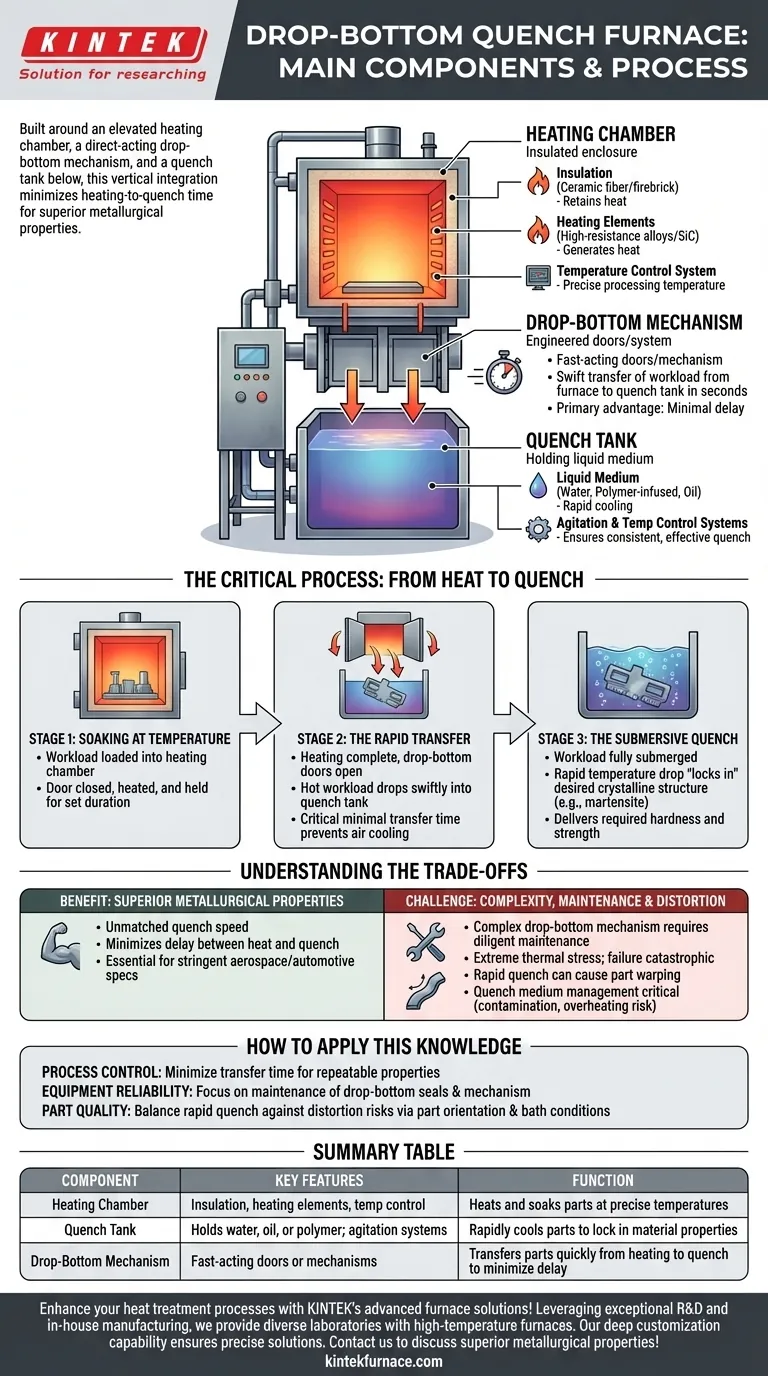
In short, a drop-bottom quench furnace is built around three essential components. These are the elevated heating chamber where parts are brought to temperature, the quench tank located directly below it, and the fast-acting drop-bottom mechanism that moves the parts between the two.
The defining characteristic of a drop-bottom furnace is not just its individual parts, but their vertical integration. This design minimizes the time between heating and quenching, which is the single most critical factor for achieving specific metallurgical properties in heat-treatable alloys.

Deconstructing the Core Components
To understand how a drop-bottom furnace achieves its results, we must look at how its primary components function in a tightly choreographed sequence.
The Heating Chamber
The heating chamber is the insulated, high-temperature enclosure where the workload is heated and "soaked" at a precise temperature. Like many industrial furnaces, it contains several key elements.
It is lined with insulation, such as ceramic fiber or firebrick, to retain heat and ensure temperature uniformity. Heating elements, often made of high-resistance metal alloys or silicon carbide, generate the required heat. A sophisticated temperature control system uses thermocouples and controllers to maintain the exact processing temperature.
The Quench Tank
Positioned directly beneath the heating chamber, the quench tank holds the liquid medium used to rapidly cool the parts.
The medium is typically water, polymer-infused water, or oil, chosen based on the material being treated and the desired cooling rate. The tank is also equipped with its own systems for agitation and temperature control to ensure the quench is consistent and effective.
The Drop-Bottom Mechanism
This is the furnace's most distinctive feature and the key to its performance. The "bottom" of the heating chamber is a movable door or set of doors.
This mechanism is engineered to open in a matter of seconds, allowing the entire workload—held in a basket or on a rack—to fall or be lowered swiftly into the quench tank below. The speed of this transfer is the furnace's primary advantage.
The Critical Process: From Heat to Quench
The value of the drop-bottom design is revealed in its operational sequence, which is optimized for speed.
Stage 1: Soaking at Temperature
First, the workload is loaded into the heating chamber. The drop-bottom door is closed, and the chamber is brought up to the specified temperature for the heat treatment process, where it is held for a set duration.
Stage 2: The Rapid Transfer
Once the heating cycle is complete, the critical transfer occurs. The drop-bottom doors open, and the entire hot workload is dropped into the quench tank in just a few seconds.
This minimal transfer time is crucial. It prevents the parts from cooling in the air, which would alter their metallurgical structure and compromise the final properties.
Stage 3: The Submersive Quench
The hot workload is fully submerged in the quenching medium. The rapid and severe temperature drop "locks in" the desired crystalline structure (e.g., martensite in steel), delivering the required hardness and strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the drop-bottom design comes with specific operational benefits and challenges.
Benefit: Superior Metallurgical Properties
The primary advantage is unmatched quench speed. For many aluminum alloys and certain steels, minimizing the delay between heat and quench is non-negotiable. This furnace design is often the only way to meet stringent aerospace or automotive specifications.
Challenge: Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
The drop-bottom door mechanism is a complex component subject to extreme thermal stress. It requires diligent maintenance to ensure reliability and safety. Failure of this mechanism can be catastrophic to the process and the equipment.
Challenge: Part Distortion and Quench Management
The rapid, sometimes violent, entry into the quench bath can cause thin or complex parts to warp or distort. Furthermore, managing the quench medium's temperature and cleanliness is critical, as contamination or overheating can lead to inconsistent results or even fire (in the case of oil).
How to Apply This Knowledge
Understanding these components helps you evaluate the furnace's role in your specific context.
- If your primary focus is process control: The key is minimizing the transfer time from furnace to quench to achieve the desired material properties repeatably.
- If your primary focus is equipment reliability: The main concern is the maintenance and integrity of the drop-bottom door seals and activation mechanism.
- If your primary focus is part quality: The goal is to balance the need for a rapid quench against the risk of part distortion by optimizing part orientation and quench bath conditions.
Ultimately, the drop-bottom furnace is a specialized tool engineered to solve the critical problem of time and temperature in heat treatment.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Features | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Chamber | Insulation, heating elements, temperature control | Heats and soaks parts at precise temperatures |
| Quench Tank | Holds water, oil, or polymer; agitation systems | Rapidly cools parts to lock in material properties |
| Drop-Bottom Mechanism | Fast-acting doors or mechanisms | Transfers parts quickly from heating to quench to minimize delay |
Enhance your heat treatment processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our drop-bottom quench furnaces can deliver superior metallurgical properties and reliability for your applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using industrial vacuum furnaces for 3003mod aluminum? Optimize H14 Temper & Material Stress
- What is the function of a vacuum drying oven in MAPbBr3@SiO2/PVDF preparation? Enhance Composite Stability & Density
- Why is long-duration temperature stability in a sintering furnace essential for Bi-2223? Master Phase Purity
- What factors influence the degassing effect in vacuum annealing? Master Key Parameters for Optimal Results
- How does a high-temperature vacuum furnace contribute to the temperature calibration of Co3O2BO3? Unlock Data Precision
- What is the function of a vacuum pyrolysis furnace in lunar ceramic 3D printing? High-Precision Debinding Solutions
- Why is a high-vacuum environment required before vacuum hot rolling? Ensure Superior Clad Plate Bonding Integrity
- Why is a high-vacuum brazing furnace required for Kovar and stainless steel? Achieve Superior Oxide-Free Joints



















