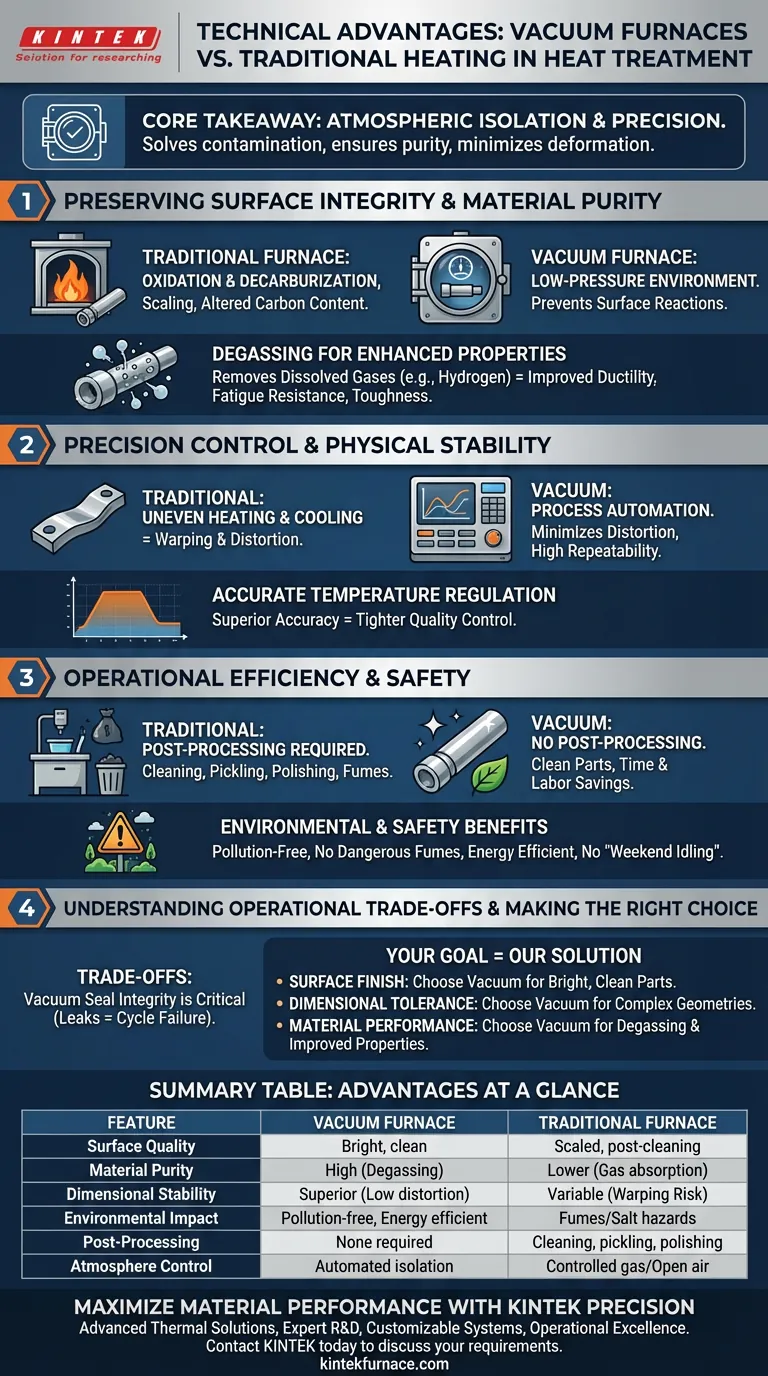
The primary technical advantage of vacuum furnaces lies in their ability to completely isolate the metal surface from chemical interactions by creating a low-pressure environment. Unlike traditional heating equipment, this isolation prevents detrimental reactions such as oxidation and decarburization while leveraging high-process automation to minimize physical deformation.
Core Takeaway Vacuum furnaces solve the fundamental problem of atmospheric contamination in heat treatment. By replacing reactive air with a vacuum and utilizing precise thermal cycling, this technology ensures surface purity and dimensional stability, effectively eliminating the need for post-process cleaning or correction.

Preserving Surface Integrity and Material Purity
Prevention of Surface Reactions
The most critical function of a vacuum furnace is the elimination of the atmosphere surrounding the workpiece. In traditional furnaces, oxygen and carbon in the air react with steel at high temperatures, causing scaling (oxidation) or altering the carbon content (decarburization).
By maintaining a low-pressure environment, vacuum furnaces physically prevent these chemical interactions. This ensures the integrity of the workpiece surface remains intact throughout the heating and cooling cycle.
Degassing for Enhanced Mechanical Properties
Beyond protecting the surface, vacuum treatment actively improves the internal structure of the metal. The vacuum environment facilitates the degassing of dissolved gases, particularly hydrogen.
removing these impurities significantly enhances mechanical properties such as ductility, fatigue resistance, and toughness. This results in a component with a longer lifespan and higher functional reliability compared to those treated in atmospheric conditions.
Precision Control and Physical Stability
Minimizing Distortion and Deformation
Traditional heat treatment often struggles with warping or distortion due to uneven heating or cooling. Vacuum furnaces utilize high levels of process automation to execute precise thermal cycle programming.
This automation ensures high repeatability and uniform thermal distribution. Consequently, the deformation and distortion of workpieces are significantly reduced, which is vital for parts with tight dimensional tolerances.
Accurate Temperature Regulation
Vacuum furnaces offer superior temperature measurement accuracy compared to standard equipment. This allows for tighter quality control over the final product.
Whether annealing, hardening, or sintering, the ability to control the thermal environment within a narrow range ensures consistent results across every batch.
Operational Efficiency and Safety
Elimination of Post-Processing
Because the vacuum process prevents oxidation and discoloration, parts emerge from the furnace clean and shiny. This eliminates the need for secondary operations such as cleaning, pickling, or polishing.
By removing these steps, manufacturers save time and reduce labor costs associated with surface finishing.
Environmental and Safety Benefits
Vacuum heat treatment is inherently safer and cleaner than traditional methods involving flammable gases or salt baths. The process is pollution-free, producing no dangerous fumes or health hazards.
Furthermore, these furnaces are energy efficient. They eliminate the need for "weekend idling"—a common inefficiency in traditional furnaces that must remain hot—thereby lowering overall operating costs.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
The Shift from Atmosphere to Vacuum
While the advantages are clear, adopting vacuum technology requires a shift in operational mindset. The process relies heavily on the integrity of the vacuum seal; any leak compromises the entire cycle.
Unlike traditional furnaces where atmosphere can be adjusted dynamically to counter leaks, a vacuum furnace requires absolute containment. This necessitates a rigorous maintenance schedule to ensure pumps and seals function perfectly to maintain the high-vacuum environment required for "bright" results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if vacuum heat treatment is the correct solution for your specific application, consider your primary technical objectives:
- If your primary focus is Surface Finish: Choose vacuum treatment to eliminate oxidation and decarburization, ensuring parts emerge bright and clean without subsequent machining.
- If your primary focus is Dimensional Tolerance: Leverage the high automation and precise thermal cycling of vacuum furnaces to minimize distortion and warping in complex geometries.
- If your primary focus is Material Performance: Prioritize vacuum processing to degas the alloy, removing hydrogen to improve fatigue resistance and ductility.
Vacuum technology transforms heat treatment from a "dirty" industrial necessity into a precise, clean manufacturing step that adds measurable value to the final component.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Furnace | Traditional Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Quality | Bright, clean, no oxidation | Scaled, requires post-cleaning |
| Material Purity | High (Degassing removes hydrogen) | Lower (Potential gas absorption) |
| Dimensional Stability | Superior (Low distortion) | Variable (Higher warping risk) |
| Environmental Impact | Pollution-free & energy efficient | Fumes/Salt bath hazards |
| Post-Processing | None required | Cleaning, pickling, or polishing |
| Atmosphere Control | Automated low-pressure isolation | Controlled gas or open air |
Maximize Material Performance with KINTEK Precision
Elevate your manufacturing standards with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Whether you need to eliminate surface oxidation or ensure the dimensional stability of complex alloys, our high-vacuum technology delivers results that traditional furnaces simply cannot match.
Why partner with KINTEK?
- Expert R&D: Systems engineered for superior degassing and material purity.
- Customizable Systems: Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum CVD systems tailored to your unique specifications.
- Operational Excellence: Automated controls designed to reduce post-processing costs and energy consumption.
Ready to transform your heat treatment process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific lab or industrial requirements with our expert team.
Visual Guide
References
- André Paulo Tschiptschin. PROCESSOS SOB VÁCUO USADOS PARA TRATAMENTOS TÉRMICOS E DE SUPERFÍCIE DE AÇOS E LIGAS ESPECIAIS. DOI: 10.17563/rbav.v43i1.1262
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Critical Applications in Aerospace, Medical, and Electronics
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- How does vacuum heat treatment improve mechanical properties of metals? Enhance Strength and Durability
- How does a vacuum furnace prevent heat transfer and contamination? Achieve Ultimate Material Purity



















