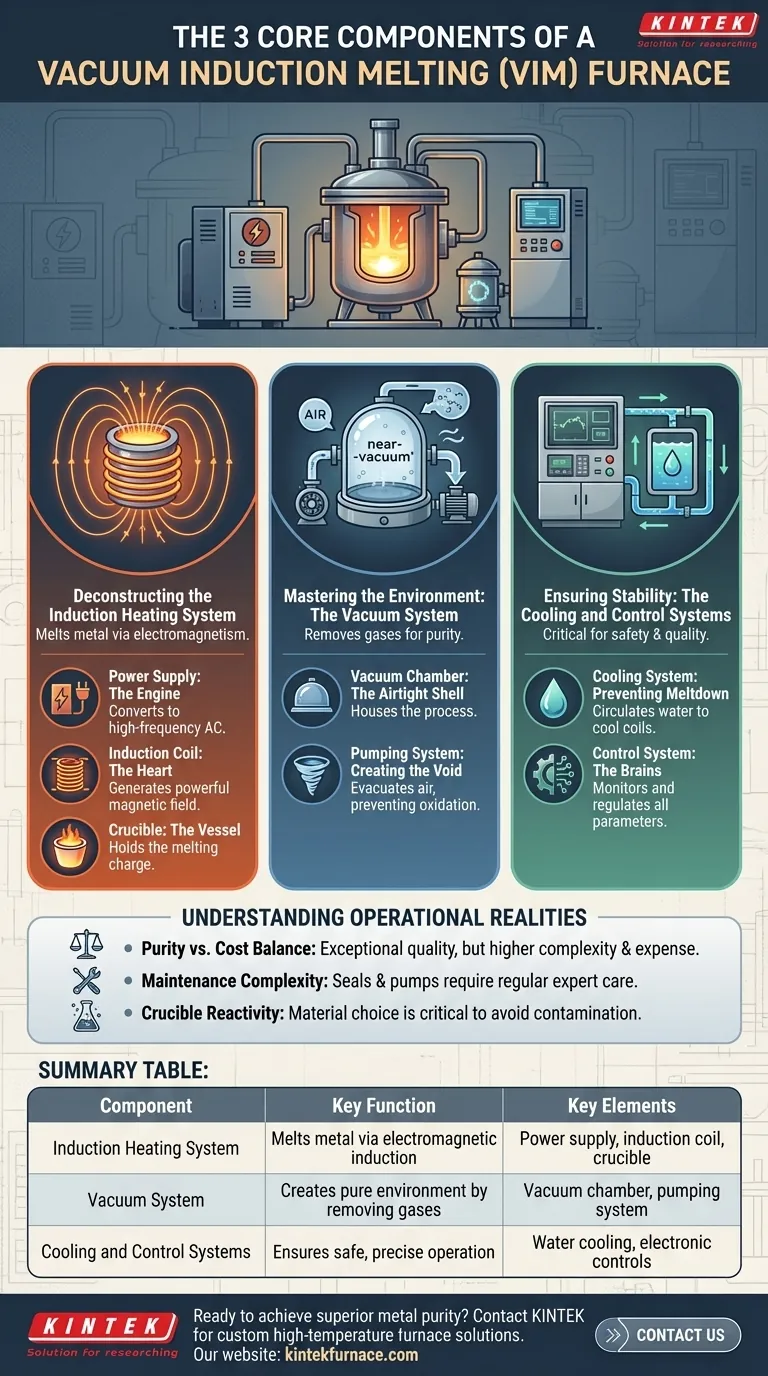
At its core, a vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnace is comprised of three primary functional systems. These are the induction heating system that melts the metal, the vacuum system that creates a controlled, pure environment, and the integrated cooling and control systems that ensure safe and precise operation.
A VIM furnace is not merely a device for melting metal. It is a sophisticated, integrated system where heating, vacuum, and control work in unison to produce materials with a level of purity and compositional accuracy that is unattainable with conventional atmospheric melting.
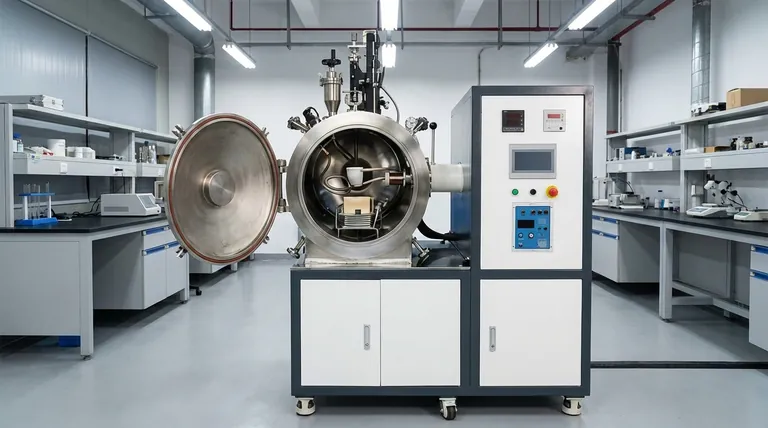

Deconstructing the Induction Heating System
The purpose of this system is to generate and apply intense heat to the metal charge without direct contact, leveraging the principles of electromagnetism.
The Power Supply: The Engine of the Furnace
The process begins with the power supply. This unit converts standard electrical power from the grid into a high-frequency alternating current (AC). The frequency can be adjusted, which is a key parameter for controlling the heating rate and the stirring effect within the molten metal.
The Induction Coil: The Heart of the Process
This high-frequency AC is fed into a water-cooled copper coil. As the current flows, the coil generates a powerful and rapidly alternating magnetic field inside the furnace chamber.
The Crucible: The Vessel for Molten Metal
The metal to be melted, known as the charge, is placed inside a crucible made of a non-conductive, high-temperature material like ceramic or graphite. When the magnetic field passes through the metal charge, it induces powerful eddy currents, which generate immense heat through electrical resistance, causing the metal to melt.
Mastering the Environment: The Vacuum System
The "vacuum" in VIM is what distinguishes it from other melting processes. Its sole purpose is to remove atmospheric gases that would otherwise contaminate the metal.
The Vacuum Chamber: The Airtight Shell
The entire process—coil, crucible, and charge—is housed within a robust, airtight chamber. This chamber is engineered to withstand both extreme internal temperatures and the external pressure of the atmosphere when a vacuum is pulled.
The Pumping System: Creating the Void
A series of powerful vacuum pumps is connected to the chamber. These pumps work to evacuate air and other gases, significantly lowering the internal pressure. This near-vacuum environment prevents the molten metal from reacting with oxygen and nitrogen, which avoids the formation of oxides and other impurities.
Ensuring Stability: The Cooling and Control Systems
These systems are not secondary; they are absolutely critical for the furnace's function, safety, and the quality of the final product.
The Cooling System: Preventing Meltdown
The immense energy required for induction heating generates a significant amount of waste heat, particularly in the induction coil itself. A closed-loop water cooling system continuously circulates water through the copper coils and often the chamber walls, preventing them from overheating and failing catastrophically.
The Control System: The Brains of the Operation
The electric control system is the central nervous system of the furnace. It allows operators to precisely monitor and regulate all critical parameters, including power input, frequency, temperature, and vacuum pressure. This level of control is essential for creating alloys with exact specifications and ensuring repeatable results.
Understanding the Operational Realities
While powerful, VIM technology involves specific trade-offs that are important to understand for any practical application.
The Purity vs. Cost Balance
The primary advantage of a VIM furnace is the exceptional purity and quality of the metal produced. However, the equipment—especially the high-capacity vacuum pumps and robust chamber—is complex and expensive to acquire and operate compared to atmospheric furnaces.
Maintenance Complexity
Maintaining a perfect vacuum seal is a constant challenge. The seals, pumps, and sophisticated electronic control systems all require specialized, regular maintenance to ensure the furnace operates reliably and continues to produce high-purity materials.
Crucible Reactivity
The crucible must be chemically stable and not react with the molten metal it holds. Choosing the right crucible material is critical, as a reaction can introduce impurities, defeating the purpose of vacuum melting. This limits the combinations of alloys and crucible materials that can be used.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these components helps you focus on what matters for your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum metal purity: The integrity of your vacuum system—the chamber seals and the power of your pumps—is your most critical factor.
- If your primary focus is precise alloying and composition control: The sophistication of your induction heating and control systems is paramount for managing temperature and electromagnetic stirring.
- If your primary focus is ensuring operational safety and efficiency: The reliability of your cooling and control systems is non-negotiable to prevent equipment failure and ensure consistent production cycles.
By understanding how these core systems interoperate, you can effectively leverage vacuum induction melting to achieve superior metallurgical results.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Key Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Induction Heating System | Melts metal via electromagnetic induction | Power supply, induction coil, crucible |
| Vacuum System | Creates pure environment by removing gases | Vacuum chamber, pumping system |
| Cooling and Control Systems | Ensures safe, precise operation | Water cooling, electronic controls |
Ready to achieve superior metal purity and precise alloy control with a custom vacuum induction melting furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're focused on maximizing purity, enhancing composition control, or ensuring operational safety, KINTEK has the expertise to deliver. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification



















