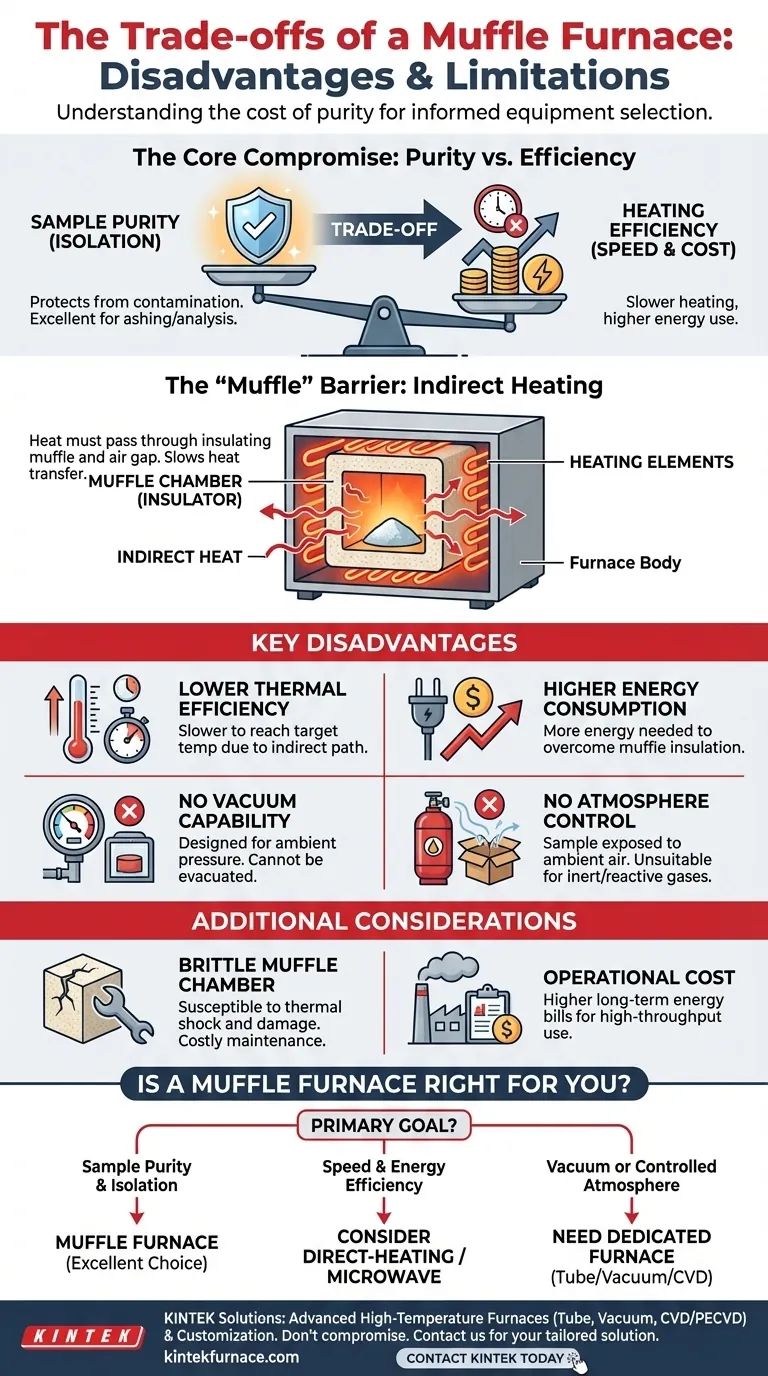
While indispensable for many applications, a muffle furnace is defined by specific design trade-offs that make it unsuitable for others. Its primary disadvantages are lower heating efficiency, higher associated energy consumption, and an inability to operate under a vacuum. These limitations stem directly from the core feature that also gives the furnace its primary advantage: the "muffle" chamber that isolates the sample from the heating elements.
The central disadvantage of a muffle furnace arises from its design for sample purity. The insulated chamber that protects materials from direct contact with heating elements also acts as a barrier to heat transfer, reducing thermal efficiency and increasing energy costs compared to direct-heating methods.

The Core Compromise: Indirect Heating
The name "muffle furnace" comes from the "muffle"—an insulated, enclosed chamber, typically made of ceramic, that contains the material being heated. Understanding this component is key to understanding the furnace's limitations.
The Purpose of the Muffle
The muffle's job is to create a barrier between the heating elements and the sample. This prevents contamination from the elements, ensuring the chemical purity of the material being processed.
This design is excellent for applications like ashing, chemical analysis, or heat-treating materials where contamination would compromise the results.
The Consequence: Lower Thermal Efficiency
This protective barrier is also an insulator. Heat from the elements must first radiate through the air gap and then conduct through the muffle walls to reach the sample.
This indirect heating path is inherently less efficient than direct radiation from the elements onto the sample. As a result, muffle furnaces often take longer to reach the target temperature.
The Result: Higher Energy Consumption
To compensate for lower thermal efficiency and heat loss, the furnace must consume more energy.
Holding a high temperature requires the heating elements to work harder to push heat through the muffle, leading to higher long-term operational costs compared to more efficient furnace types.
Critical Application Limitations
The design that makes a muffle furnace ideal for some tasks makes it completely unsuitable for others. It is not a universally applicable high-temperature tool.
Inability to Create a Vacuum
A standard muffle furnace is not designed for vacuum applications. The chamber and door seals are built for ambient atmospheric pressure, not for being evacuated.
For processes requiring a vacuum to prevent oxidation or remove gases, such as sintering sensitive metals or advanced ceramics, a dedicated vacuum furnace is the correct choice.
Unsuitability for Reactive Atmospheres
While the muffle protects samples from the heating elements, it does not control the atmosphere inside the chamber. The sample is still exposed to the ambient air (primarily nitrogen, oxygen, and argon) that fills the box.
If your process requires an inert atmosphere (like pure argon) or a reactive one (like hydrogen), a tube furnace with gas flow capabilities is the necessary equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a muffle furnace involves weighing its primary benefit—purity—against its inherent inefficiencies and limitations.
Purity vs. Efficiency
This is the fundamental trade-off. The muffle furnace prioritizes sample purity by isolating it from contamination. The price for this purity is lower heating efficiency and slower processing cycles.
If your application can tolerate potential minor contamination from direct heating elements, other furnace types may offer faster and more energy-efficient performance.
Cost: Upfront vs. Operational
Muffle furnaces can be relatively cost-effective to purchase. However, their higher energy consumption translates directly to higher operational costs over the lifetime of the equipment.
For high-throughput industrial use, this higher energy bill can become a significant financial factor.
Safety and Maintenance
Like any high-temperature equipment, safety is a critical concern. The ceramic muffle itself can be brittle and susceptible to thermal shock if heated or cooled too rapidly, or if mishandled.
A cracked muffle compromises the core function of the furnace and can be costly to replace, representing a key maintenance consideration.
Is a Muffle Furnace Right for Your Application?
Choosing the correct furnace requires a clear understanding of your primary goal. Use this guide to make an informed decision.
- If your primary focus is sample purity and preventing contamination: A muffle furnace is an excellent choice, as its core design is built for sample isolation.
- If your primary focus is speed and maximum energy efficiency: You should evaluate direct-heating or microwave furnaces, as the indirect nature of a muffle furnace inherently slows heat transfer.
- If your primary focus is processing in a vacuum or a controlled gas atmosphere: A dedicated vacuum or tube furnace is required, as a standard muffle furnace cannot provide these environments.
Understanding these inherent limitations allows you to select the right thermal processing tool, ensuring your results are both accurate and efficiently obtained.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Lower Thermal Efficiency | Slower heating cycles due to indirect heat transfer through the muffle chamber. |
| Higher Energy Consumption | Increased operational costs from the energy required to heat the insulating muffle. |
| No Vacuum Capability | Cannot create a vacuum environment, limiting use for oxidation-sensitive processes. |
| No Atmosphere Control | Sample is exposed to ambient air; unsuitable for inert or reactive gas atmospheres. |
| Brittle Muffle Chamber | The ceramic muffle is susceptible to thermal shock and damage, requiring careful maintenance. |
Need a High-Temperature Solution Tailored to Your Specific Process?
Understanding the limitations of standard equipment is the first step to selecting the perfect furnace for your unique requirements. The trade-offs of a muffle furnace make it unsuitable for applications demanding speed, atmosphere control, or vacuum conditions.
KINTEK solves these challenges. We leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces for gas atmospheres, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces for critical environments, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental needs.
Don't let equipment limitations compromise your results. Let our experts help you select or custom-build a furnace that prioritizes your application's primary focus—whether it's purity, efficiency, or atmosphere control.
Contact KINTEL today for a personalized consultation and discover the right thermal processing tool for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















