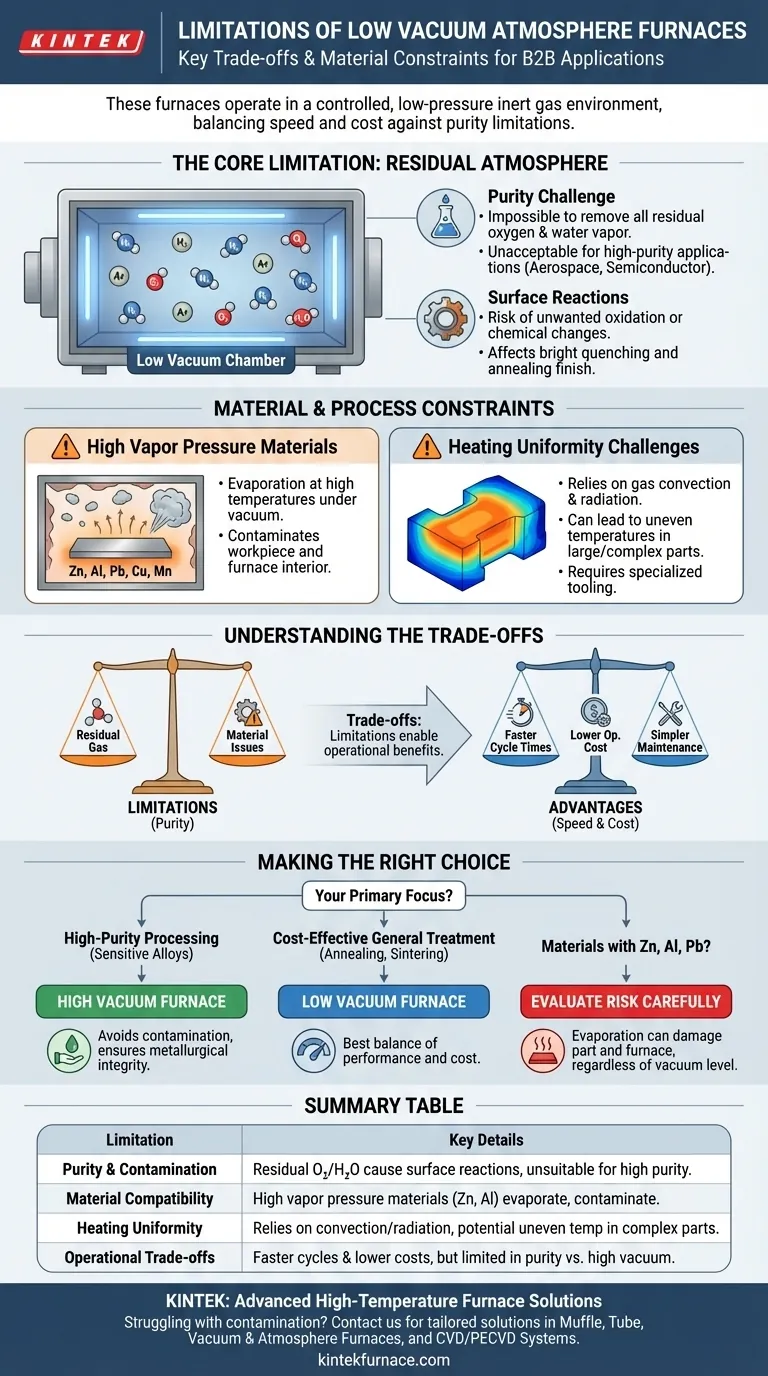
Fundamentally, the limitations of a low vacuum atmosphere furnace stem from the presence of a residual atmosphere. Unlike high vacuum systems that aim to remove nearly all molecules, these furnaces operate in a controlled, low-pressure inert gas environment, which introduces a higher risk of contamination and restricts their use with certain materials.
A low vacuum atmosphere furnace is not an inferior tool, but a specialized one. Its limitations in purity and material compatibility are the direct trade-offs for significantly faster cycle times, lower operational costs, and simpler maintenance.
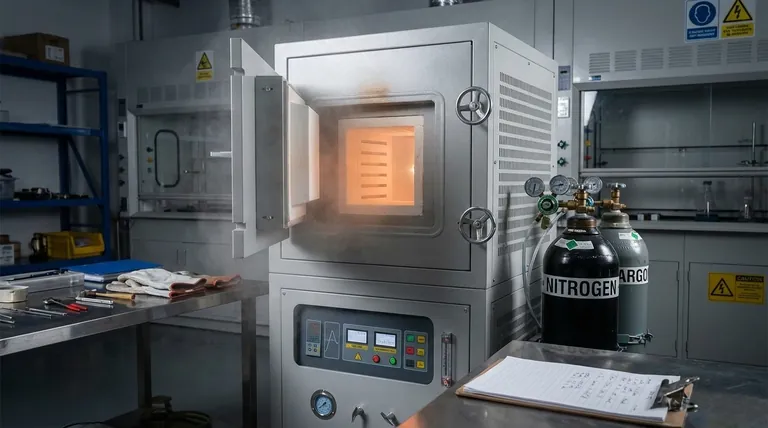

The Core Limitation: Residual Atmosphere and Contamination
A "low vacuum" is not empty space; it is a chamber filled with a specific, low-pressure gas. This defining characteristic is the source of its primary limitations.
The Challenge of Purity
A low vacuum atmosphere furnace first evacuates ambient air and then backfills with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon. While this displaces most oxygen, it is impossible to remove all residual oxygen and water vapor.
These remaining molecules create a level of contamination that is unacceptable for applications demanding the highest purity, such as in the aerospace, medical implant, or semiconductor industries.
Risk of Unwanted Surface Reactions
The residual atmosphere can cause subtle but critical surface reactions. For materials highly sensitive to oxidation or other chemical changes, this can impact performance, appearance, and metallurgical properties.
Processes requiring an exceptionally clean, non-reactive environment, often called bright quenching or annealing, may not achieve a perfect finish in a low vacuum system.
Material and Process Constraints
Beyond general purity, these furnaces are unsuitable for specific materials and part geometries due to the physics of heat and vacuum.
The Problem of High Vapor Pressure Materials
Certain elements turn to gas (evaporate) at high temperatures, especially under vacuum. This is known as having a high saturated vapor pressure.
Materials like zinc, aluminum, lead, copper, and manganese are poor candidates for vacuum heat treatment. They can outgas from the workpiece, altering its surface composition and contaminating the furnace's interior and heating elements.
Challenges with Heating Uniformity
Low vacuum furnaces rely on a combination of gas convection and radiation for heating. For large or complex-shaped workpieces, this can lead to uneven temperatures.
Achieving uniform heating often requires specialized tooling, careful part placement, and longer soak times to allow heat to penetrate the entire workpiece consistently.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The limitations of a low vacuum furnace exist for a reason—they enable significant operational advantages. Understanding this balance is key to making an informed decision.
Advantage: Speed and Throughput
Pulling a low vacuum is significantly faster than pulling a high or ultra-high vacuum. This shortens the pump-down time, leading to faster overall cycle times and higher factory throughput.
Advantage: Lower Operational Cost
Achieving and maintaining a low vacuum requires simpler, less expensive pumping systems and seals. This results in lower initial investment and reduced ongoing maintenance costs compared to high vacuum technology.
Advantage: Simplicity and Maintenance
The hardware for a low vacuum system is less complex and more robust. This makes the furnaces easier to operate, troubleshoot, and maintain, reducing reliance on specialized technicians.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use a low vacuum atmosphere furnace depends entirely on your process requirements and material characteristics.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing for sensitive alloys: A high vacuum furnace is the necessary choice to avoid contamination and ensure metallurgical integrity.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective general heat treatment: For processes like annealing, sintering, or brazing common steels and ceramics, a low vacuum furnace offers the best balance of performance and cost.
- If you are working with materials containing zinc, lead, or aluminum: You must carefully evaluate the risk of evaporation, as this can damage both the part and the furnace itself, regardless of the vacuum level.
By aligning the furnace's capabilities with your specific goal, you ensure both process integrity and economic efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Purity and Contamination | Residual oxygen and water vapor can cause surface reactions, unsuitable for high-purity applications like aerospace or semiconductors. |
| Material Compatibility | High vapor pressure materials (e.g., zinc, aluminum) may evaporate, leading to contamination and damage. |
| Heating Uniformity | Relies on gas convection and radiation, potentially causing uneven temperatures in large or complex workpieces. |
| Operational Trade-offs | Faster cycle times and lower costs, but limited in purity compared to high vacuum systems. |
Struggling with contamination or material compatibility in your heat treatment processes? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, or general manufacturing, our expertise ensures precise temperature control and enhanced efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your laboratory operations and deliver reliable, cost-effective solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment



















