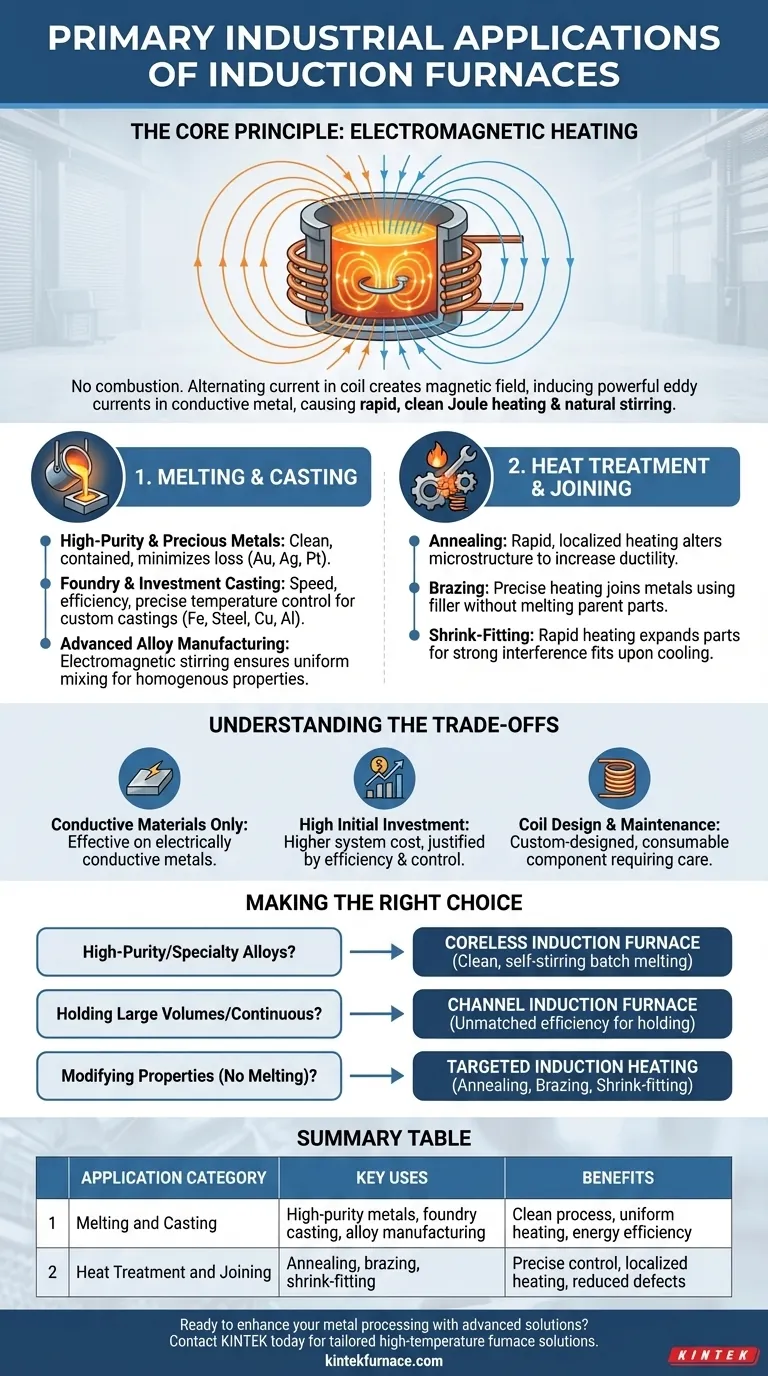
The primary industrial applications of induction furnaces fall into two main categories: melting and casting metals, and heat-treating or joining metal components. These furnaces excel at tasks requiring rapid, clean, and precisely controlled heating, making them essential in foundries, alloy manufacturing, and specialized metal fabrication processes.
The core value of an induction furnace is not just its ability to melt metal, but its use of clean, non-contact electromagnetic energy. This fundamental principle enables exceptional control over temperature and material purity, making it the ideal choice for applications ranging from high-volume foundries to the creation of high-performance specialty alloys.
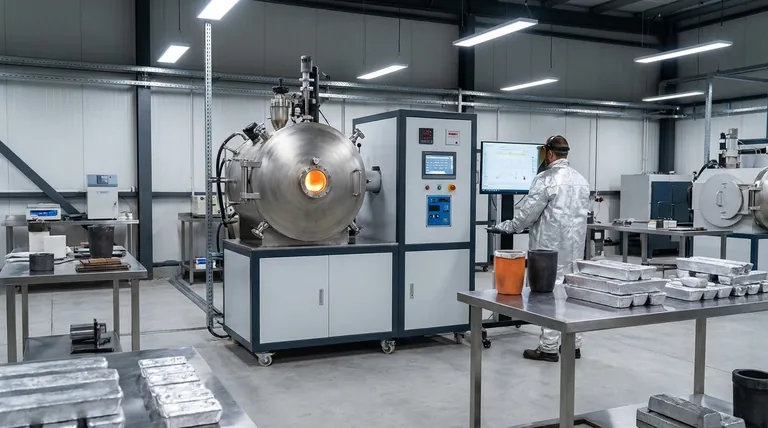

How Induction Furnaces Work: The Core Principle
To understand its applications, you must first understand the technology. An induction furnace does not use combustion or external heating elements to melt material.
The Role of Electromagnetism
An induction furnace uses a powerful alternating current passed through a copper coil. This creates a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field around the crucible holding the metal charge.
This magnetic field induces powerful eddy currents within the metal itself. The metal's natural electrical resistance causes it to heat up rapidly and melt, a process known as Joule heating.
Coreless vs. Channel Furnaces
There are two main designs. Coreless induction furnaces consist of a simple refractory-lined crucible surrounded by the power coil. They are ideal for batch melting and are prized for their flexibility in changing alloys.
Channel induction furnaces operate more like a transformer, with a "channel" of molten metal forming a secondary loop. These are extremely efficient for holding large volumes of molten metal at a constant temperature or for continuous melting operations of a single alloy.
Key Application 1: Melting and Casting
The most common use of induction furnaces is for melting metals. The electromagnetic action provides a natural stirring effect, which is critical for producing uniform, high-quality melts.
High-Purity and Precious Metals
Induction melting is the standard for precious metals like platinum, gold, and silver. The process is clean and contained, minimizing the loss of valuable material and preventing contamination.
Foundry and Investment Casting
Induction furnaces are the workhorses of modern foundries for melting iron, steel, copper, and aluminum. Their speed and energy efficiency allow foundries to produce custom castings on demand with precise temperature control, reducing defects.
Advanced Alloy Manufacturing
When creating specialty alloys, uniformity is paramount. The inherent electromagnetic stirring of an induction furnace ensures all alloying elements are thoroughly mixed, resulting in a homogenous final product with consistent properties.
Key Application 2: Heat Treatment and Joining
Induction technology is not just for melting. The same heating principle can be applied with more control to alter a material's physical properties without melting it.
Annealing
Annealing is a heat treatment process that alters a metal's microstructure to increase its ductility and reduce hardness, making it easier to work with. Induction provides rapid and localized heating for this purpose.
Brazing
Brazing is a process for joining two pieces of metal using a filler metal. Induction heating can be targeted precisely at the joint, efficiently melting the filler material without overheating the parent components.
Shrink-Fitting
This clever assembly technique uses induction to rapidly heat a metal part (like a gear or bearing), causing it to expand. It is then placed onto a shaft or into a housing and, as it cools, shrinks to create an extremely strong interference fit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction technology is not a universal solution. It comes with specific requirements and limitations that are critical to understand.
Best Suited for Conductive Materials
The core principle relies on inducing electrical currents within the material. Therefore, induction heating is only effective on electrically conductive materials, primarily metals.
High Initial Investment
The cost of an induction furnace system, including its power supply and cooling infrastructure, can be significantly higher than that of traditional fuel-fired furnaces. This cost is typically justified by higher efficiency and better process control.
Coil Design and Maintenance
The induction coil is the heart of the furnace and is often custom-designed for a specific application. It is a consumable item that requires periodic maintenance or replacement and is critical to the furnace's performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right process depends entirely on your industrial objective.
- If your primary focus is high-purity melting or creating specialty alloys: The clean, contained, and self-stirring nature of a coreless induction furnace is your best choice.
- If your primary focus is holding large volumes of metal at temperature for casting: A channel induction furnace offers unmatched efficiency for continuous, single-alloy operations.
- If your primary focus is modifying a part's properties instead of melting it: Look to targeted induction heating processes like annealing, brazing, or shrink-fitting for precise energy application.
By understanding its core principle of electromagnetic heating, you can effectively leverage induction technology to solve a vast range of industrial challenges.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Uses | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Melting and Casting | High-purity metals, foundry casting, alloy manufacturing | Clean process, uniform heating, energy efficiency |
| Heat Treatment and Joining | Annealing, brazing, shrink-fitting | Precise control, localized heating, reduced defects |
Ready to enhance your metal processing with advanced induction furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can boost your efficiency and productivity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors



















