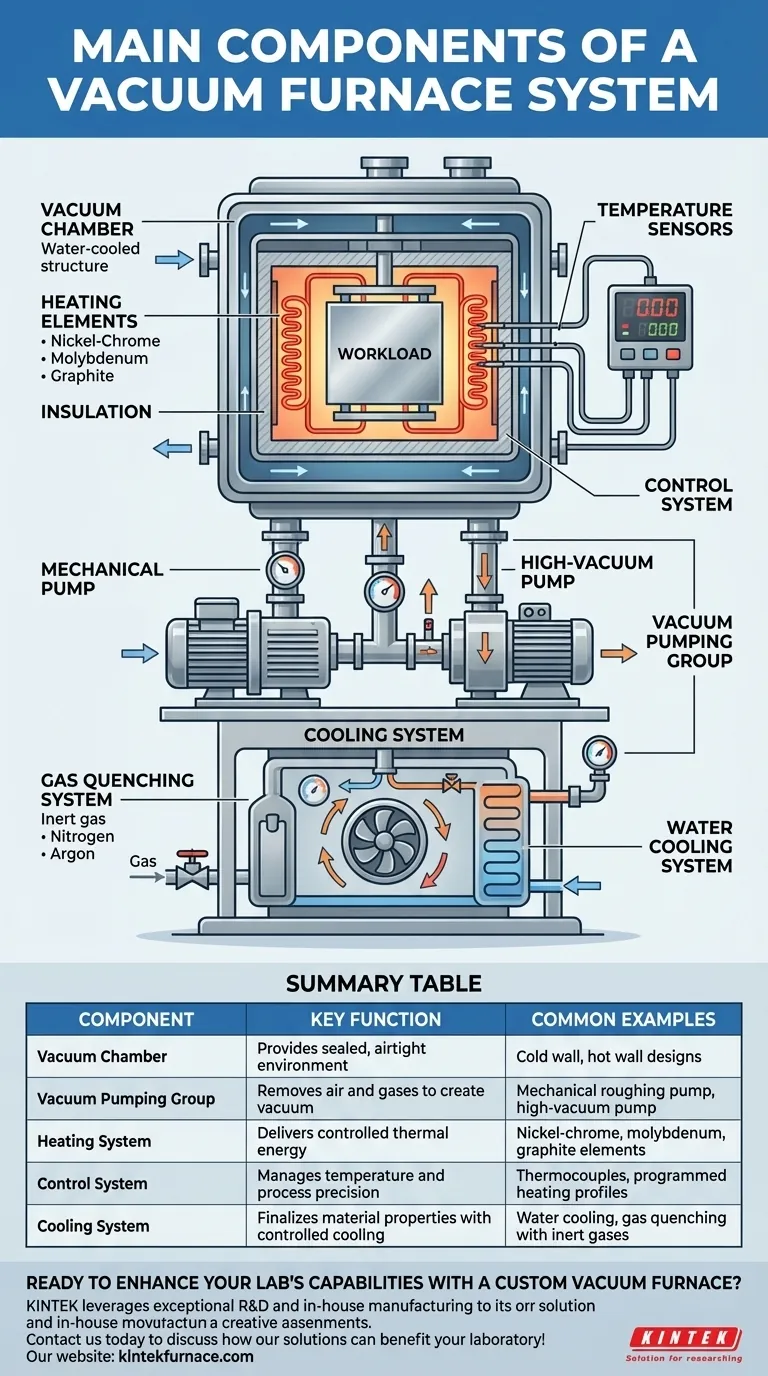
At its core, a vacuum furnace is a highly controlled environment built from several critical, interconnected systems. The main components are the vacuum chamber which provides the sealed enclosure, a vacuum system to remove the atmosphere, a heating system to provide thermal energy, a control system for process precision, and a cooling system to finalize the material properties.
Understanding a vacuum furnace isn't about memorizing a parts list. It's about seeing it as an integrated system designed for one purpose: to precisely control a material's entire thermal cycle in an environment free from atmospheric contamination.

The Foundation: The Vacuum Chamber
The entire process takes place within the vacuum chamber, which serves as the furnace's primary structure.
The Sealed Environment
The vacuum chamber, or furnace shell, is the airtight vessel that contains the workload and heating elements. It is typically a double-walled, water-cooled structure made from stainless steel to withstand pressure differences and prevent corrosion.
Hot Wall vs. Cold Wall Designs
While some designs exist where the vessel wall itself is heated (hot wall), most modern high-temperature furnaces use a cold wall design. In this configuration, the heating elements and insulation are located inside the water-cooled chamber, allowing for much higher operating temperatures, faster cycle times, and better temperature uniformity.
The Heart of the System: The Vacuum Pumping Group
This is the key differentiator from a standard atmospheric furnace. Its job is to remove air and other gases before and during the heating process.
The Role of Vacuum Pumps
No single pump can efficiently create a deep vacuum. Therefore, systems use a series of pumps, typically a mechanical "roughing" pump to remove the bulk of the air, followed by a high-vacuum pump (like a diffusion or turbomolecular pump) to achieve the required low pressure.
Valves and Gauges
A system of vacuum valves is used to isolate different parts of the system, such as separating the pumps from the main chamber. Vacuum gauges are the critical instruments that measure the pressure inside the chamber, providing essential feedback to the control system.
Generating the Heat: The Heating System
This system is responsible for delivering thermal energy to the workload in a controlled manner.
Heating Elements
The heating elements are what generate the heat inside the furnace. Their material composition dictates the furnace's maximum operating temperature. Common materials include:
- Nickel-Chrome or other resistance wires for lower temperatures (up to ~1150°C).
- Molybdenum for mid-to-high temperatures (up to ~1700°C).
- Graphite for very high temperatures (over 2000°C).
Power Supply
A dedicated power supply system provides the electricity to the heating elements. This system is managed by the temperature controller to precisely regulate the amount of energy delivered, controlling the heating rate.
Precision and Repeatability: Control and Cooling
These systems ensure the thermal process is accurate, repeatable, and concludes with the desired material characteristics.
The Temperature Control System
This is the brain of the furnace. It uses input from thermocouples (temperature sensors) placed near the workload to execute a programmed heating profile. It precisely manages heating rates, holding times (soaks), and the initiation of the cooling cycle.
The Controlled Cooling System
Cooling is not a passive process; it is a critical, controlled step. Most furnaces use a water cooling system to keep the chamber walls and seals from overheating. To cool the actual workload, a gas quenching system is often used, which involves backfilling the chamber with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon and circulating it at high velocity with a fan.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Ancillary Systems
The design and components of a furnace involve choices that impact its performance and suitability for a given task.
Material and Atmosphere Compatibility
The choice of heating element and insulation is a primary constraint. Graphite elements, for example, are excellent for high temperatures but cannot be used in an oxidizing environment, which would occur if the furnace had a significant air leak.
Critical Safety and Support Systems
Furnaces rely on ancillary systems for safe operation. A common example is a high-altitude water tank or an emergency water supply. This ensures that even if the primary water supply is cut, cooling flow continues to critical components like seals and power feedthroughs to prevent catastrophic failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
By understanding the function of each component, you can better specify a system that meets your specific materials processing needs.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature brazing or sintering: Your priority should be a system with graphite or molybdenum heating elements and a robust high-vacuum pumping group.
- If your primary focus is tempering or annealing of steels: A more cost-effective furnace with metallic heating elements and a simpler mechanical vacuum system may be perfectly adequate.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific hardness or grain structures: The capability and power of the gas quenching and cooling system is the most critical component to evaluate.
By understanding how these components integrate, you can move from simply operating a furnace to mastering a sophisticated materials processing tool.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber | Provides sealed, airtight environment | Cold wall, hot wall designs |
| Vacuum Pumping Group | Removes air and gases to create vacuum | Mechanical roughing pump, high-vacuum pump |
| Heating System | Delivers controlled thermal energy | Nickel-chrome, molybdenum, graphite elements |
| Control System | Manages temperature and process precision | Thermocouples, programmed heating profiles |
| Cooling System | Finalizes material properties with controlled cooling | Water cooling, gas quenching with inert gases |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a custom vacuum furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're focused on brazing, sintering, tempering, or achieving specific material properties, we can help you achieve precise, repeatable results. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance



















