In short, a digital muffle furnace is used for a range of high-temperature applications that require precise thermal control in a clean environment. The primary uses include ashing samples for analysis, heat-treating metals to alter their properties, sintering powdered materials into solid forms, and performing calcination to induce chemical changes. Its ability to reach and hold temperatures up to 1700°C (3092°F) or more makes it a cornerstone of materials science, analytical chemistry, and industrial quality control.
A muffle furnace is more than just an oven; it's a high-precision instrument for thermally transforming materials. Its core value lies in creating an extremely hot, uniform, and clean environment, making it indispensable for processes that require controlled chemical changes, material phase transitions, or the complete removal of combustible substances.

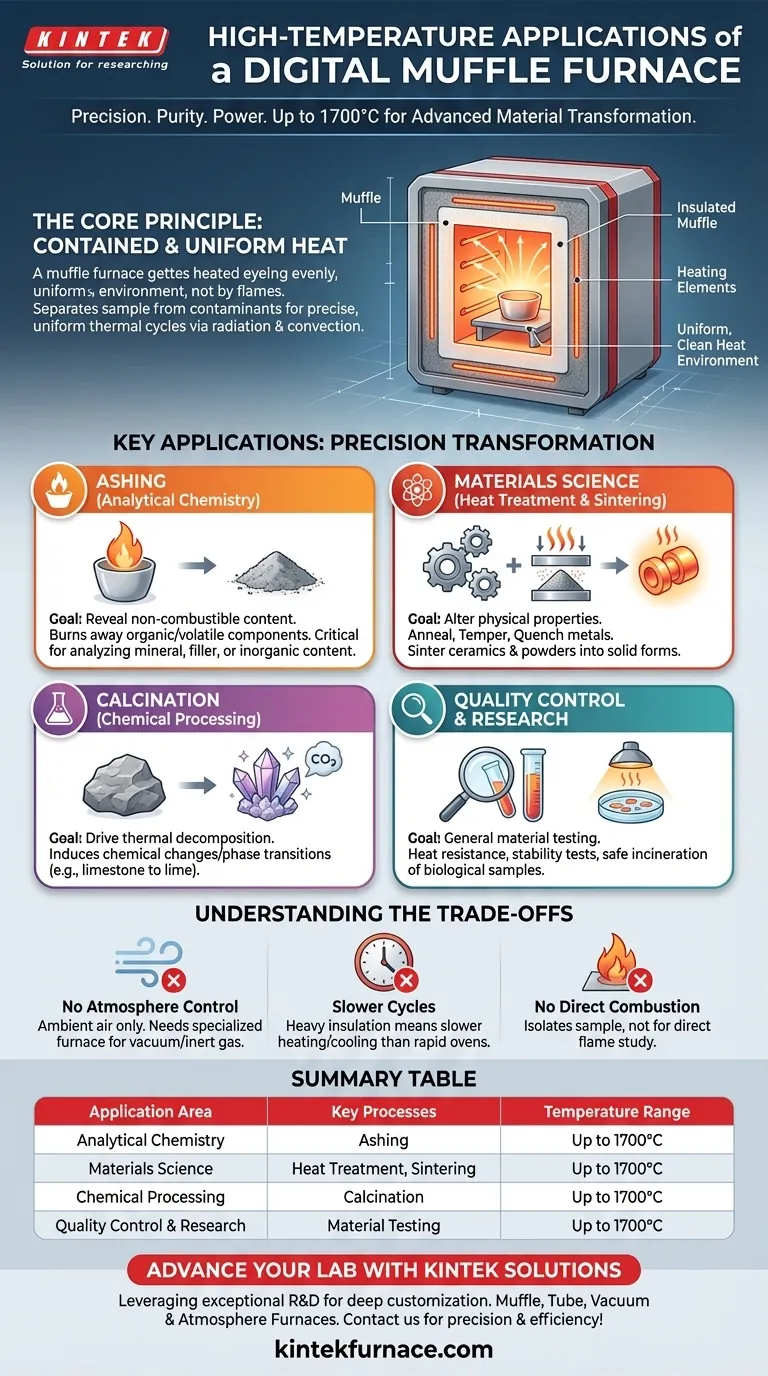
The Core Principle: Contained & Uniform Heat
A muffle furnace's unique capability comes from its design. The term "muffle" refers to the insulated inner chamber that separates the sample from the heating elements and any contaminants.
This design ensures two critical outcomes:
- Uniform Heating: The sample is heated evenly from all sides via radiation and convection, not by direct contact with a flame or element.
- Clean Environment: There is no contamination from the byproducts of combustion, which is crucial for analytical or high-purity processes.
The "digital" aspect adds a layer of precise programmable control over temperature and time, allowing for repeatable and documented thermal cycles.
Key Applications in Detail
The combination of high heat, uniformity, and a clean environment makes the muffle furnace essential across several disciplines.
Analytical Chemistry: Revealing What's Left Behind
The most common analytical application is ashing. The goal is to heat a sample to a temperature where all organic and volatile components burn away completely.
What remains is the non-combustible ash content. This is critical for determining the mineral, filler, or inorganic content in materials like food products, plastics, pharmaceuticals, and environmental samples.
Materials Science: Altering Physical Properties
Muffle furnaces are fundamental in metallurgy and ceramics for modifying a material's internal structure and, therefore, its physical properties.
Key processes include:
- Heat Treatment: This includes annealing (softening metals), tempering (increasing toughness), and quenching (hardening) small steel or metal parts.
- Sintering: This process uses heat to fuse powdered materials, like ceramics or metal powders, into a solid, coherent mass without melting them.
Chemical Processing: Driving Thermal Reactions
Calcination is a thermal treatment process used to bring about a chemical change or phase transition in a material.
Unlike ashing, the goal is not to burn material away but to decompose it. A classic example is heating limestone (calcium carbonate) to produce lime (calcium oxide) and carbon dioxide.
Quality Control & Research
Beyond specific named processes, muffle furnaces are workhorses for general material testing.
This can involve testing the heat resistance of a new component, performing stability tests on pharmaceutical compounds at elevated temperatures, or incinerating biological samples safely.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not a universal solution for all high-temperature needs. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Lack of Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace operates in an ambient air atmosphere. If your process requires a vacuum, inert gas (like argon or nitrogen), or a reactive gas, you need a specialized vacuum furnace or controlled-atmosphere furnace.
Slower Heating and Cooling Cycles
The heavy insulation required to reach and maintain extreme temperatures means muffle furnaces do not heat up or cool down instantly. For applications requiring very rapid thermal cycling, other specialized ovens may be more suitable.
Not Designed for Direct Combustion
The muffle's purpose is to isolate the sample. If your process requires direct flame impingement or is intended to study the effects of direct combustion, a different type of equipment is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a muffle furnace is the correct tool, match it to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: Use the furnace for ashing to precisely measure the non-combustible content of a sample.
- If your primary focus is improving material properties: Use it for heat treatment of metals or for sintering ceramic and powdered metal components.
- If your primary focus is creating new compounds via heat: Use it for calcination to drive specific thermal decomposition reactions.
- If your primary focus requires a specific gas atmosphere: You must seek out a specialized vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnace instead of a standard muffle furnace.
Ultimately, a digital muffle furnace is the definitive tool for any process demanding precise, clean, and uniform high-temperature transformation.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Chemistry | Ashing | Up to 1700°C |
| Materials Science | Heat Treatment, Sintering | Up to 1700°C |
| Chemical Processing | Calcination | Up to 1700°C |
| Quality Control & Research | Material Testing | Up to 1700°C |
Enhance your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can bring precision and efficiency to your high-temperature applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How do repeat sintering processes and specialized sintering molds address the technical challenges of manufacturing oversized flywheel rotor components? Expand Scale and Integrity
- What role does a muffle furnace play in g-C3N4 synthesis? Mastering Thermal Polycondensation for Semiconductors
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the conversion of S-1@TiO2? Achieve Precision Calcination of Nanospheres
- What role does a muffle furnace play in analyzing the combustion residues? Optimize Your Composite Char Analysis
- How does a stainless steel reactor function within a muffle furnace for PET to graphene? Master Carbon Synthesis



















