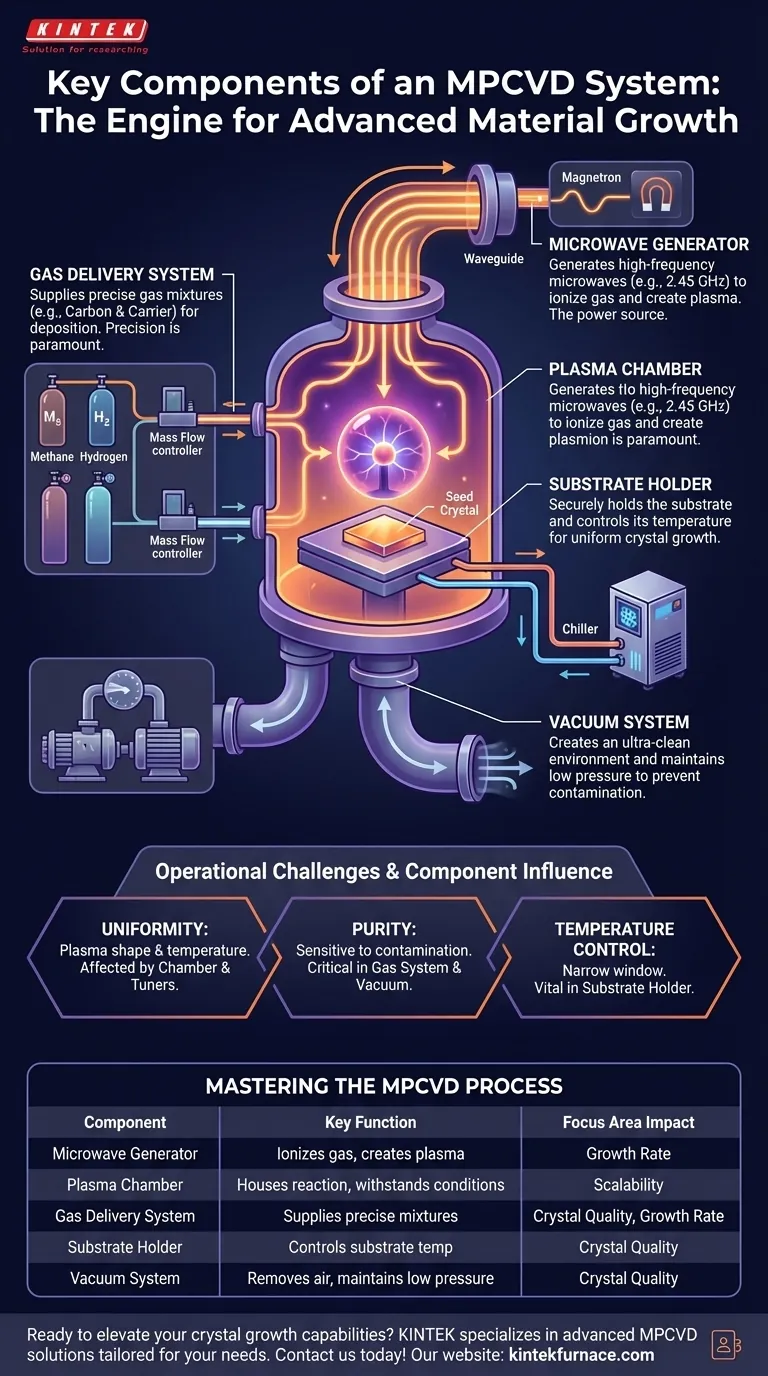
At its core, a Microwave Plasma-Assisted Chemical Vapor Deposition (MPCVD) system is an advanced apparatus for growing high-purity crystalline materials, such as lab-grown diamonds and graphene. Its essential components are a Microwave Generator, Plasma Chamber, Gas Delivery System, Substrate Holder, and a Vacuum System, all working in concert to create a highly controlled environment for atomic-level construction.
An MPCVD system isn't just a collection of parts; it's an integrated engine for turning simple gases into high-value crystalline structures. The key is its ability to use microwave energy to create a precise, high-energy plasma that facilitates the controlled deposition of atoms onto a substrate.

The Engine of Deposition: How MPCVD Components Work Together
Understanding an MPCVD system requires seeing its components not as a list, but as a sequence of functions that enable crystal growth. Each part plays a critical, non-negotiable role in establishing and maintaining the perfect conditions for deposition.
The Microwave Generator: Igniting the Process
The process begins with the microwave generator, typically a magnetron. This is the power source for the entire system, analogous to the engine of a car.
It generates high-frequency microwaves (often at 2.45 GHz) that are channeled through a waveguide into the reaction chamber. This energy is what will ultimately ionize the gas and create the plasma.
The Plasma Chamber: The Reaction Arena
The plasma chamber is the heart of the machine—a sealed, robust vessel where the entire growth process occurs. It is designed to withstand both high temperatures and vacuum conditions.
This chamber is where the microwave energy interacts with the process gases. It often includes viewports allowing for direct observation and measurement of the process, such as using an optical pyrometer to monitor the substrate temperature without physical contact.
The Gas Delivery System: Supplying the Raw Materials
The gas delivery system is responsible for feeding the building blocks into the chamber. For diamond growth, this typically involves a precise mixture of a carbon source gas (like methane) and a carrier gas (like hydrogen).
This system uses mass flow controllers to ensure the exact ratio and volume of gases are injected. The precision here is paramount, as even minor variations in the gas mixture can dramatically alter the quality of the final product.
The Substrate Holder: The Foundation for Growth
Inside the chamber, the substrate holder, or stage, performs two critical functions. First, it securely holds the substrate—often a small "seed" crystal upon which the new material will grow.
Second, and more importantly, it controls the substrate's temperature. This is a crucial parameter for controlling the crystal's structure and quality. The stage is often connected to a cooling system, such as a controlled chiller, to maintain a stable, optimal temperature throughout the hours or days of growth.
The Vacuum System: Creating the Perfect Environment
Before the process begins, the vacuum system—a series of pumps—removes virtually all the air and impurities from the plasma chamber. This creates an ultra-clean environment to prevent contamination of the growing crystal.
During the process, the vacuum system maintains the necessary low pressure inside the chamber. This low-pressure state is essential for the microwaves to effectively ionize the gas and form a stable plasma ball around the substrate.
Understanding the Operational Demands
While the concept is straightforward, operating an MPCVD system requires overcoming significant technical challenges. The quality of the final product is directly tied to how well these challenges are managed.
The Challenge of Uniformity
The plasma generated by the microwaves is not always perfectly uniform in shape or temperature. This can lead to uneven growth across the substrate, affecting the size and consistency of the final crystal. Advanced systems use features like stub tuners to help shape the plasma for better uniformity.
The Importance of Purity
The process is extremely sensitive to contamination. Any leak in the vacuum system or impurity in the gas lines can introduce unwanted elements (like nitrogen from the air), which can disrupt crystal formation, causing defects and discoloration.
Temperature Control is Non-Negotiable
The substrate temperature must be held within a very narrow window, often just a few degrees. If the temperature is too high or too low, it can lead to the formation of undesirable materials (like graphite instead of diamond) or introduce stress and defects into the crystal lattice. This is why precise temperature measurement and control are vital.
How Each Component Influences the Final Product
Your focus will determine which component's performance is most critical. Understanding this relationship is key to achieving your specific goal, whether it's research, development, or production.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Quality: Your success depends on the precision of the Gas Delivery System for purity and the Substrate Holder for exact temperature control.
- If your primary focus is Growth Rate: Your efforts should center on optimizing the output of the Microwave Generator and the flow rates managed by the Gas Delivery System.
- If your primary focus is Scalability: You must prioritize the design of the Plasma Chamber and its ability to create a large, stable, and uniform plasma field.
Mastering an MPCVD system is a process of mastering the precise control and interplay between each of these core components.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Microwave Generator | Generates microwaves to ionize gas and create plasma |
| Plasma Chamber | Houses the reaction and withstands high temperatures and vacuum |
| Gas Delivery System | Supplies precise gas mixtures for deposition |
| Substrate Holder | Holds and controls temperature of the substrate for growth |
| Vacuum System | Removes air and maintains low pressure to prevent contamination |
Ready to elevate your crystal growth capabilities? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD systems tailored for diverse laboratories. With our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring superior performance in applications like diamond and graphene synthesis. Contact us today to discuss how our MPCVD expertise can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the process for synthesizing transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) using CVD tube furnaces? Master High-Quality Thin Film Growth
- What are the advantages of CVD tube furnace sintering systems? Achieve Superior Material Control and Purity
- What are the operational benefits of using a CVD Tube Furnace? Enhance Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab
- What future trends are expected in the development of CVD tube furnaces? Discover Smarter, More Versatile Systems
- What are the practical applications of gate media prepared by CVD tube furnaces? Unlock Advanced Electronics and More



















