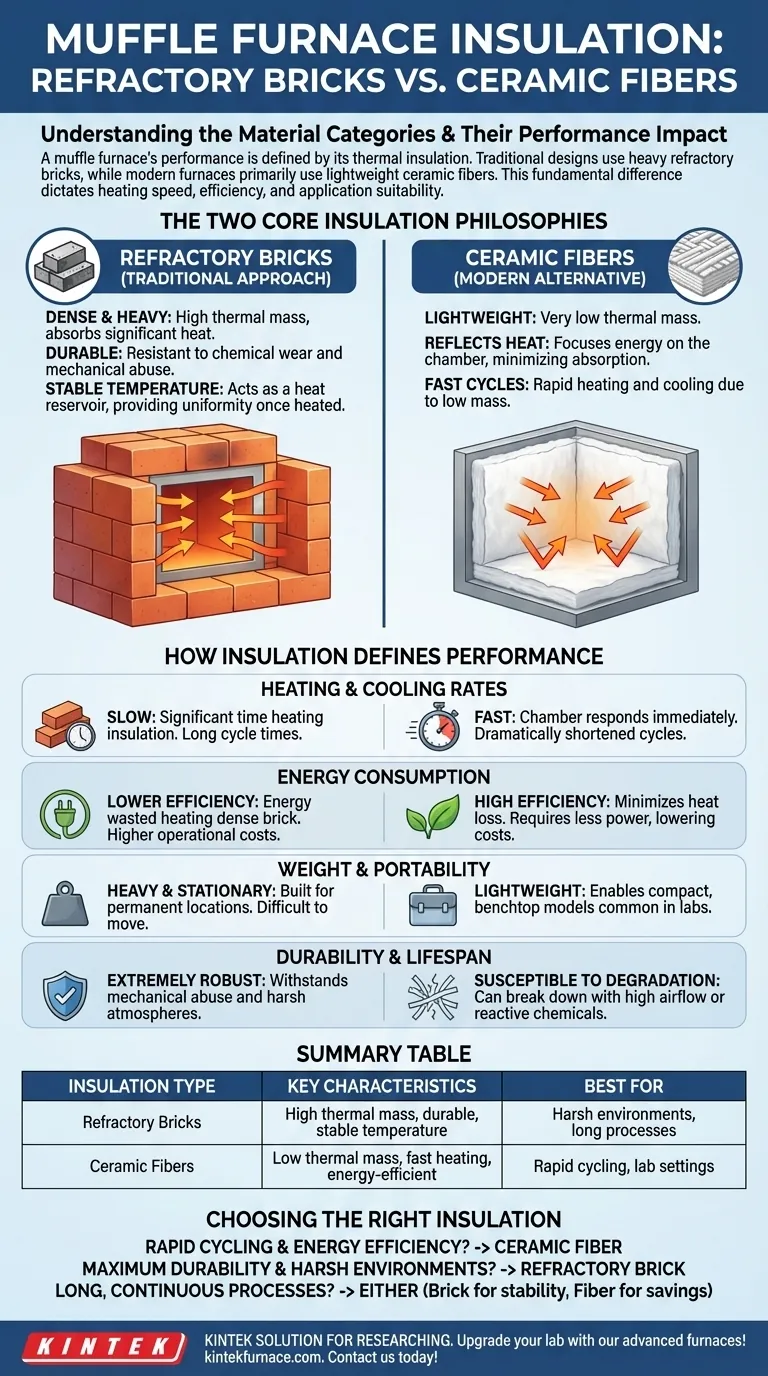
At its core, a muffle furnace's performance is defined by its thermal insulation, which falls into two primary categories. The traditional design uses heavy refractory bricks, while modern furnaces primarily use lightweight ceramic fibers. This fundamental difference in material dictates the furnace's heating speed, energy efficiency, and overall application suitability.
The choice between insulation types is a critical trade-off. Refractory brick furnaces offer durability and thermal stability at the cost of slow performance and high energy use, while ceramic fiber furnaces provide rapid heating and efficiency at the expense of long-term robustness.

The Two Core Insulation Philosophies
A muffle furnace's function is to contain extreme heat. The material used for this containment is the single most important factor in its design, creating a clear distinction between two approaches.
Refractory Bricks: The Traditional Approach
Refractory brick furnaces are built using dense, heavy ceramic bricks. These materials are known for their high thermal mass, meaning they absorb a significant amount of heat.
This construction results in a furnace that is exceptionally durable and resistant to chemical wear. The high mass also helps maintain a very stable and uniform temperature once the furnace is fully heated.
Ceramic Fibers: The Modern Alternative
Modern furnaces are constructed using insulation made of lightweight ceramic fibers, such as high-purity alumina fiber. This material has a very low thermal mass.
Instead of absorbing heat, ceramic fiber reflects it, keeping the energy focused on the chamber. This makes fiber-insulated furnaces significantly more energy-efficient and allows for much faster heating and cooling cycles.
How Insulation Defines Furnace Performance
The choice between brick and fiber is not merely a matter of material preference; it directly impacts the furnace's day-to-day operation and utility.
Heating and Cooling Rates
A refractory brick furnace heats and cools slowly. A significant amount of energy and time is spent heating the insulation itself before the chamber reaches its setpoint temperature.
A ceramic fiber furnace heats and cools very quickly. Because the low-mass fibers do not absorb much heat, the chamber can respond almost immediately to the heating elements, dramatically shortening cycle times.
Energy Consumption
Brick furnaces are less energy-efficient. The energy used to heat the dense brick insulation is essentially wasted with every cycle and contributes to higher operational costs, especially for processes requiring frequent heating and cooling.
Fiber furnaces are highly energy-efficient. By reflecting heat instead of absorbing it, they minimize heat loss and require less power to reach and maintain temperature, lowering operational costs.
Weight and Portability
The sheer weight of the bricks makes these furnaces extremely heavy and stationary. They are built for a permanent location and are not easily moved.
The lightweight nature of ceramic fiber insulation allows for the construction of much lighter, more compact benchtop models that are common in laboratory settings.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While ceramic fiber offers clear advantages in speed and efficiency, it is not the superior choice for every application. Understanding the limitations is key to selecting the right tool.
Durability and Lifespan
Refractory bricks are extremely robust. They can withstand mechanical abuse and are generally more resistant to the harsh chemical atmospheres that can be generated during certain processes.
Ceramic fibers, while effective insulators, can be more susceptible to degradation over time. High-velocity airflow or reactive chemicals can cause the fibers to break down, potentially reducing their lifespan and insulating properties.
Temperature Uniformity
Once "heat-soaked," the high thermal mass of a brick furnace provides exceptional temperature stability and uniformity throughout the chamber. It acts as a large, stable heat reservoir.
Fiber furnaces can exhibit slightly more temperature fluctuation as they respond very quickly to the heating elements cycling on and off. However, modern temperature controllers have largely mitigated this issue for most applications.
Choosing the Right Insulation for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific demands of your work. Consider the primary goal of your heating process to make an informed choice.
- If your primary focus is rapid cycling and energy efficiency: A ceramic fiber furnace is the definitive choice for quick heat-up and cool-down.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability for harsh environments: A traditional refractory brick furnace provides unmatched robustness and longevity.
- If you are running very long, continuous high-temperature processes: Either can work, but the stability of a brick furnace may be an advantage, while the energy savings of a fiber furnace become significant over extended run times.
Understanding the insulation material moves you from simply buying a furnace to investing in the right tool for your specific scientific or industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Insulation Type | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Refractory Bricks | High thermal mass, durable, stable temperature | Harsh environments, long processes |
| Ceramic Fibers | Low thermal mass, fast heating, energy-efficient | Rapid cycling, lab settings |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with tailored solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures your unique experimental needs are met precisely. Contact us today to enhance efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















