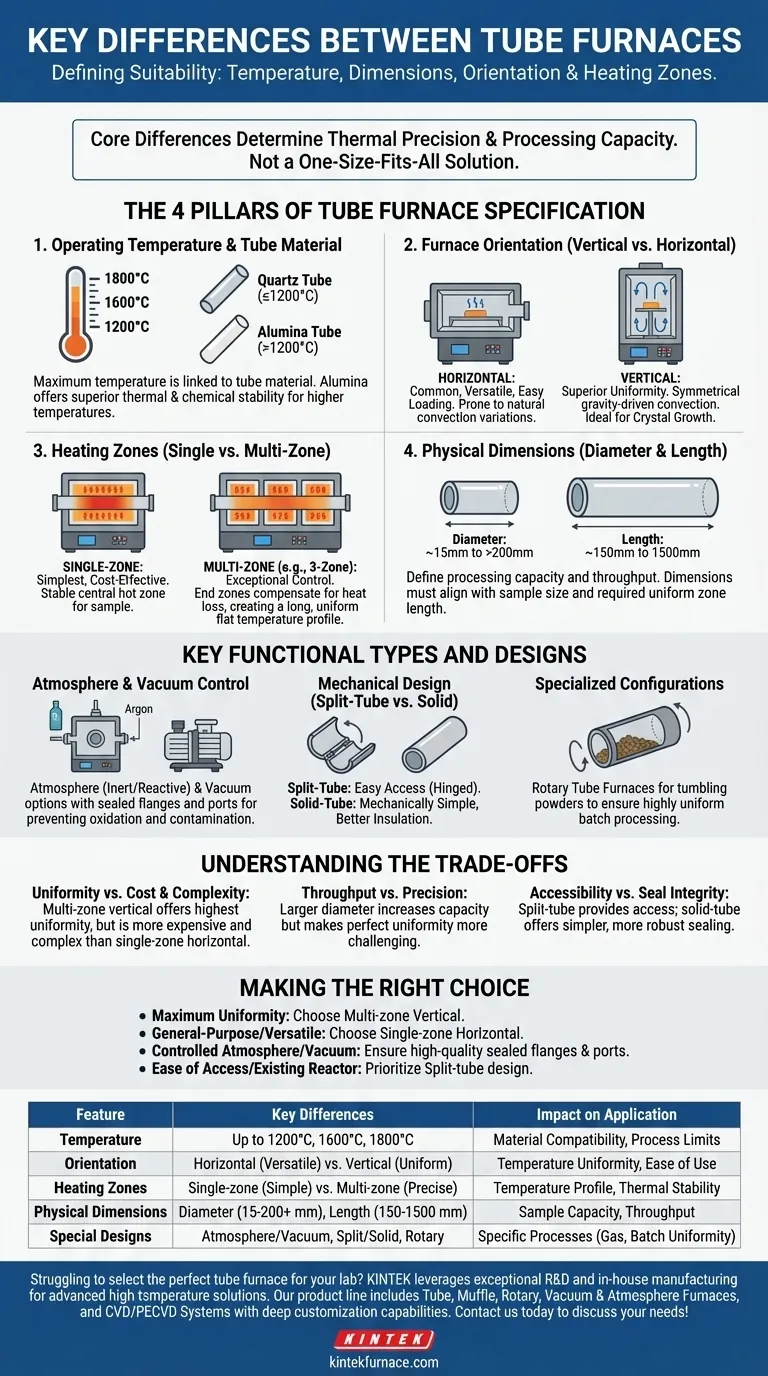
At their core, the key differences between tube furnaces are defined by their operating temperature, physical dimensions (diameter and length), orientation (vertical or horizontal), and the number of independent heating zones. These factors directly influence the furnace's suitability for specific applications, such as material synthesis, annealing, or crystal growth, by determining its thermal precision and processing capacity.
A tube furnace is not a one-size-fits-all tool. Understanding the fundamental design differences is essential because each choice—from orientation to the number of heating zones—represents a direct trade-off between temperature uniformity, operational simplicity, and cost.
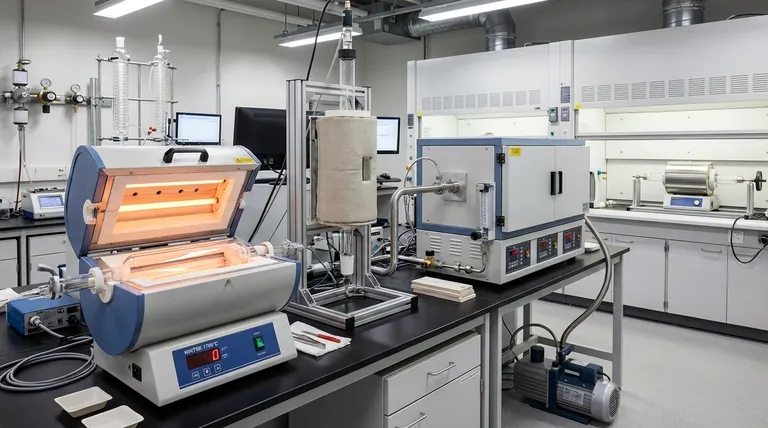

The Pillars of Tube Furnace Specification
To select the correct instrument, you must evaluate four primary characteristics. Each one dictates the furnace's performance envelope and its compatibility with your scientific or industrial process.
Pillar 1: Operating Temperature and Tube Material
The maximum achievable temperature is a primary specification, typically falling into ranges up to 1200°C, 1600°C, or 1800°C.
This temperature rating is intrinsically linked to the material of the process tube itself. Quartz tubes are common for applications up to 1200°C, while high-purity alumina tubes are required for higher temperatures due to their superior thermal and chemical stability.
Pillar 2: Furnace Orientation (Vertical vs. Horizontal)
The physical orientation of the tube significantly impacts thermal performance and is a critical decision point.
Horizontal furnaces are the most common configuration. They are versatile and easy to load for a wide range of applications, but can be susceptible to slight temperature variations along the tube's length due to natural convection.
Vertical furnaces offer superior temperature uniformity. Gravity-driven convection is more symmetrical along the tube's axis, resulting in a more consistent thermal environment, which is critical for processes like crystal growth or semiconductor fabrication.
Pillar 3: Heating Zones (Single vs. Multi-Zone)
The number of independently controlled heating elements, or zones, determines the level of control you have over the temperature profile.
A single-zone furnace is the simplest and most cost-effective. It is ideal for heating a sample located in the central hot zone where the temperature is most stable.
Multi-zone furnaces, most commonly three-zone, provide exceptional control over temperature uniformity. The two end zones are programmed to compensate for heat loss at the tube's openings, creating a significantly longer and more uniform flat temperature profile in the center zone.
Pillar 4: Physical Dimensions (Diameter & Length)
The furnace's heated diameter (from ~15 mm to over 200 mm) and length (from ~150 mm to 1500 mm) define its processing capacity.
These dimensions must be chosen based on your sample size, required throughput, and the length of the uniform temperature zone needed for your process.
Key Functional Types and Designs
Beyond the core specifications, several functional designs cater to specific process requirements.
Atmosphere and Vacuum Control
Many processes require a non-ambient environment. Atmosphere furnaces are designed with sealed end flanges and gas ports to allow for processing under inert (e.g., Argon) or reactive gases.
Vacuum furnaces are a subset of this, equipped with higher-grade seals and vacuum ports to remove air and other gases, which is essential for preventing oxidation and contamination.
Mechanical Design (Split-Tube vs. Solid)
This distinction relates to how you access the process tube. Split-tube furnaces are hinged and can be opened along their length, allowing for easy placement and removal of the tube or samples. This is invaluable when working with fixed reactors or delicate substrates.
Solid-tube furnaces, or integrated furnaces, have a fixed cylindrical chamber that the process tube slides into. They are mechanically simpler and can offer better insulation.
Specialized Configurations
For niche industrial applications, you may encounter specialized designs like rotary tube furnaces. In these models, the entire tube rotates to tumble powders or granules, ensuring every particle is exposed to the same thermal conditions for highly uniform batch processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Your choice is not about finding the "best" furnace, but the right one for your goal. Every design feature involves a compromise.
Uniformity vs. Cost and Complexity
A three-zone vertical furnace provides the highest possible temperature uniformity. However, it is more expensive and requires more complex programming and setup than a simple single-zone horizontal model.
Throughput vs. Precision
A large-diameter furnace can process larger samples or higher volumes of material. Achieving perfect thermal uniformity across that wider diameter is more challenging and may require a multi-zone configuration.
Accessibility vs. Seal Integrity
A split-tube furnace offers unparalleled ease of access for loading and unloading. A solid-tube design, however, can sometimes provide a simpler and more robust platform for achieving a high-integrity vacuum seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate furnace, align its capabilities directly with your primary process requirement.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity: Choose a multi-zone (preferably three-zone) vertical furnace to minimize thermal gradients.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab heating and versatility: A single-zone horizontal furnace offers a robust, cost-effective, and flexible solution for many applications.
- If your primary focus is processing under a controlled atmosphere or vacuum: Ensure the model is specifically designed with high-quality sealed end flanges and the necessary gas or vacuum ports.
- If your primary focus is ease of sample loading or using an existing reactor: Prioritize a split-tube design to allow the furnace to be opened and placed around your setup.
Ultimately, a clear understanding of your process needs is the only factor that can guide you to the correct instrument.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Key Differences | Impact on Application |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | Ranges up to 1200°C, 1600°C, 1800°C | Determines material compatibility and process limits |
| Orientation | Horizontal (versatile) vs. Vertical (uniform) | Affects temperature uniformity and ease of use |
| Heating Zones | Single-zone (simple) vs. Multi-zone (precise) | Controls temperature profile and thermal stability |
| Physical Dimensions | Diameter (15-200+ mm), Length (150-1500 mm) | Defines sample capacity and throughput |
| Special Designs | Atmosphere/Vacuum, Split/Solid Tube, Rotary | Enables specific processes like gas control or batch uniformity |
Struggling to select the perfect tube furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in research, material science, or industrial processing, we can help you achieve precise thermal control and enhanced efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how our expertise can benefit your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















