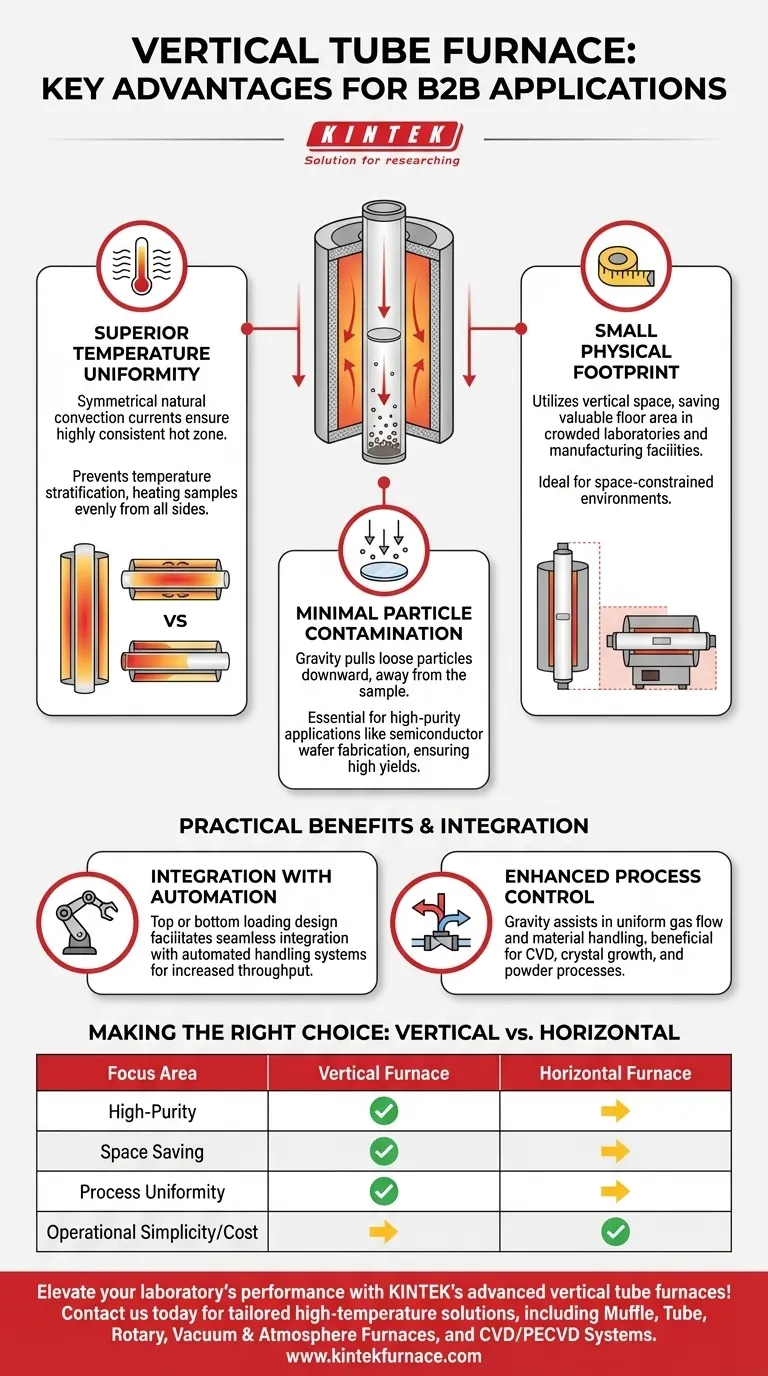
At its core, a vertical tube furnace offers three distinct advantages over its horizontal counterpart: superior temperature uniformity, significantly reduced particle contamination, and a much smaller physical footprint. These benefits stem directly from its vertical orientation, which leverages gravity to enhance process control and save valuable lab space.
The decision to use a vertical tube furnace is not just about heating a sample. It is a strategic choice for applications where process purity, temperature stability, and efficient use of space are paramount, particularly in semiconductor manufacturing and advanced materials research.

The Core Design Advantage: Leveraging Gravity
The primary distinction of a vertical furnace is its orientation. This simple change has profound implications for heat transfer and material handling, creating benefits that are impossible to achieve in a horizontal setup.
Superior Temperature Uniformity
In a vertical tube, natural convection currents are symmetrical and stable. This creates a highly uniform and consistent hot zone along the length of the process tube.
Unlike horizontal furnaces where convection can cause temperature stratification (hotter at the top, cooler at the bottom), the vertical design ensures the sample is heated evenly from all sides.
Minimal Particle Contamination
This is arguably the most critical advantage for high-purity applications. Gravity pulls any loose particles generated during the process downward, away from the sample.
In fields like semiconductor wafer fabrication, where a single microscopic particle can ruin a device, this self-cleaning effect is essential for achieving high yields and reliable results.
Enhanced Process Control
For certain processes, gravity becomes an asset. In chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or crystal growth, the vertical orientation helps ensure a uniform flow of precursor gases and even deposition onto a substrate.
Gravity can also assist in processes involving powders or melts, preventing material from slumping to one side and ensuring consistent outcomes.
Practical Benefits for Labs and Production
Beyond the physics of the process, a vertical furnace delivers tangible benefits for facility planning and operational efficiency.
Significant Space Savings
A vertical furnace has a much smaller footprint than a horizontal furnace of the same capacity. This makes it an ideal solution for crowded laboratories or manufacturing facilities where floor space is a premium resource.
Integration with Automation
The top-loading or bottom-loading design of a vertical furnace is highly conducive to automated handling systems.
In industrial settings, automatic wafer and boat transfer systems can be integrated seamlessly, increasing throughput and reducing the need for manual intervention.
Inherited Strengths of Tube Furnaces
While its orientation provides unique benefits, a vertical furnace also shares the core advantages of all tube furnaces. These include precise temperature and atmosphere control, high thermal efficiency, and operational simplicity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No design is universally superior. A vertical furnace has specific limitations that make it less suitable for certain applications.
Sample Loading and Handling
Loading and unloading a sample can be more complex than in a horizontal furnace. It often requires specialized tongs, elevators, or boat holders to position the sample correctly within the hot zone.
Observational Challenges
It is inherently more difficult to observe a sample during processing in a vertical furnace. Horizontal furnaces often provide a clearer, more direct line of sight for in-situ monitoring.
Potential Cost and Complexity
The specialized construction, and sometimes the need for lifting mechanisms, can make vertical furnaces a more significant initial investment compared to simpler, more common horizontal models.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace orientation depends entirely on your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing (e.g., semiconductors, wafers): A vertical furnace is the superior choice due to its minimal particle contamination.
- If your primary focus is conserving laboratory space: The small footprint of a vertical furnace makes it the clear winner.
- If your primary focus is process uniformity (e.g., crystal growth, annealing): A vertical furnace provides the most stable and symmetrical heating environment.
- If your primary focus is operational simplicity and cost-effectiveness for general tasks: A horizontal furnace often provides the most straightforward and economical solution.
Ultimately, choosing a vertical furnace is a deliberate decision to prioritize process purity and uniformity in a space-efficient design.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Superior Temperature Uniformity | Symmetrical convection ensures even heating for stable processes like annealing and crystal growth. |
| Minimal Particle Contamination | Gravity pulls particles away from samples, ideal for high-purity applications in semiconductor manufacturing. |
| Compact Footprint | Vertical design saves valuable lab space, enhancing efficiency in crowded facilities. |
| Enhanced Process Control | Gravity aids in uniform gas flow and material handling for processes like CVD and powder treatments. |
| Integration with Automation | Top/bottom-loading design supports automated systems, boosting throughput and reducing manual work. |
Elevate your laboratory's performance with KINTEK's advanced vertical tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide tailored high-temperature solutions for diverse labs, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering superior purity, uniformity, and space efficiency. Don't compromise on quality—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and drive innovation in your research or production!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment



















