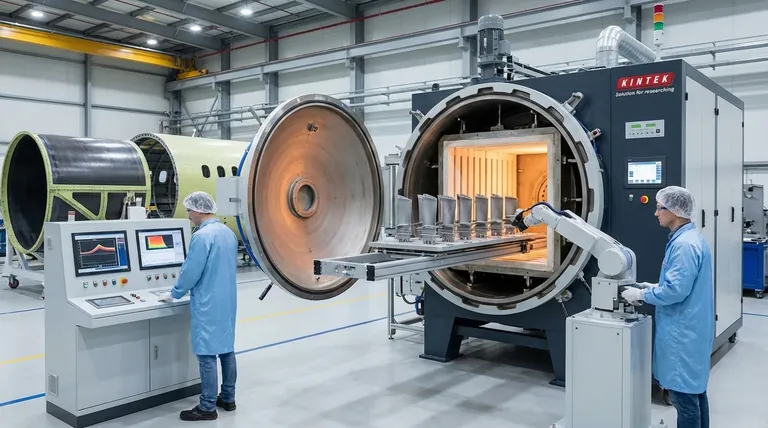
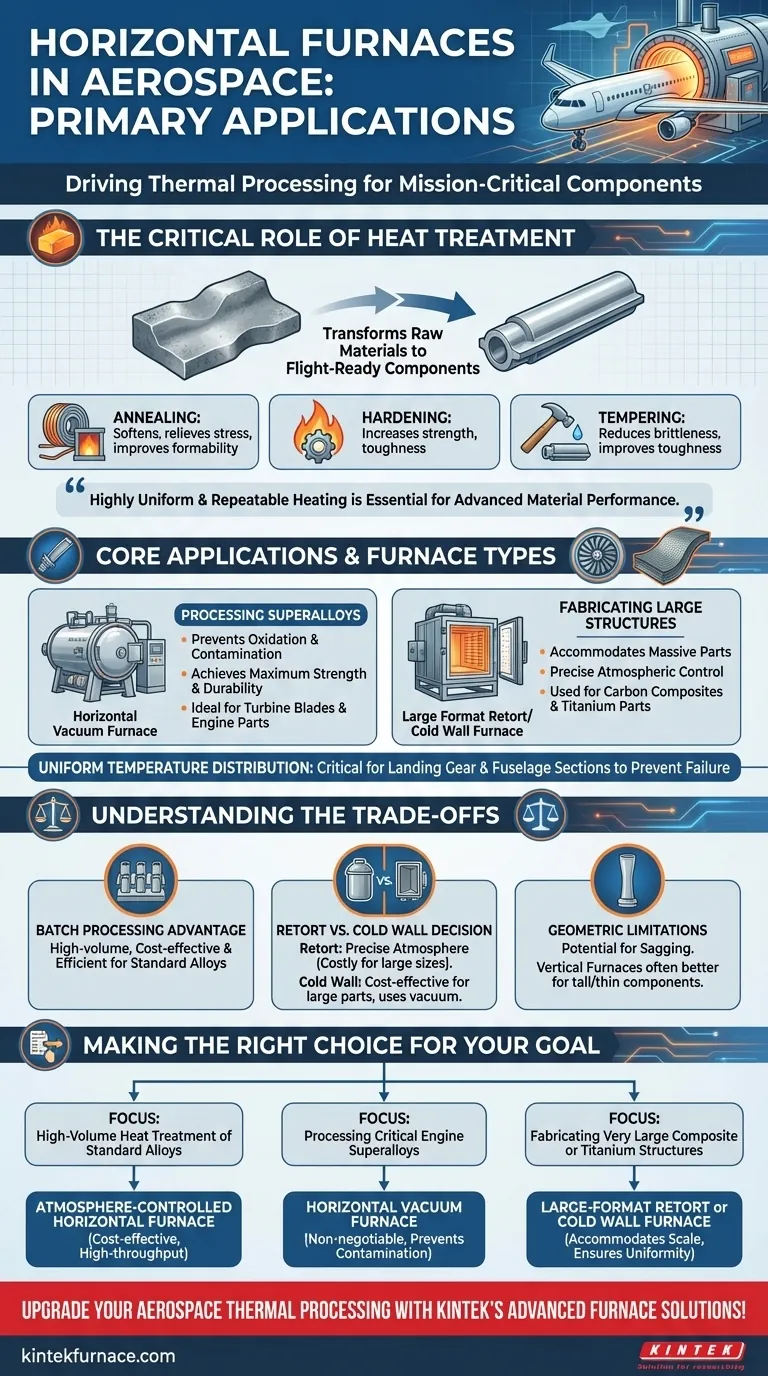
In the aerospace industry, horizontal furnaces are fundamental tools used for the thermal processing of mission-critical components. Their primary applications involve the precision heat treatment of high-performance metal alloys and the fabrication of large-scale composite structures to ensure they meet the sector's uncompromising standards for strength, durability, and safety.
The core value of horizontal furnaces in aerospace is their ability to provide highly uniform and repeatable heating across large volumes. This capability is essential for developing the specific microstructures in advanced materials that give aircraft components their required performance characteristics under extreme operating conditions.

The Critical Role of Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is not an optional step; it is a required manufacturing process that transforms raw or formed materials into components capable of withstanding the immense stresses of flight.
Why Heat Treatment is Non-Negotiable
Raw metal alloys and as-formed parts rarely possess the final mechanical properties needed for aerospace applications. Heat treatment is a carefully controlled cycle of heating and cooling that modifies a material's internal structure to optimize its strength, toughness, and resistance to fatigue and high temperatures.
Key Processes Enabled by Horizontal Furnaces
Horizontal furnaces facilitate several essential heat treatment processes. These include annealing, which softens metal to relieve stress and improve formability, and hardening, which increases its strength. This is often followed by tempering, a process that reduces brittleness and improves the overall toughness of the hardened part.
Core Applications and Furnace Types
The specific application dictates the type and configuration of the horizontal furnace used, from processing engine blades to curing massive composite assemblies.
Processing High-Performance Superalloys
Critical components like turbine blades and engine parts are often made from heat-resistant superalloys. These are processed in horizontal vacuum furnaces, which prevent oxidation and contamination at extreme temperatures, ensuring the material achieves its maximum potential strength and durability.
Fabricating Large Structural Components
The fabrication of macro-scale carbon composite assemblies and the processing of large titanium aircraft parts often rely on large format retort furnaces. A retort is a sealed container that holds the part inside the furnace, allowing for precise atmospheric control.
Ensuring Uniformity in Critical Parts
The horizontal design inherently promotes uniform temperature distribution along the length of a component. This is critical for parts like landing gear or fuselage sections, where inconsistent material properties would introduce a catastrophic point of failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, horizontal furnaces are not a universal solution. The choice involves balancing cost, scale, and specific material requirements.
The Advantage of Batch Processing
A key benefit of many horizontal furnaces is their capacity for large-volume processing. This configuration is highly efficient and cost-effective, whether for processing a single massive part or a large batch of smaller components simultaneously.
The Retort vs. Cold Wall Decision
For extremely large titanium or composite parts, the cost and complexity of a massive retort can be prohibitive. In these cases, a cold wall furnace is often used. Here, the outer vacuum chamber walls remain cool while internal heating elements process the part, avoiding the need for a costly inner retort.
Potential Geometric Limitations
The horizontal orientation can be a disadvantage for certain part geometries. Tall, thin parts or components susceptible to gravity-induced distortion (sagging) at high temperatures may be better suited for processing in a vertical furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal processing technology is fundamental to achieving the desired outcome for any aerospace component.
- If your primary focus is high-volume heat treatment of standard alloy parts: A large, atmosphere-controlled horizontal furnace offers the most cost-effective and high-throughput solution.
- If your primary focus is processing critical engine superalloys: A horizontal vacuum furnace is non-negotiable for preventing contamination and achieving precise metallurgical control.
- If your primary focus is fabricating very large composite or titanium structures: A large-format horizontal retort or cold wall furnace is necessary to accommodate the component's scale and ensure uniform processing.
Ultimately, mastering the application of thermal energy is what allows advanced materials to become the backbone of modern aviation.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Process | Furnace Type | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment of Superalloys | Annealing, Hardening, Tempering | Horizontal Vacuum Furnace | Prevents oxidation, ensures strength and durability |
| Fabrication of Large Components | Curing composites, Processing titanium | Large Format Retort or Cold Wall Furnace | Accommodates large parts, uniform temperature distribution |
| Batch Processing | High-volume heat treatment | Atmosphere-Controlled Horizontal Furnace | Cost-effective, efficient for standard alloys |
Upgrade your aerospace thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing material performance and safety. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your aerospace component production!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance



















