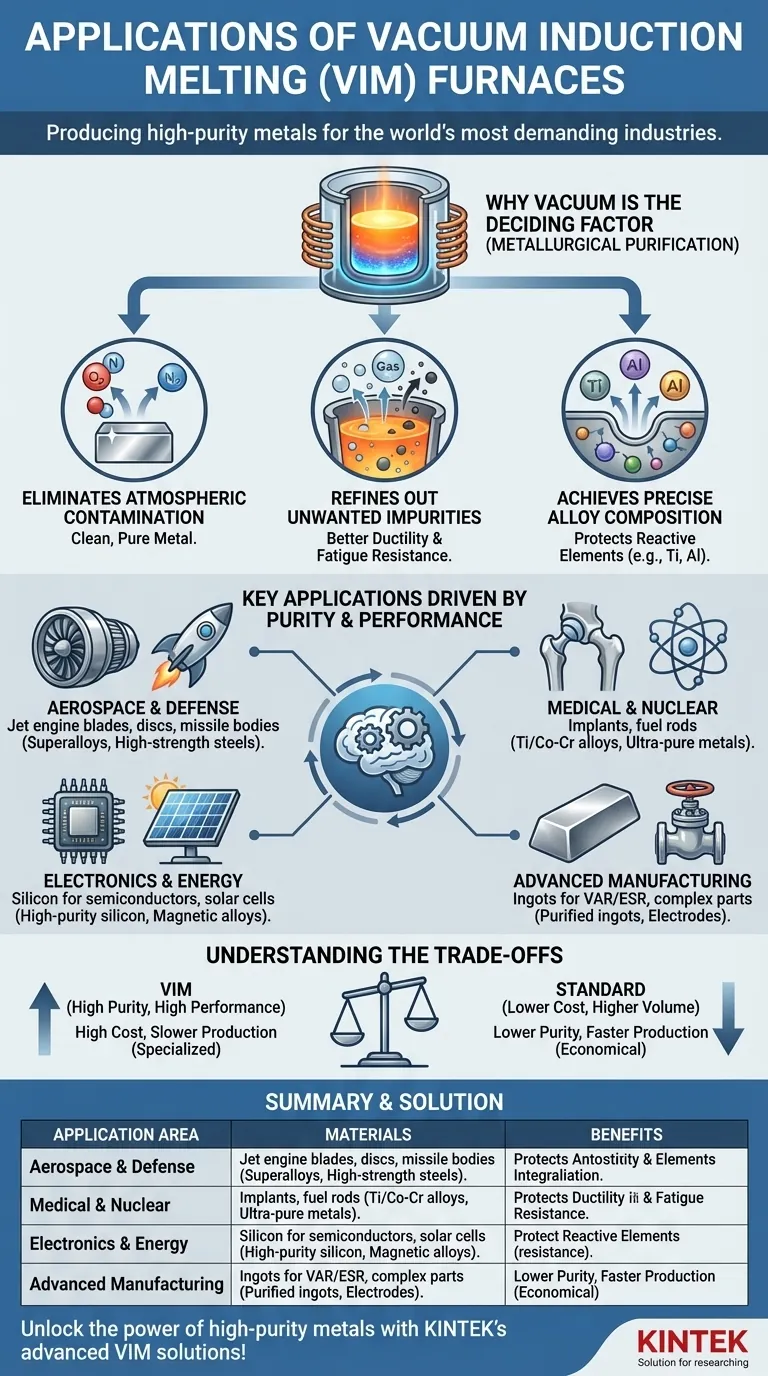
At its core, a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace is used to produce the highest purity metals and alloys required by the world’s most demanding industries. Its primary applications are in sectors like aerospace, defense, nuclear energy, and medical, where material failure can have catastrophic consequences. VIM is the go-to process for creating superalloys, high-strength specialty steels, and other advanced materials that cannot be produced in an air-melting environment.
The crucial insight is that VIM isn't just about melting metal; it's about metallurgical purification. The vacuum environment is the key feature, allowing for the removal of atmospheric contaminants and undesirable elements to create materials with superior strength, purity, and performance.
Why the Vacuum is the Deciding Factor
The "vacuum" in VIM is what separates it from all other induction melting processes. This controlled environment fundamentally changes how the metal behaves, enabling a level of quality that is otherwise unattainable.
Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
In a standard furnace, molten metal reacts with oxygen and nitrogen from the air, forming oxides and nitrides. These impurities become trapped in the final product, creating weak points that can lead to premature failure.
A VIM furnace pulls a strong vacuum, removing virtually all the air. This prevents these reactions from ever occurring, resulting in an exceptionally clean and pure metal.
Refining Out Unwanted Impurities
The vacuum environment also actively refines the molten metal. Unwanted elements with high vapor pressure, such as lead, bismuth, sulfur, and dissolved gases like hydrogen, are literally boiled out of the melt and removed by the vacuum system.
This refining step is critical for improving mechanical properties like ductility and fatigue resistance.
Achieving Precise Alloy Composition
Many advanced materials, particularly superalloys, rely on reactive elements like titanium and aluminum for their high-temperature strength. In an air melt, these valuable elements would rapidly oxidize and be lost.
Inside a VIM furnace, these reactive elements are protected. This allows for the creation of alloys with extremely precise and repeatable chemical compositions, ensuring every batch meets exact specifications.
Key Applications Driven by Purity and Performance
The unique capabilities of VIM directly enable the production of components for critical, high-stakes applications.
Aerospace and Defense
This is the largest user of VIM technology. The process is essential for producing nickel-based superalloys used in jet engine turbine blades, discs, and other components that must withstand extreme temperatures and rotational stress. It is also used for high-strength steels in missile bodies and rocket components.
Medical and Nuclear
The human body is an aggressive environment, and medical implants like artificial joints require materials that are both biocompatible and highly corrosion-resistant. VIM is used to produce the ultra-pure titanium and cobalt-chrome alloys for these devices.
Similarly, the absolute reliability required for nuclear fuel rods and other reactor components mandates the use of VIM to ensure material integrity and purity.
Electronics and Energy
The production of high-purity silicon for semiconductors and solar cells relies on vacuum melting to achieve the necessary electronic properties. The process is also used for creating specialized magnetic alloys and other materials for the electronics industry.
Advanced Manufacturing
VIM is often the first step in a multi-stage manufacturing process. It is used to cast large, purified ingots or electrodes that will be further refined using secondary processes like Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) or Electroslag Remelting (ESR). It's also used to cast intricate parts, such as high-performance valves for corrosive chemical processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, VIM is a specialized tool. It is not the right choice for every melting application due to its inherent complexities and costs.
High Cost and Complexity
VIM furnaces are significantly more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than standard air-melt furnaces. The vacuum systems, sophisticated controls, and robust chamber designs contribute to this high cost.
Slower Production Cycles
The process of loading the furnace, evacuating the chamber to a deep vacuum, melting, refining, and cooling is time-consuming. This results in lower throughput compared to continuous or higher-volume melting methods.
Not a Universal Solution
For standard-grade steel, cast iron, or aluminum alloys where extreme purity is not the primary requirement, VIM is overkill. More economical methods like conventional induction furnaces or electric arc furnaces are better suited for these high-volume applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a melting process requires aligning the technology's capability with the material's end-use requirements.
- If your primary focus is extreme performance and purity: VIM is the essential choice for applications like aerospace superalloys or medical implants where material integrity is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is precise and complex alloy chemistry: VIM is necessary to protect reactive elements and achieve the exact compositional targets required for many advanced alloys.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume metal production: Simpler air-induction or arc furnaces are a far more economical solution for materials that do not demand VIM's level of purification.
Ultimately, choosing VIM is a decision to prioritize unparalleled material quality and performance above all other considerations.

Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Materials Produced | Main Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Nickel-based superalloys, high-strength steels | Extreme temperature resistance, high strength for jet engines and missiles |
| Medical | Titanium, cobalt-chrome alloys | Biocompatibility, corrosion resistance for implants |
| Nuclear | Ultra-pure metals for fuel rods | Reliability, material integrity in reactors |
| Electronics & Energy | High-purity silicon, magnetic alloys | Superior electronic properties for semiconductors and solar cells |
| Advanced Manufacturing | Purified ingots, electrodes for further processing | Enables complex alloys and parts for high-performance applications |
Unlock the power of high-purity metals with KINTEK's advanced vacuum induction melting solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering superior material quality and performance for critical applications in aerospace, medical, and beyond. Contact us today to discuss how our VIM furnaces can elevate your research and production!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries



















