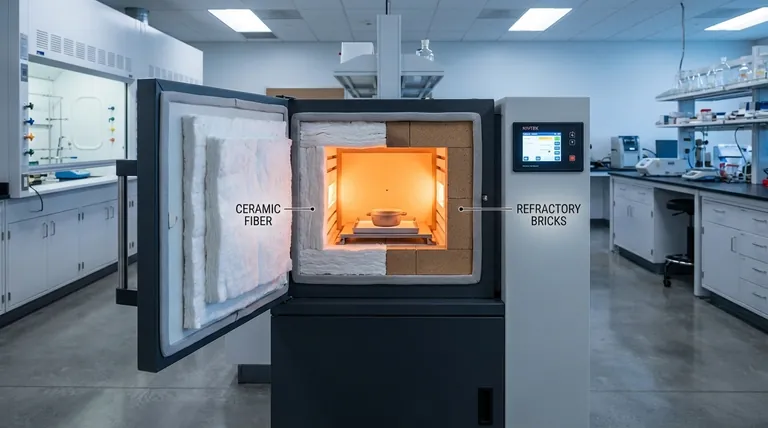
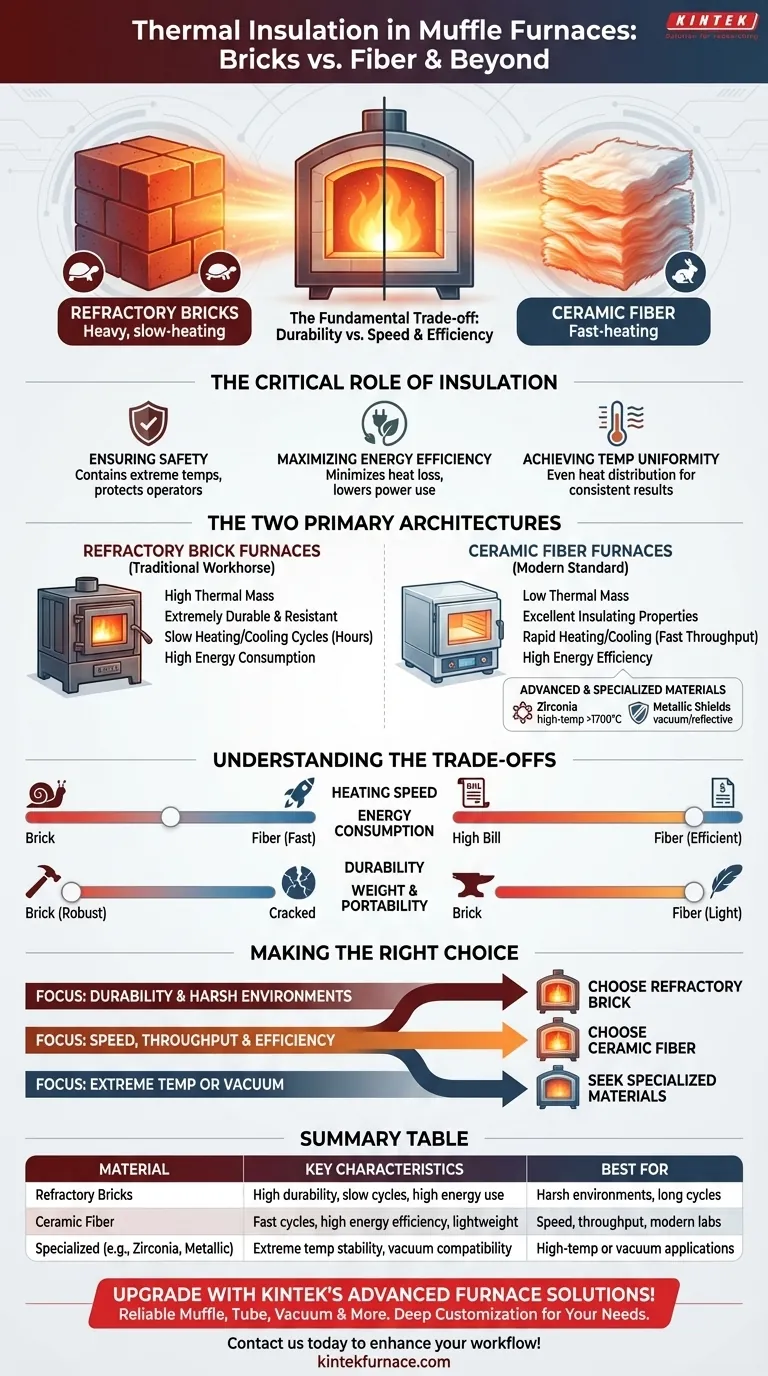
At its core, a muffle furnace's performance is defined by its thermal insulation. The vast majority of these furnaces rely on one of two primary materials: dense refractory bricks or lightweight ceramic fiber. These materials dictate not only the furnace's efficiency and safety but also its entire operational character, from heating speed to durability.
The choice between insulation materials represents a fundamental trade-off. Refractory bricks offer exceptional durability at the cost of slow performance and high energy use, while ceramic fiber provides rapid heating and superb efficiency but is mechanically more fragile.

The Critical Role of Insulation
Proper insulation is not a secondary feature; it is central to the furnace's function, safety, and efficiency. Understanding its purpose is key to appreciating the differences between furnace types.
Ensuring Safety and Stability
High-quality insulation contains extreme temperatures within the heating chamber. This prevents the furnace's outer shell from becoming dangerously hot, protecting both operators and sensitive nearby equipment from heat damage.
Maximizing Energy Efficiency
Heat loss is wasted energy and money. Effective insulation minimizes the thermal energy that escapes the furnace, leading to significantly lower power consumption and more stable internal temperatures during operation.
Achieving Temperature Uniformity
Good insulation ensures that heat is distributed evenly throughout the chamber. This uniformity is critical for applications requiring precise and consistent thermal processing of materials.
The Two Primary Insulation Architectures
Muffle furnaces are fundamentally categorized by their insulation design. Each approach has a distinct profile of strengths and weaknesses.
Refractory Brick Furnaces: The Traditional Workhorse
These furnaces are built with heavy, dense firebricks. This construction gives them a very high thermal mass, meaning they absorb a large amount of heat.
This high mass makes them extremely durable and resistant to mechanical wear. However, it also means they heat up and cool down very slowly, often taking several hours for a complete cycle.
Ceramic Fiber Furnaces: The Modern Standard
Modern furnaces predominantly use insulation made from lightweight, porous ceramic fiber. This material has a very low thermal mass and excellent insulating properties.
The primary benefit is speed. A ceramic fiber furnace can reach its target temperature and cool down much more rapidly than a brick-lined model. This leads to faster throughput and significantly better energy efficiency, as less energy is wasted heating the insulation itself.
Advanced and Specialized Materials
For extreme-temperature or specialized applications like vacuum environments, other materials are used. These can include high-performance zirconia-grade ceramic fibers for better stability above 1700°C or reflective metallic shields (molybdenum, tungsten) that block heat radiation.
It is also important to distinguish insulation from the muffle chamber itself. The inner chamber, which holds the sample, is often made of materials like quartz or alumina for their chemical inertness and high-temperature integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Brick vs. Fiber
Choosing a furnace requires weighing the clear trade-offs between these two insulation technologies.
Heating and Cooling Speed
Ceramic fiber is the undisputed winner for speed. Its low thermal mass allows for rapid temperature changes, making it ideal for labs with high sample throughput. Brick furnaces are inherently slow.
Energy Consumption
Because they don't have to heat up tons of dense brick, ceramic fiber furnaces are far more energy-efficient. A brick furnace consumes a significant portion of its energy just bringing the insulation up to temperature.
Durability and Contamination
Refractory bricks are mechanically robust and can withstand rough handling and chemical spills better than fiber. Ceramic fibers can degrade over time, especially if physically disturbed, and may release particulates into the chamber.
Weight and Portability
The difference is dramatic. Ceramic fiber furnaces are significantly lighter and more compact, making them easier to install and move. Brick furnaces are extremely heavy and are considered permanent installations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your specific operational needs and priorities.
- If your primary focus is durability and withstanding a harsh environment: Choose a refractory brick furnace, especially if long cycle times are acceptable.
- If your primary focus is speed, throughput, and energy efficiency: A ceramic fiber furnace is the clear choice for most modern laboratory and production settings.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature or vacuum work: Seek out specialized furnaces that specify zirconia-grade insulation or metallic heat shields.
Understanding the insulation material allows you to look past the spec sheet and select a tool that truly matches your workflow.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Refractory Bricks | High durability, slow heating/cooling, high energy use | Harsh environments, long cycles |
| Ceramic Fiber | Fast heating/cooling, high energy efficiency, lightweight | Speed, throughput, modern labs |
| Specialized (e.g., Zirconia, Metallic Shields) | Extreme temperature stability, vacuum compatibility | High-temp or vacuum applications |
Upgrade your lab's thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for improved efficiency and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific requirements and enhance your workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















