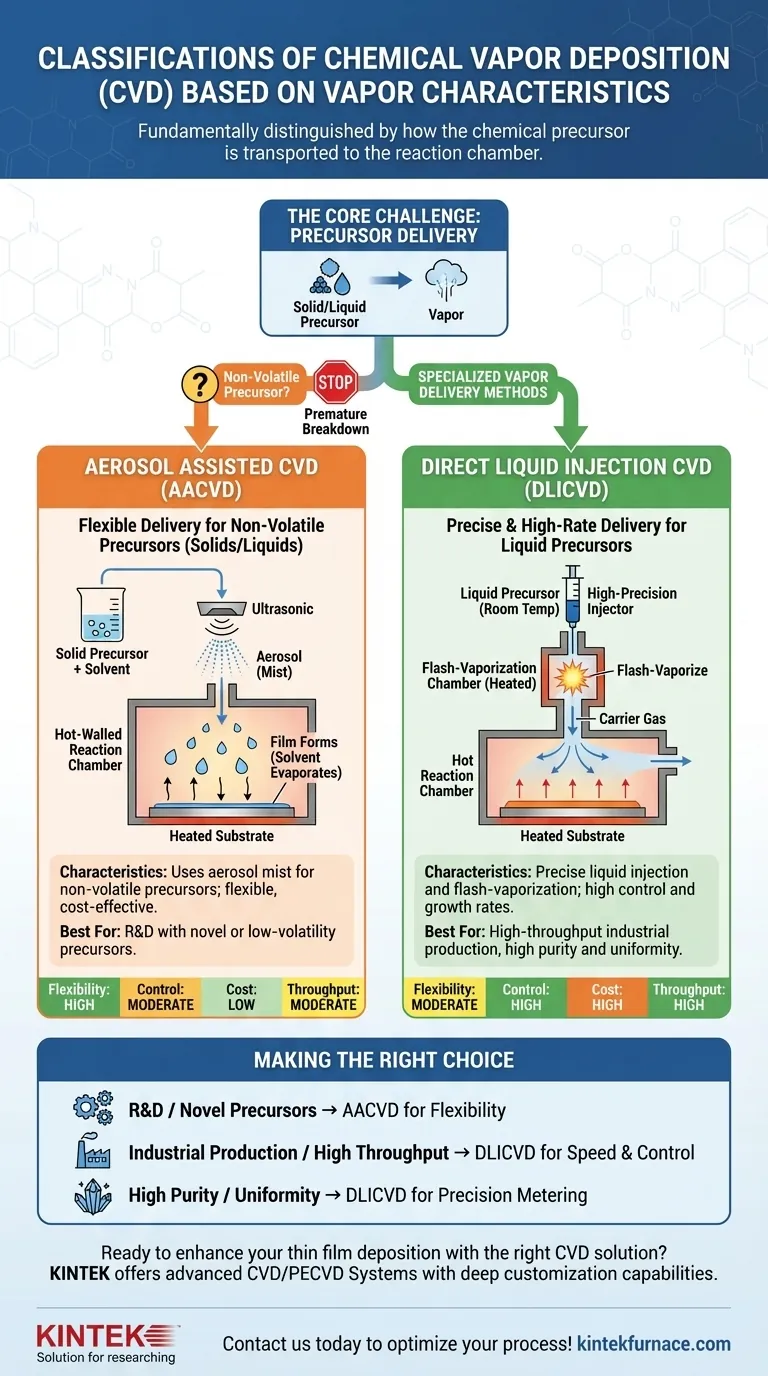
Fundamentally, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) processes classified by vapor characteristics are distinguished by how the chemical precursor is transported to the reaction chamber. The two primary methods in this category are Aerosol Assisted CVD (AACVD), which uses a fine mist to carry non-volatile precursors, and Direct Liquid Injection CVD (DLICVD), which precisely injects and vaporizes liquid precursors for high-growth-rate applications.
The choice between these methods is not academic; it is a practical engineering decision. It hinges on solving the core challenge of controllably delivering a specific precursor—whether it's a stable liquid, a thermally sensitive compound, or a solid dissolved in a solvent—to the substrate surface.
The Core Challenge: Precursor Delivery
The success of any CVD process relies on turning a precursor material into a gas and delivering it to a substrate in a highly controlled manner. The precursor's physical state dictates the best method for this delivery.
From Precursor to Vapor
The ideal CVD precursor is a substance that readily turns into a gas at a relatively low temperature and pressure without decomposing. This allows for simple delivery into the reaction chamber.
However, many advanced materials require precursors that are not so simple. They may be liquids with low volatility or even solids at room temperature.
The Problem of Non-Volatile Precursors
A non-volatile precursor is one that does not easily evaporate. Trying to heat it to force evaporation can cause it to break down prematurely, before it ever reaches the substrate. This is the central problem that specialized vapor delivery methods are designed to solve.
CVD Classifications by Vapor Delivery Method
When a precursor cannot be easily vaporized, engineers turn to methods that either carry it in a different medium or flash-vaporize it just in time.
Aerosol Assisted CVD (AACVD)
In AACVD, the precursor—often a solid—is first dissolved in a suitable solvent. This solution is then atomized into a fine mist, or aerosol, typically using an ultrasonic generator.
An inert carrier gas then transports this aerosol into the hot-walled reaction chamber. As the aerosol droplets approach the hot substrate, the solvent evaporates and the precursor decomposes to form the thin film. This method effectively bypasses the need to heat and vaporize a non-volatile precursor directly.
Direct Liquid Injection CVD (DLICVD)
DLICVD is a high-precision technique used for liquid precursors. The liquid precursor is stored at room temperature and injected in precisely metered micro-droplets into a vaporization chamber located close to the reactor.
This chamber is heated to a temperature high enough to instantly "flash-vaporize" the droplets into a gas. This vapor is then immediately swept into the reaction zone by a carrier gas. The key advantage is exceptional control over the precursor flow rate, leading to highly reproducible processes and enabling high film growth rates.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a delivery method involves balancing precursor compatibility with process requirements like cost, control, and throughput.
Precursor Flexibility
AACVD is exceptionally versatile. It is the go-to method for precursors that are solid or have very low volatility, as it depends on solubility rather than vapor pressure.
DLICVD is limited to precursors that are liquid and can be vaporized without decomposition.
Process Control and Repeatability
DLICVD offers superior control. The use of high-precision liquid flow controllers allows for a very stable and repeatable flow of precursor to the reactor. This translates to excellent control over film thickness and composition.
In AACVD, controlling the exact concentration of precursor in the aerosol can be more challenging, potentially leading to less uniformity.
System Complexity and Deposition Rate
AACVD systems are generally simpler and less expensive to set up. However, deposition rates can be limited.
DLICVD systems are more complex, requiring specialized pumps and vaporizers. This higher initial cost is justified by the ability to achieve the high deposition rates required for many industrial applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific needs will determine the most appropriate vapor delivery method.
- If your primary focus is R&D with novel or low-volatility precursors: AACVD provides the flexibility to experiment with a wide range of materials, including solids, that are unusable in other systems.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput industrial production: DLICVD delivers the precise control, repeatability, and high growth rates necessary for manufacturing environments.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest film purity and uniformity: DLICVD's ability to precisely meter the precursor flow makes it the more reliable choice for highly controlled processes.
Ultimately, selecting the right CVD classification is about matching the delivery technology to the physical properties of your precursor and the performance demands of your final product.

Summary Table:
| Classification | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Aerosol Assisted CVD (AACVD) | Uses aerosol mist for non-volatile precursors; flexible, cost-effective | R&D with novel or low-volatility precursors |
| Direct Liquid Injection CVD (DLICVD) | Precise liquid injection and flash-vaporization; high control and growth rates | High-throughput industrial production, high purity and uniformity |
Ready to enhance your thin film deposition with the right CVD solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your process with tailored AACVD or DLICVD systems!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the drawbacks of CVD compared to PECVD? Key Limitations for Your Lab
- What is resistance heating and how is it classified? Discover the Best Method for Your Thermal Needs
- How does chemical vapour deposition (CVD) differ from PVD? Key Differences in Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What is PECVD specification? A Guide to Choosing the Right System for Your Lab
- How is silicon dioxide deposited from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) in PECVD? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality SiO2 Films



















