At their core, ceramic and semiconductor heating elements are defined by their ability to operate reliably at extremely high temperatures where many metals would degrade. Their key properties include moderate density, very high melting points, and the ability to form a protective silicon dioxide layer, which prevents oxidation and extends their operational lifespan in harsh industrial environments.
The true value of ceramic and semiconductor heaters lies not just in getting hot, but in their capacity for stable, controlled, and long-lasting performance at temperatures that would destroy conventional metal elements. This makes them indispensable for specialized high-temperature industrial processes.
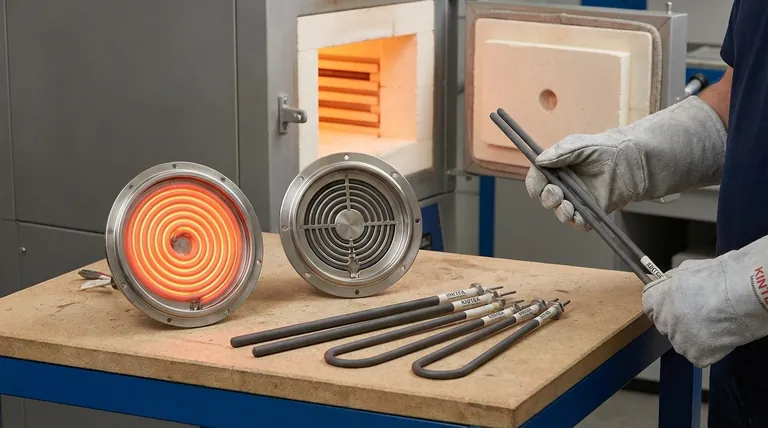

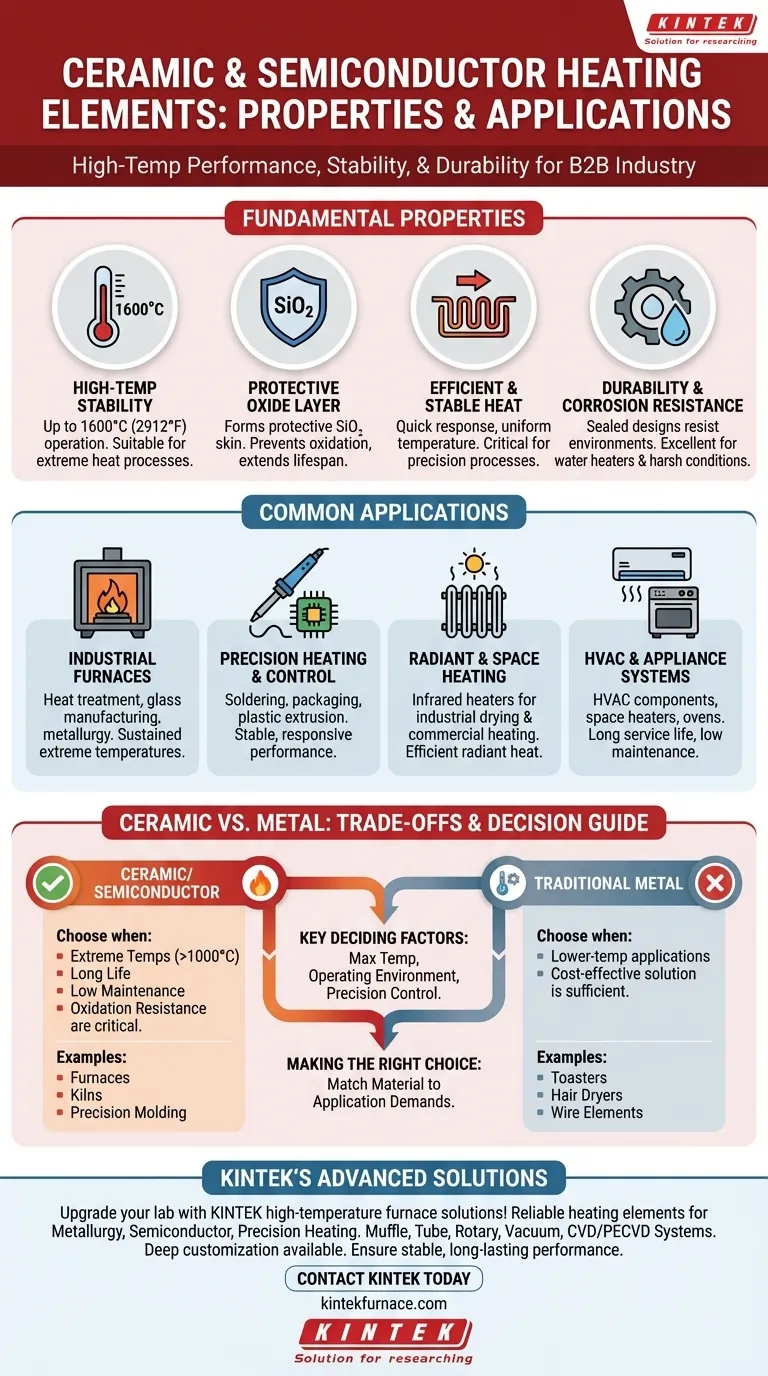
The Fundamental Properties of Ceramic Heaters
The unique characteristics of ceramic and semiconductor materials directly translate to their performance advantages in demanding applications. Understanding these properties is key to selecting the right tool for the job.
High-Temperature Stability
Ceramic and semiconductor materials like silicon carbide are engineered for extreme heat. They possess exceptionally high melting points, allowing them to operate at temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F).
This makes them suitable for processes that are far beyond the capabilities of many standard metal heating elements.
The Protective Oxide Layer
A defining feature of materials like silicides is their ability to form a thin, protective layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂) on their surface when heated to high temperatures.
This self-healing "skin" acts as a barrier against further oxidation, dramatically increasing the element's durability and lifespan in high-heat, open-air environments.
Efficient and Stable Heat Transfer
Ceramic elements are known for their quick response times and ability to maintain highly consistent temperatures.
This stability is critical for processes requiring uniform heat, such as plastic extrusion or semiconductor manufacturing, where temperature fluctuations can ruin the final product.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Many ceramic heaters are available in sealed configurations, making them highly durable and resistant to environmental factors.
Their inherent resistance to corrosion also makes them an excellent choice for applications like industrial water heaters, where metal elements would be prone to rapid degradation.
Common Applications Driven by These Properties
The physical properties of ceramic heaters make them the superior choice for a specific range of industrial and commercial uses.
High-Temperature Industrial Furnaces
The primary application is in furnaces for heat treatment, glass manufacturing, and metallurgy. Their ability to sustain extreme temperatures for long periods is essential for these processes.
Precision Heating and Control
Applications requiring precise and uniform heat, such as soldering irons, packaging machinery, and plastic extrusion, rely on the stable and responsive nature of ceramic heaters.
Radiant and Space Heating
Ceramic elements are widely used in infrared heaters for both industrial drying and commercial space heating. They efficiently convert electricity into radiant heat, warming objects and people directly.
HVAC and Appliance Systems
Due to their durability, long service life, and low maintenance, ceramic heaters are found in a wide range of systems, from HVAC components to common appliances like space heaters and ovens.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Ceramic vs. Metal
Choosing a heating element is not just about picking the one that gets the hottest. It's about matching the material to the application's specific demands and constraints.
When to Choose Ceramic/Semiconductor
These elements are the definitive choice for applications where extreme temperatures (above 1000°C) are required. They are also superior when long service life, low maintenance, and resistance to oxidation are critical operational priorities.
When to Choose Traditional Metal
For many lower-temperature applications, traditional metal resistance heaters are more than sufficient and often more cost-effective.
Materials like nichrome wire, used in toasters and hair dryers, are perfect for devices that don't require the extreme resilience of ceramics. These metal elements typically operate by simply glowing hot in the form of coils, ribbons, or strips.
Key Deciding Factors
Your decision should be based on a clear assessment of the maximum required temperature, the operating environment (e.g., presence of moisture or corrosive agents), and the need for precise temperature control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary goal to guide your selection.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature industrial processes: Choose a high-performance semiconductor element like silicon carbide for unmatched stability in furnaces and kilns.
- If your primary focus is precision control and uniform heat: A ceramic element is ideal for applications like soldering, plastic molding, or packaging machinery.
- If your primary focus is long-life and low maintenance in a consumer product: Sealed ceramic heaters offer superior durability and energy efficiency for devices like space heaters and water heaters.
- If your primary focus is a simple, low-cost heating solution: A traditional metal wire element is often the most practical choice for everyday appliances like toasters and hair dryers.
Ultimately, selecting the right heating element is about matching the material's inherent capabilities to the unique demands of your task.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Details |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Stability | Operates up to 1600°C, ideal for extreme heat processes |
| Protective Oxide Layer | Forms SiO₂ layer for oxidation resistance and long lifespan |
| Efficient Heat Transfer | Quick response and stable temperatures for uniform heating |
| Durability & Corrosion Resistance | Sealed designs resist environmental factors and degradation |
| Common Applications | Industrial furnaces, precision heating, radiant heaters, HVAC systems |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable heating elements tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in metallurgy, semiconductor manufacturing, or precision heating, KINTEK ensures stable, long-lasting performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your processes and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan



















