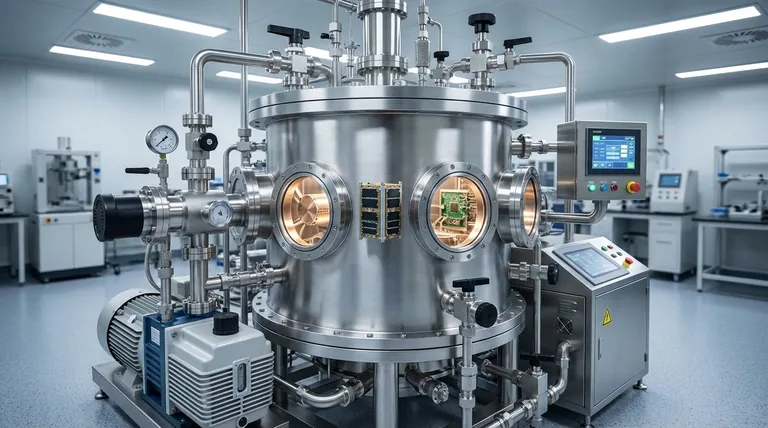
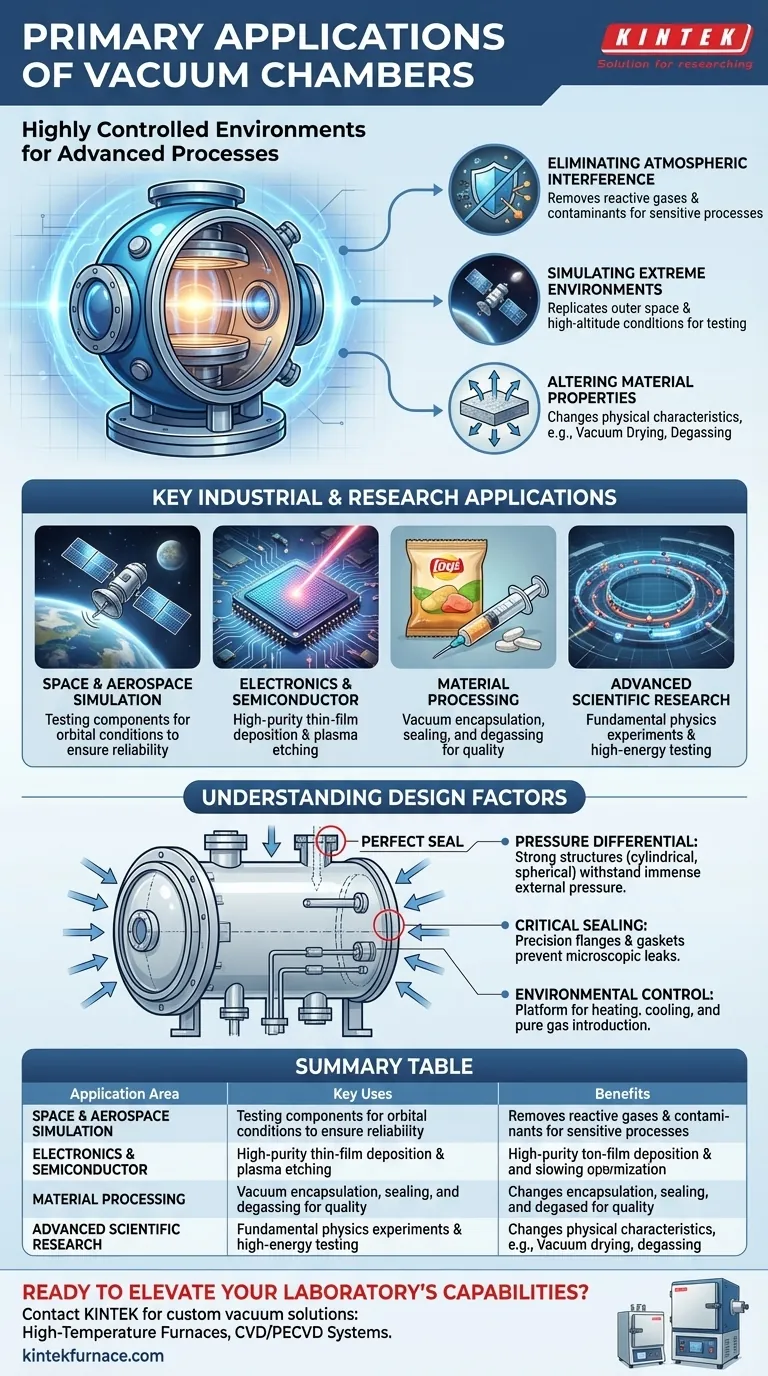
At their core, vacuum chambers are enclosures designed to remove air and other gases, creating an environment with a pressure significantly lower than the surrounding atmosphere. Their primary applications range from simulating the conditions of outer space and testing product durability to enabling high-purity manufacturing processes in electronics and advanced materials research.
The true purpose of a vacuum chamber is not simply to create emptiness, but to create a highly controlled environment. By removing the unpredictable and reactive elements of our atmosphere, you gain precise control over processes that would otherwise be impossible.

The Core Principle: Why Remove Air?
Understanding the "why" behind creating a vacuum is key to grasping its wide-ranging applications. Removing atmospheric gases solves several fundamental engineering and scientific problems.
Eliminating Atmospheric Interference
Our atmosphere is a reactive mix of gases, water vapor, and particulates. For many sensitive processes, these elements are contaminants that can cause defects or complete failure. A vacuum removes them.
This is critical in industries like semiconductor manufacturing, where a single dust particle or water molecule can ruin a microchip during deposition or etching.
Simulating Extreme Environments
Many products must function reliably in environments with little to no atmospheric pressure. A vacuum chamber is the only way to replicate these conditions on Earth.
This is essential for testing satellites, spacecraft components, and avionics to ensure they can withstand the vacuum and temperature extremes of outer space or high-altitude flight.
Altering Material Properties
Removing air and lowering pressure can directly change the physical characteristics of a material. This principle is used to improve product quality and integrity.
Processes like vacuum drying remove moisture from sensitive products (like food or pharmaceuticals) without using high heat that would damage them. Vacuum degassing pulls trapped air bubbles out of liquid compounds like epoxies and silicones before they cure, preventing structural weaknesses.
Key Industrial and Research Applications
The principles of vacuum control are applied across a vast spectrum of industries. The specific goal dictates the type and quality of the vacuum required.
Space and Aerospace Simulation
This is one of the most intuitive applications. Chambers are used to subject components, or even entire satellites, to the pressure and thermal conditions they will experience in orbit, ensuring everything from electronics to mechanical systems functions as designed.
Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing
The production of microprocessors and other integrated circuits requires an environment of extreme purity. Vacuum chambers are essential for processes like thin-film deposition and plasma etching, where atomic-level precision would be disrupted by atmospheric gases.
Material Processing and Product Integrity
Many manufacturing processes rely on a vacuum to ensure the final product is free of defects. Vacuum encapsulation removes air from a mold before injecting a potting compound, ensuring complete coverage without air voids. Vacuum sealing is used in food packaging to remove oxygen, dramatically extending shelf life.
Advanced Scientific Research
From fundamental physics to defense research, vacuum chambers are a cornerstone tool. Particle accelerators require an ultra-high vacuum to prevent high-energy particles from colliding with air molecules. Defense labs use them to test materials and systems under simulated high-altitude or space-based conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Factors
Creating and maintaining a vacuum is a significant engineering challenge. The "empty" space is constantly under assault from the roughly 14.7 pounds per square inch of atmospheric pressure at sea level.
The Challenge of Pressure Differential
The chamber's structure must be strong enough to withstand immense external pressure without collapsing. This is why vacuum chambers are typically cylindrical or spherical, as these shapes distribute the stress evenly. The choice of material (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum) depends on the required vacuum level and process chemistry.
The Critical Importance of the Seal
Every joint, port, and door is a potential leak point. A perfect seal is non-negotiable, as even a microscopic leak can prevent the chamber from reaching the target pressure or can introduce contaminants. This requires precision-machined flanges, high-quality gaskets, and meticulous assembly.
Maintaining Environmental Control
A vacuum chamber is rarely just an empty box. It is a platform for a controlled process. This means it must be compatible with accessories like feedthroughs for power and data, manipulators for moving items, and systems for heating, cooling, or introducing specific, high-purity gases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The design and requirements of a vacuum chamber are dictated entirely by its intended mission.
- If your primary focus is product reliability testing: You need a robust chamber that excels at simulating specific environmental stresses like pressure cycling and thermal changes.
- If your primary focus is high-purity manufacturing: You need an ultra-high vacuum (UHV) system built with specialized materials and seals to minimize contamination at the molecular level.
- If your primary focus is material processing: You need a chamber optimized for thermal management and the efficient removal of outgassed volatiles from your product.
Understanding these fundamental applications and trade-offs empowers you to select or design the precise tool needed for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Space and Aerospace | Simulating outer space conditions, testing satellites and components | Ensures reliability in extreme environments, prevents failure |
| Electronics and Semiconductor | Thin-film deposition, plasma etching for microchips | Achieves high purity, enables atomic-level precision |
| Material Processing | Vacuum drying, degassing, sealing for products like food and epoxies | Improves product integrity, extends shelf life, prevents defects |
| Scientific Research | Particle accelerators, defense testing in controlled environments | Facilitates advanced experiments, supports high-energy physics |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities with custom vacuum solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, whether for space simulation, electronics, or material processing. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored vacuum chambers can drive your research and manufacturing success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 304 316 Stainless Steel High Vacuum Ball Stop Valve for Vacuum Systems
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Stainless Steel Quick Release Vacuum Chain Three Section Clamp
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
People Also Ask
- Why is a high vacuum system critical for sealing the quartz tube used in Fe3GeTe2 single crystal preparation?
- What components make up the vacuum system of a vacuum furnace? Unlock Precision for High-Temperature Processing
- What role do the exhaust branch pipes at the top of a vacuum chamber play? Optimize Your Pressure Control Today
- Why is it necessary to achieve a vacuum level of 3 x 10^-2 mm Hg for quartz tube sealing? Ensure Safety and Purity
- What is the significance of high-precision mass flow controllers in testing NiFe2O4? Ensure Data Integrity



















