Ultimately, the cost of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is dominated by significant capital investment and ongoing operational expenses. The equipment, particularly systems designed for high-temperature and high-vacuum processes, represents a major upfront cost, which is compounded by continuous expenses for maintenance, energy, and precursor materials.
The decision to use CVD is not about finding the cheapest deposition method. It is a strategic choice where higher costs are accepted as a direct trade-off for achieving superior film purity, uniformity, and conformal coverage that other techniques often cannot deliver.
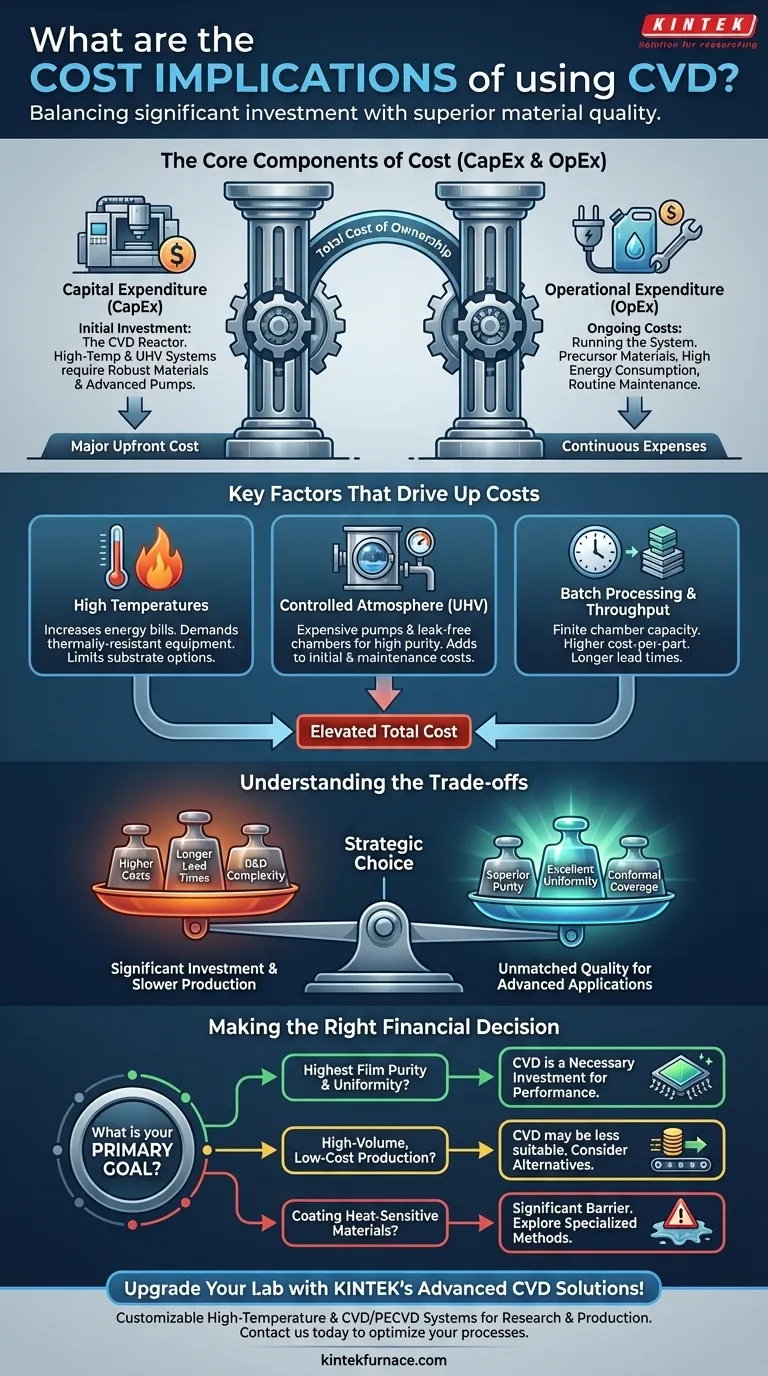
The Core Components of CVD Cost
Understanding the cost of CVD requires looking at both the initial purchase and the long-term expenses associated with running the equipment.
Capital Expenditure (CapEx): The Initial Investment
The most visible cost is the CVD reactor itself. The price of this equipment can vary dramatically based on its specifications.
Systems that operate at very high temperatures or require an ultra-high vacuum (UHV) environment are substantially more expensive due to the need for robust materials, advanced heating elements, and sophisticated vacuum pumps and seals.
Operational Expenditure (OpEx): The Ongoing Costs
Running a CVD system involves several continuous costs that can significantly impact the total cost of ownership.
Key operational expenses include the precursor materials (the chemical gases or vapors used for deposition), the high energy consumption needed to maintain process temperatures, and the cost of routine maintenance for components like vacuum pumps and heating systems.
Factors That Drive Up Costs
Several technical requirements inherent to the CVD process are primary drivers of its high cost structure.
The Need for High Temperatures
Many CVD processes require elevated temperatures to facilitate the necessary chemical reactions. This not only increases energy bills but also demands more expensive, thermally-resistant equipment.
Furthermore, this high heat can limit the types of substrates you can use, potentially forcing you to choose more expensive, heat-tolerant materials or ruling out the process for heat-sensitive components.
The Demand for a Controlled Atmosphere
Achieving high-purity films often requires a high-vacuum environment to eliminate contaminants. The equipment needed to create and maintain this vacuum—including turbo-molecular pumps, gauges, and leak-free chambers—adds significantly to both the initial purchase price and maintenance costs.
Throughput and Batch Processing
CVD reactors have a finite chamber capacity, which limits the size and number of parts that can be coated at one time. This often necessitates batch processing.
This constraint on throughput can increase the cost-per-part and lead to longer production lead times, making CVD less cost-effective for high-volume manufacturing compared to more continuous processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The high cost of CVD is a direct consequence of the capabilities it provides. The decision to invest in it hinges on balancing cost against performance requirements.
Cost vs. Unmatched Quality
The primary justification for CVD's expense is its ability to produce exceptionally high-purity films. For applications in semiconductors, optics, and advanced materials, this level of quality is often non-negotiable.
Throughput vs. Conformal Coverage
CVD excels at creating films with excellent uniformity that conform perfectly to complex, three-dimensional shapes. The trade-off is that achieving this often requires slower deposition rates and batch processing, sacrificing manufacturing speed for superior coating geometry.
Versatility vs. Complexity
The technology is highly versatile, capable of depositing a wide range of materials, from metals and ceramics to polymers. This flexibility is valuable but comes with the complexity of developing and fine-tuning a specific chemical process for each material and substrate combination, which can involve significant R&D costs.
Making the Right Financial Decision
Choosing whether to absorb the costs of CVD depends entirely on your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity and uniformity: The high cost of CVD is a necessary investment to meet stringent performance specifications that alternative methods cannot reach.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production: The batch-processing nature and high operational costs may make CVD less suitable than technologies like PVD or electroplating, unless its unique performance is an absolute requirement.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials: The high temperatures of many CVD processes present a significant cost and compatibility barrier, requiring you to explore specialized low-temperature CVD variants or entirely different deposition technologies.
Ultimately, the cost of CVD is best understood as an investment in a specific and often unparalleled level of material quality and performance.

Summary Table:
| Cost Component | Key Factors | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Expenditure (CapEx) | High-temperature, UHV systems, robust materials | Major upfront investment |
| Operational Expenditure (OpEx) | Precursor materials, energy, maintenance | Ongoing expenses affecting total cost |
| Throughput | Batch processing, limited chamber capacity | Higher cost-per-part, longer lead times |
| Quality Trade-offs | Superior purity, uniformity, conformal coverage | Justifies cost for high-performance applications |
Upgrade Your Laboratory with KINTEK's Advanced CVD Solutions!
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need superior film purity, uniform coatings, or tailored setups for semiconductors and advanced materials, KINTEK delivers reliable, cost-effective solutions that enhance your research and production outcomes.
Contact us today to discuss how our CVD systems can optimize your processes and drive innovation in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection



















