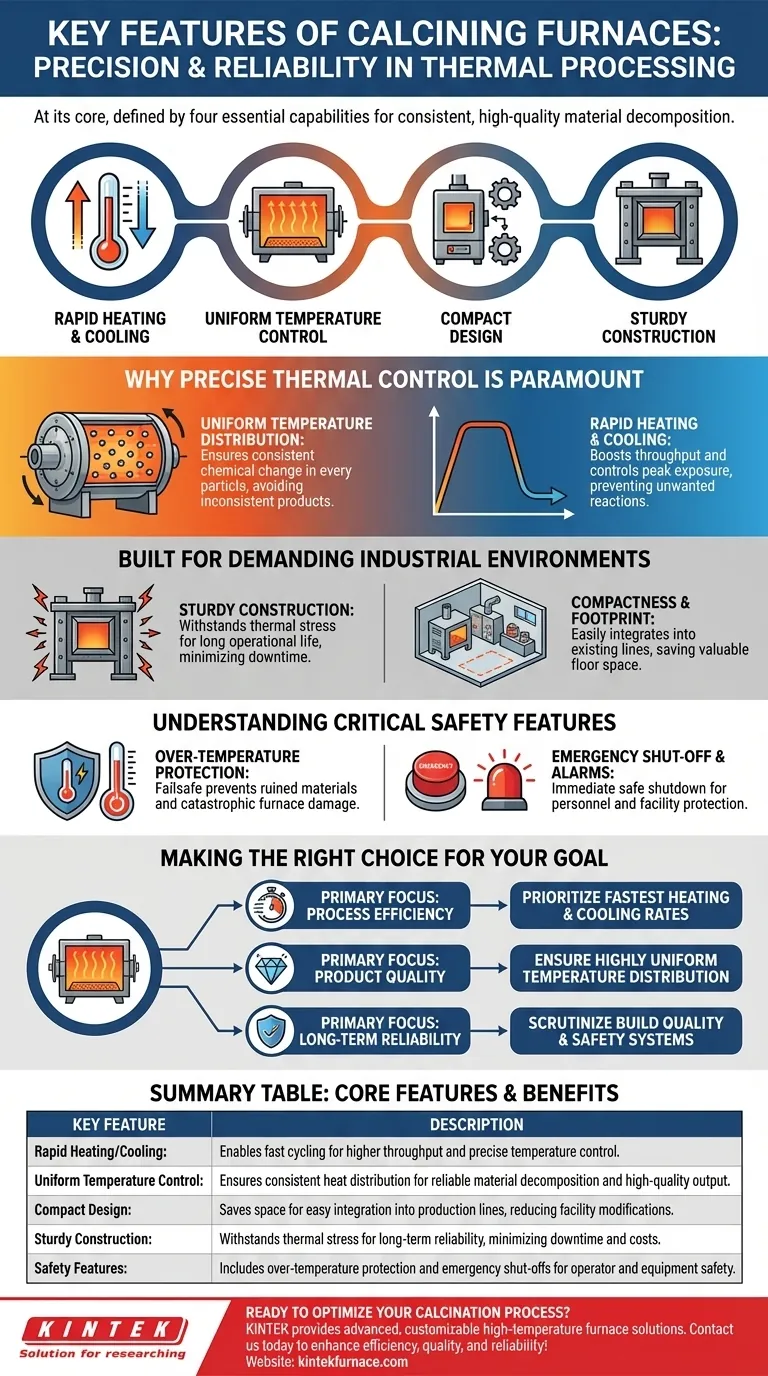
At its core, a modern calcining furnace is defined by a combination of four key features. These are its ability to achieve rapid heating and cooling rates, maintain uniform temperature control across the material, its compact design for easy integration, and its sturdy construction for long-term operational reliability.
The essential features of a calcining furnace are not arbitrary; they are direct solutions to the demands of the calcination process itself—a thermal decomposition that requires absolute precision to yield consistent, high-quality materials.
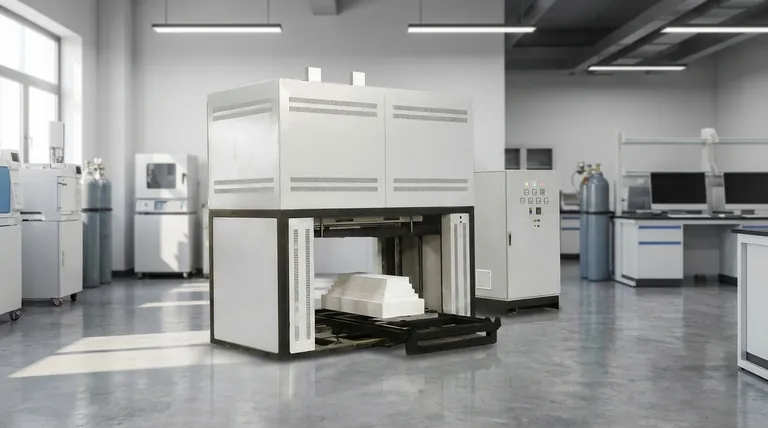

Why Precise Thermal Control is Paramount
The entire purpose of calcination is to induce a specific chemical change through heat. Without precise control over that heat, the process fails.
Achieving Uniform Temperature Distribution
Calcination is a thermal decomposition process that breaks down materials. For this transformation to be consistent throughout the entire batch, every particle must experience the same temperature.
Uneven heating leads to an inconsistent product, with some parts under-processed and others potentially damaged. This is why features like rotating furnace chambers are often used to ensure all material is exposed to uniform heat treatment.
The Role of Rapid Heating and Cooling
The ability to heat up and cool down quickly is not just about convenience; it is about efficiency and control.
Rapid cycling allows for higher throughput in production environments and provides tighter control over the material's exposure to peak temperatures, preventing unwanted secondary reactions.
Built for Demanding Industrial Environments
A calcining furnace must withstand extreme thermal stress and continuous operation, making its physical design a critical feature.
The Importance of Sturdy Construction
Constant heating and cooling cycles exert immense stress on a furnace's structure. A sturdy construction ensures the furnace has a long operational life, minimizing downtime and replacement costs. This reliability is fundamental for industrial applications.
Compactness and Footprint
In a busy production facility, floor space is a premium asset. A compact design allows the furnace to be integrated into existing process lines without requiring significant facility modifications, making it a more practical and cost-effective solution.
Understanding Critical Safety Features
Given the high temperatures involved, safety mechanisms are not optional additions but core features of any professionally designed furnace.
Over-Temperature Protection
This is a crucial failsafe that automatically cuts power if the temperature exceeds a preset limit. It protects the material being processed from being ruined and, more importantly, prevents catastrophic damage to the furnace itself.
Emergency Shut-Off and Alarms
Clear alarm systems and easily accessible emergency shut-off mechanisms are essential for operator safety. In the event of a malfunction, these features allow for an immediate and safe shutdown of the system, protecting personnel and the facility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating a calcining furnace, your specific application will determine which features to prioritize.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Prioritize furnaces with the fastest possible heating and cooling rates to maximize throughput.
- If your primary focus is product quality: Ensure the furnace guarantees highly uniform temperature distribution, as this is critical for consistent results in materials like ceramics and cement.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: Scrutinize the build quality, materials used in construction, and the robustness of its safety systems.
Understanding these core features empowers you to select a tool that is not just functional, but perfectly aligned with your process goals.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Rapid Heating/Cooling | Enables fast cycling for higher throughput and precise temperature control to prevent unwanted reactions. |
| Uniform Temperature Control | Ensures consistent heat distribution for reliable material decomposition and high-quality output. |
| Compact Design | Saves space for easy integration into production lines, reducing facility modifications. |
| Sturdy Construction | Withstands thermal stress for long-term reliability, minimizing downtime and costs. |
| Safety Features | Includes over-temperature protection and emergency shut-offs for operator and equipment safety. |
Ready to optimize your calcination process? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our calcining furnaces can enhance your efficiency, quality, and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















