In short, processing heavy raw materials in a conventional tube furnace introduces significant operational and economic disadvantages. The primary limitations are a severe tendency for coke formation (coking), reduced cracking efficiency, and the subsequent increase in low-value byproducts, all of which negatively impact profitability and equipment lifespan.
The core issue is that the properties of heavy feedstocks are fundamentally mismatched with the design of traditional tube furnaces. This mismatch forces operators into a cycle of compromises that lead to lower yields, higher costs, and reduced operational uptime.
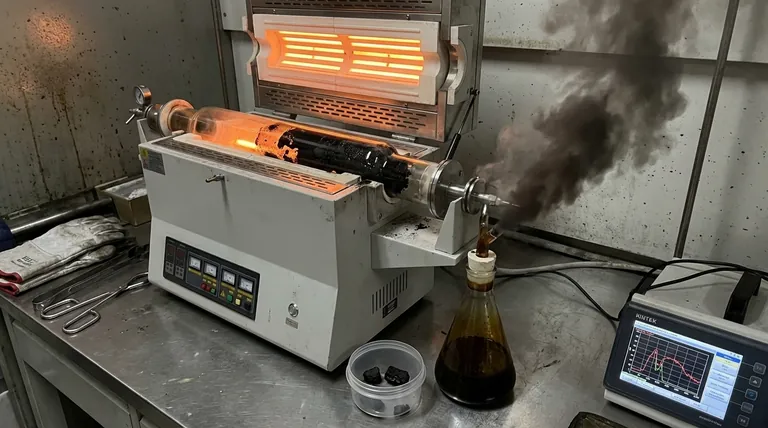

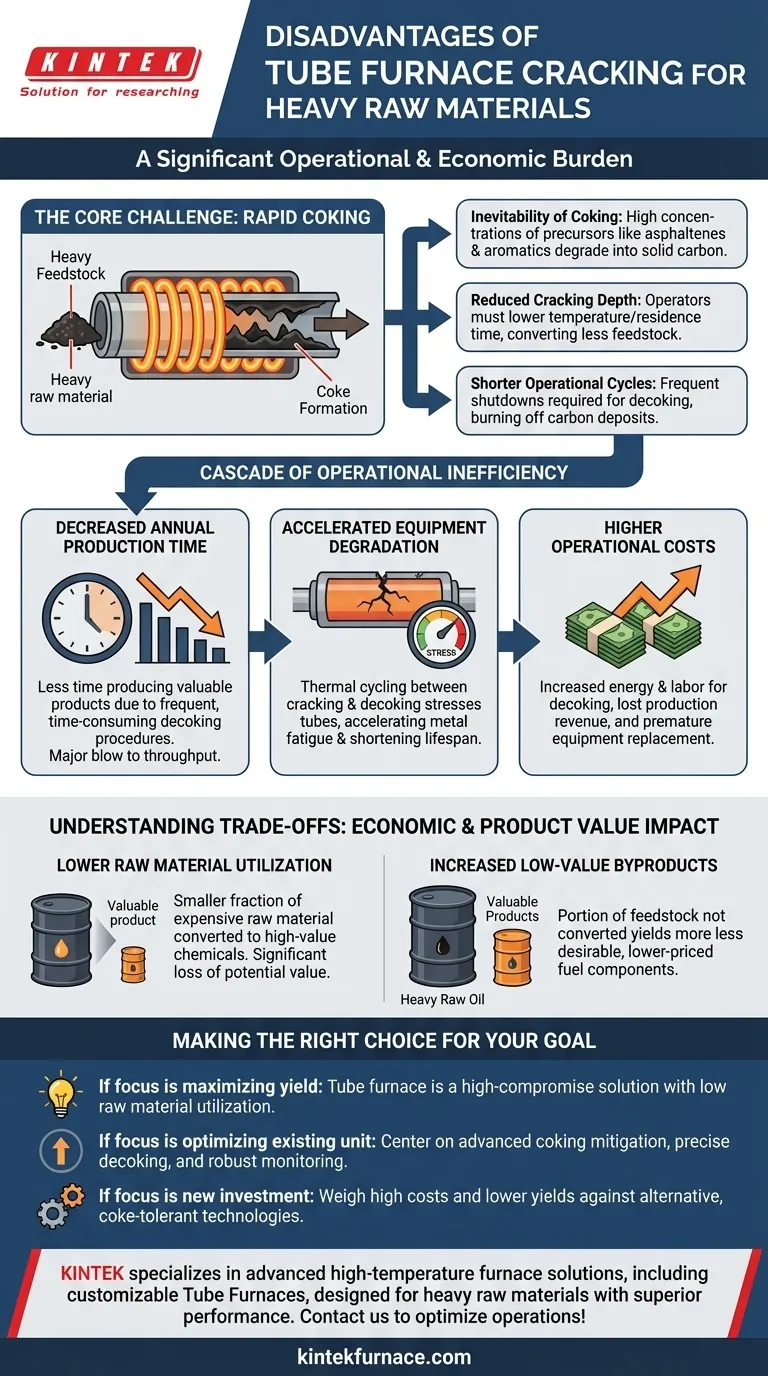
The Core Challenge: Rapid Coking
When processing heavy raw materials, which are rich in complex hydrocarbons, the primary engineering challenge is managing the rapid formation of coke. This single issue is the root cause of most other disadvantages.
The Inevitability of Coking
Heavy feedstocks contain higher concentrations of coke precursors like asphaltenes and aromatics. Under the high-heat conditions of a cracking furnace, these compounds polymerize and degrade into a solid carbon layer, known as coke, on the inner walls of the furnace tubes.
Reduced Cracking Depth
To slow the rate of coke formation, operators are forced to reduce the process severity, meaning lower temperatures or shorter residence times. This reduced cracking depth means less of the heavy raw material is converted into valuable products like ethylene and propylene per pass.
Shorter Operational Cycles
Even with reduced severity, coke buildup is inevitable. This requires the furnace to be taken offline frequently for decoking, a process to burn off the carbon deposits. These frequent shutdowns drastically shorten the productive operational cycle of the furnace.
The Cascade of Operational Inefficiency
The need to manage coking sets off a chain reaction of problems that directly impact the facility's overall productivity and maintenance burden.
Decreased Annual Production Time
Shorter cycles and frequent, time-consuming decoking procedures directly translate to less time spent producing valuable products. This reduction in effective annual production time is a major blow to plant throughput and revenue.
Accelerated Equipment Degradation
The constant thermal cycling between high-temperature cracking and even higher-temperature decoking puts immense stress on the furnace tubes. This stress accelerates metal fatigue and shortens the lifespan of the furnace and its tubes, leading to costly, premature replacement.
Higher Operational Costs
The disadvantages manifest directly on the balance sheet. Costs increase due to the energy and labor required for frequent decoking, the lost production during downtime, and the capital expenditure needed for earlier-than-planned equipment replacement.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Economic and Product Value Impact
The operational compromises forced by coking have a direct and negative impact on the economic viability of the process. You are forced to trade potential profit for manageable operation.
Lower Raw Material Utilization
Because the cracking depth must be kept low, a smaller fraction of the expensive raw material is converted into the target high-value chemicals. This represents a significant loss of potential value from the feedstock.
Increased Low-Value Byproducts
The portion of the feedstock that is not converted into valuable light olefins is instead yielded as heavy raw oil and other low-value byproducts. Instead of producing premium chemicals, the process generates a higher volume of less desirable, lower-priced fuel components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these inherent disadvantages is critical for making sound strategic decisions about feedstock selection and technology investment.
- If your primary focus is maximizing yield from heavy feeds: A traditional tube furnace is a high-compromise solution, and its low raw material utilization will be a persistent economic drag.
- If your primary focus is optimizing an existing tube furnace unit: Your strategy must center on advanced coking mitigation, precise decoking schedule optimization, and robust process monitoring to balance uptime against tube life.
- If your primary focus is new capital investment for heavy feed cracking: The high operational costs and lower yields of tube furnaces must be carefully weighed against alternative, more coke-tolerant cracking technologies.
Ultimately, a clear-eyed assessment of these limitations is essential to align your technology with your specific raw material and profitability targets.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Impact |
|---|---|
| Rapid Coking | Leads to frequent shutdowns and decoking, reducing operational uptime |
| Reduced Cracking Efficiency | Lowers yield of valuable products like ethylene and propylene |
| Increased Low-Value Byproducts | Generates more heavy raw oil, decreasing profitability |
| Accelerated Equipment Degradation | Shortens furnace lifespan, raising replacement costs |
| Higher Operational Costs | Includes energy, labor for decoking, and lost production revenue |
Struggling with coking and inefficiency in your lab's tube furnace processes? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Tube Furnaces, designed to handle heavy raw materials with superior performance. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to minimize coking, enhance cracking efficiency, and extend equipment life—tailored precisely to your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to optimize your operations and boost profitability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety



















