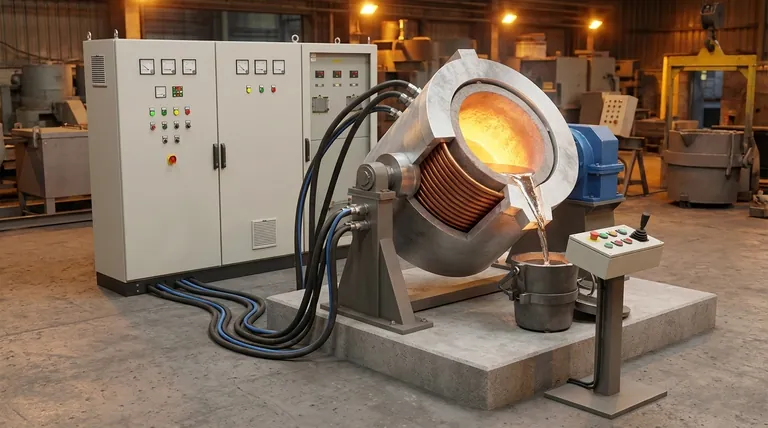
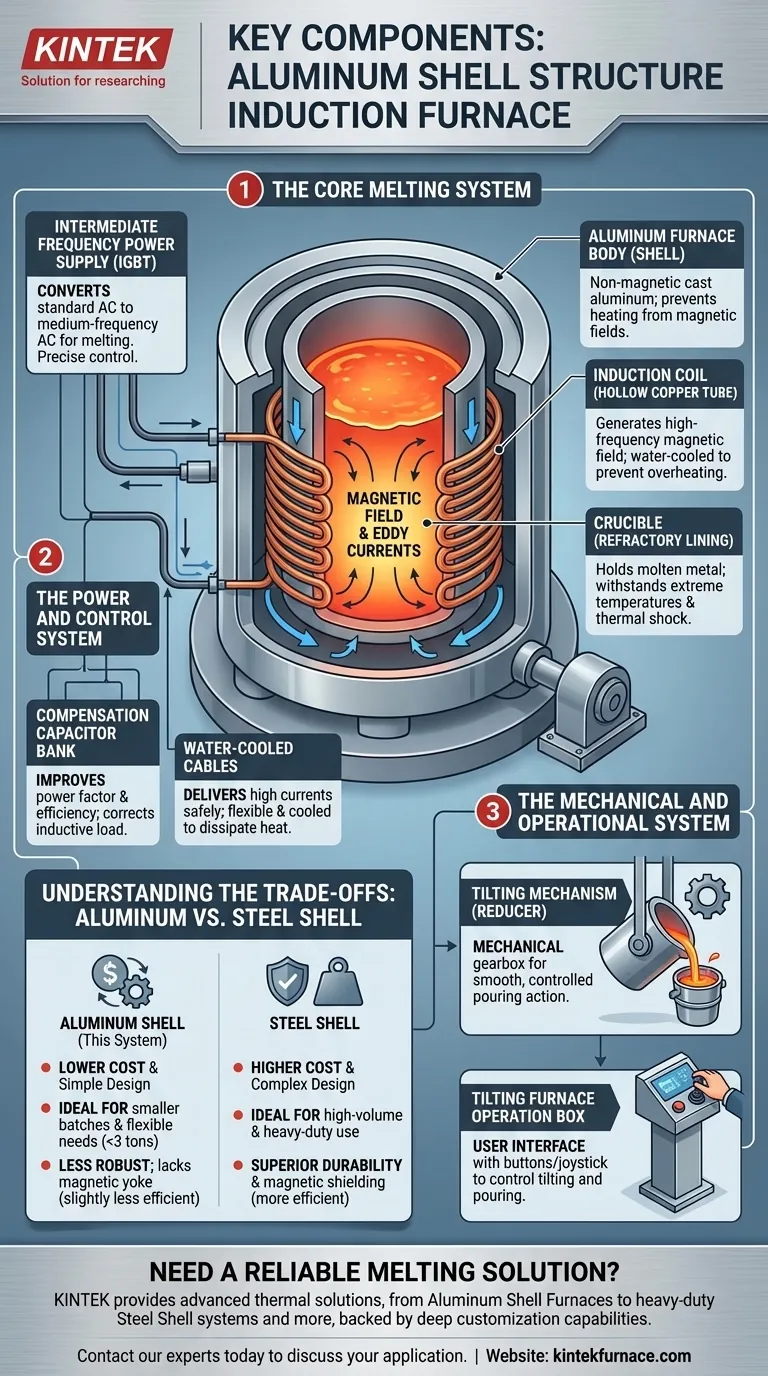
At its core, an aluminum shell induction furnace is a system comprised of six primary components. These are the intermediate frequency power supply, a compensation capacitor bank, the aluminum furnace body which houses the coil and crucible, water-cooled cables to deliver power, a reducer for tilting, and an operation box to control the pouring process.
An induction furnace is not just a collection of parts, but an integrated system designed for a specific purpose. The aluminum shell design prioritizes simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making it a distinct choice from more robust steel shell alternatives. Understanding each component's role is key to grasping its operational strengths and limitations.

The Core Melting System
The heart of the furnace is the assembly that contains and melts the metal. Its design is fundamental to the entire process.
The Furnace Body (Aluminum Shell)
The furnace body is the structural framework that holds everything together. In this design, it is constructed from a cast aluminum alloy.
This material choice is deliberate. Aluminum is non-magnetic, which prevents the shell itself from heating up due to the powerful magnetic fields generated by the induction coil.
The Induction Coil
This is the engine of the furnace. The coil is a precision-wound helix made from a rectangular copper tube.
During operation, high-frequency electrical current flows through the coil, creating a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field. This field induces powerful eddy currents within the metal charge inside the crucible, generating intense heat and causing it to melt. The coil is hollow to allow cooling water to pass through it continuously, preventing it from overheating.
The Crucible
Nested inside the induction coil is the crucible, which is the refractory-lined vessel that directly contains the molten metal.
It must be made from materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and thermal shock, such as magnesia, alumina, or graphite. The crucible acts as a container and isolates the molten metal from the induction coil.
The Power and Control System
This system takes standard electrical power and transforms it into the high-frequency energy needed for induction melting, delivering it safely and efficiently.
Intermediate Frequency Power Supply
This cabinet is the brain of the electrical system. It converts standard three-phase AC power from the grid into the single-phase, medium-frequency power required by the induction coil.
Modern power supplies often use IGBT (Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistor) technology for high efficiency and precise control over the melting process.
Compensation Capacitor Bank
Induction coils are highly inductive loads, which creates a poor power factor and draws excessive current. The capacitor bank is connected in parallel with the coil to correct this.
By compensating for the inductive nature of the coil, the capacitor bank improves the system's overall electrical efficiency, reducing energy costs and strain on the power supply.
Water-Cooled Cables
These specialized, flexible cables connect the power supply to the furnace coil. They must carry very high currents and are water-cooled for the same reason as the coil: to dissipate the significant heat generated and prevent failure.
The Mechanical and Operational System
These components allow the operator to safely handle and pour the molten metal once it has reached the target temperature.
The Tilting Mechanism (Reducer)
The entire furnace body is mounted on a pivot. The tilting mechanism, typically a mechanical reducer (a gearbox), allows the operator to smoothly and controllably tilt the furnace forward to pour the molten metal into a ladle or mold.
Tilting Furnace Operation Box
This is the user interface for the mechanical system. It is usually a simple control station, often on a pedestal or pendant, with buttons or a joystick that the operator uses to control the reducer and manage the tilting and pouring speed.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Aluminum vs. Steel Shell
The choice of an aluminum shell is not arbitrary; it represents a specific set of design compromises focused on cost and application.
Cost and Simplicity (Aluminum's Advantage)
The primary driver for choosing an aluminum shell furnace is lower initial cost. The manufacturing is simpler, and the use of a mechanical reducer for tilting is less expensive than the hydraulic systems found on steel shell furnaces.
Durability and Magnetic Shielding (Steel's Disadvantage)
This is the most significant trade-off. Aluminum shells are less mechanically robust than their steel counterparts.
More importantly, they lack a magnetic yoke. A yoke, made of laminated silicon steel sheets, is used in steel shell furnaces to surround the coil. It contains the magnetic field, directing it toward the metal charge and preventing it from escaping. This increases efficiency and protects the steel shell from heating. The absence of a yoke in an aluminum shell furnace means it is slightly less efficient and more prone to stray magnetic fields.
Capacity and Duty Cycle
Due to their simpler construction and lack of a magnetic yoke, aluminum shell furnaces are typically best suited for smaller capacities (generally under 3 tons) and less continuous, demanding production schedules. Steel shell furnaces are built for larger volumes and constant, heavy-duty industrial use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace type requires aligning its design philosophy with your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and smaller batches: The aluminum shell furnace's simpler design and lower initial investment make it the ideal choice for foundries with flexible or lower-volume needs.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and maximum efficiency: A steel shell furnace, with its robust frame and magnetic yoke for superior energy containment, is the more appropriate long-term investment.
Ultimately, understanding the function of each component empowers you to choose the right tool for your specific melting objective.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Induction Coil & Crucible | Generates heat and contains molten metal | Hollow copper coil with water cooling; refractory-lined crucible |
| Intermediate Frequency Power Supply | Converts grid power to medium-frequency AC | Often uses IGBT technology for efficiency |
| Compensation Capacitor Bank | Improves power factor and electrical efficiency | Corrects inductive load from the coil |
| Aluminum Furnace Body | Structural framework; houses coil and crucible | Non-magnetic aluminum shell prevents heating |
| Tilting Mechanism (Reducer) | Allows controlled pouring of molten metal | Mechanical reducer for smooth operation |
| Water-Cooled Cables & Operation Box | Delivers power and provides user control | Flexible, cooled cables; simple interface for tilting |
Need a Reliable Melting Solution Tailored to Your Needs?
Understanding the components is the first step; implementing the right furnace is the next. At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced thermal solutions for diverse laboratories and foundries.
Whether you require a standard Aluminum Shell Induction Furnace for cost-effective batch melting or a heavy-duty Steel Shell Furnace for high-volume production, our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities. We precisely engineer our equipment to meet your unique experimental and production requirements, ensuring maximum efficiency and durability.
Ready to enhance your melting process? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover the ideal KINTEK solution for your goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors



















