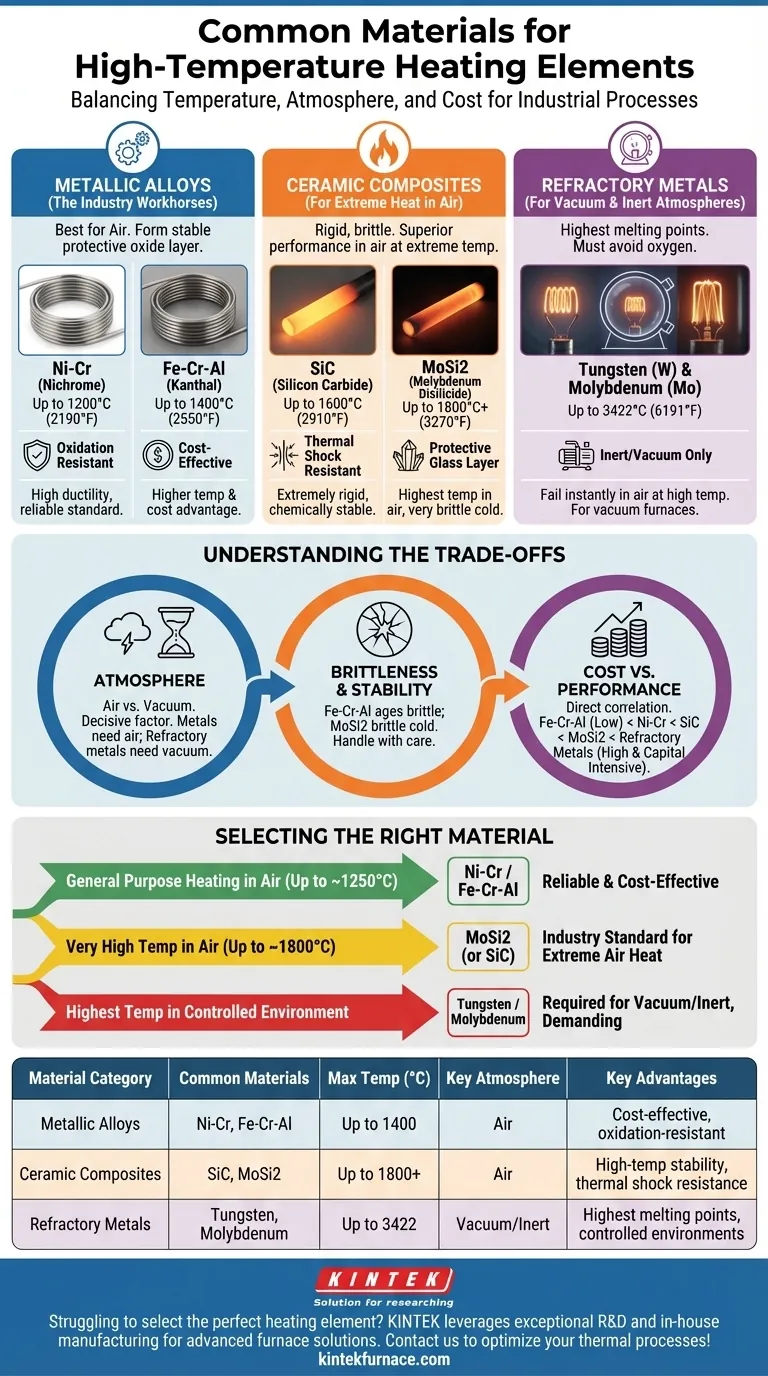
For high-temperature industrial processes, the most common heating element materials fall into three distinct families. These include metallic alloys like Nickel-Chromium (Ni-Cr) and Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (Fe-Cr-Al), non-metallic ceramics such as Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2), and refractory metals like Tungsten (W) for specialized, non-oxidizing environments.
The selection of a high-temperature heating element is never about a single material being "best." It is a critical engineering decision that balances three factors: the maximum required temperature, the chemical environment (i.e., air, inert gas, or vacuum), and the total cost of ownership.

Understanding the Primary Material Categories
Choosing the correct element requires understanding the fundamental properties of each material family. They are not interchangeable; each is engineered for a specific set of operating conditions.
Metallic Alloys: The Industry Workhorses
These materials are the default choice for a vast range of industrial heating applications in air. They are typically formed into wires or ribbons.
Their key advantage is the formation of a stable, protective oxide layer (like alumina or chromia) on their surface. This layer shields the underlying metal from further oxidation, dramatically extending its life at high temperatures.
Nickel-Chromium (Ni-Cr) alloys, often known by the trade name Nichrome, are valued for their high ductility and excellent resistance to oxidation. They are a reliable standard for applications up to approximately 1200°C (2190°F).
Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (Fe-Cr-Al) alloys, known by trade names like Kanthal, offer a performance and cost advantage. They can operate at higher temperatures than Ni-Cr alloys, up to 1400°C (2550°F), and are generally more cost-effective.
Ceramic Composites: For Extreme Heat in Air
When temperatures in an air-filled furnace must exceed the limits of metallic alloys, ceramic elements are the solution. They are rigid and more brittle than metals but offer superior performance at extreme heat.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements are extremely rigid and have excellent thermal shock resistance. They are chemically stable and can operate reliably up to 1600°C (2910°F), making them ideal for high-temperature kilns and furnaces.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements are the gold standard for the highest temperatures achievable in air, capable of reaching over 1800°C (3270°F). They form a protective quartz-glass layer on their surface, but they are very brittle, especially at room temperature.
Refractory Metals: For Vacuum & Inert Atmospheres
Refractory metals have the highest melting points of all materials but have a critical weakness: they oxidize and fail almost instantly in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures.
Tungsten (W) and Molybdenum (Mo) are the primary choices in this category. Tungsten has the highest melting point of any metal (3422°C / 6191°F) and is used for the most demanding applications.
These elements must be operated in a vacuum or a protective, inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent burnout. They are the foundation of vacuum furnaces used for heat treating, sintering, and brazing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
An element that excels in one environment will fail catastrophically in another. Understanding these limitations is key to successful system design.
The Decisive Impact of Atmosphere
The single most important factor after temperature is the operating atmosphere.
Elements like Ni-Cr and Fe-Cr-Al are designed for use in air. Their protective oxide layer is their primary defense mechanism. Using them in a vacuum can cause this layer to break down, leading to premature failure.
Conversely, Tungsten and Molybdenum must be isolated from oxygen. Even a small air leak in a vacuum furnace can destroy these elements in minutes at operating temperature.
Brittleness and Mechanical Stability
Material properties change with temperature. Fe-Cr-Al alloys can become brittle after extended use at high temperatures, a phenomenon known as aging.
MoSi2 elements are notoriously brittle when cold and require careful handling during installation and maintenance. This brittleness is a significant design consideration for the furnace's support structure.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between temperature capability and cost. Fe-Cr-Al is a cost-effective workhorse, while Ni-Cr is a moderate step up.
Ceramic elements like SiC and especially MoSi2 represent a significant increase in cost. The expense of refractory metals is compounded by the need for a vacuum chamber and pumping system, making it the most capital-intensive option.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on your specific process goals. Focus on the required temperature and atmosphere first.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating in air (up to ~1250°C): Nickel-Chromium (Ni-Cr) or Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (Fe-Cr-Al) alloys are your most reliable and cost-effective choices.
- If your primary focus is reaching very high temperatures in air (up to ~1800°C): Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) is the industry standard, with Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a robust alternative for slightly lower temperatures or harsher chemical environments.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures in a controlled environment: Tungsten or Molybdenum are required and must be used within a vacuum or inert gas furnace to prevent oxidation.
By understanding these core trade-offs, you can confidently select a heating element that ensures both performance and longevity for your specific thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Materials | Max Temperature (°C) | Key Atmosphere | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic Alloys | Ni-Cr, Fe-Cr-Al | Up to 1400 | Air | Cost-effective, oxidation-resistant |
| Ceramic Composites | SiC, MoSi2 | Up to 1800+ | Air | High-temperature stability, thermal shock resistance |
| Refractory Metals | Tungsten, Molybdenum | Up to 3422 | Vacuum/Inert | Highest melting points, ideal for controlled environments |
Struggling to select the perfect heating element for your high-temperature applications? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Don't let material selection hold you back—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















