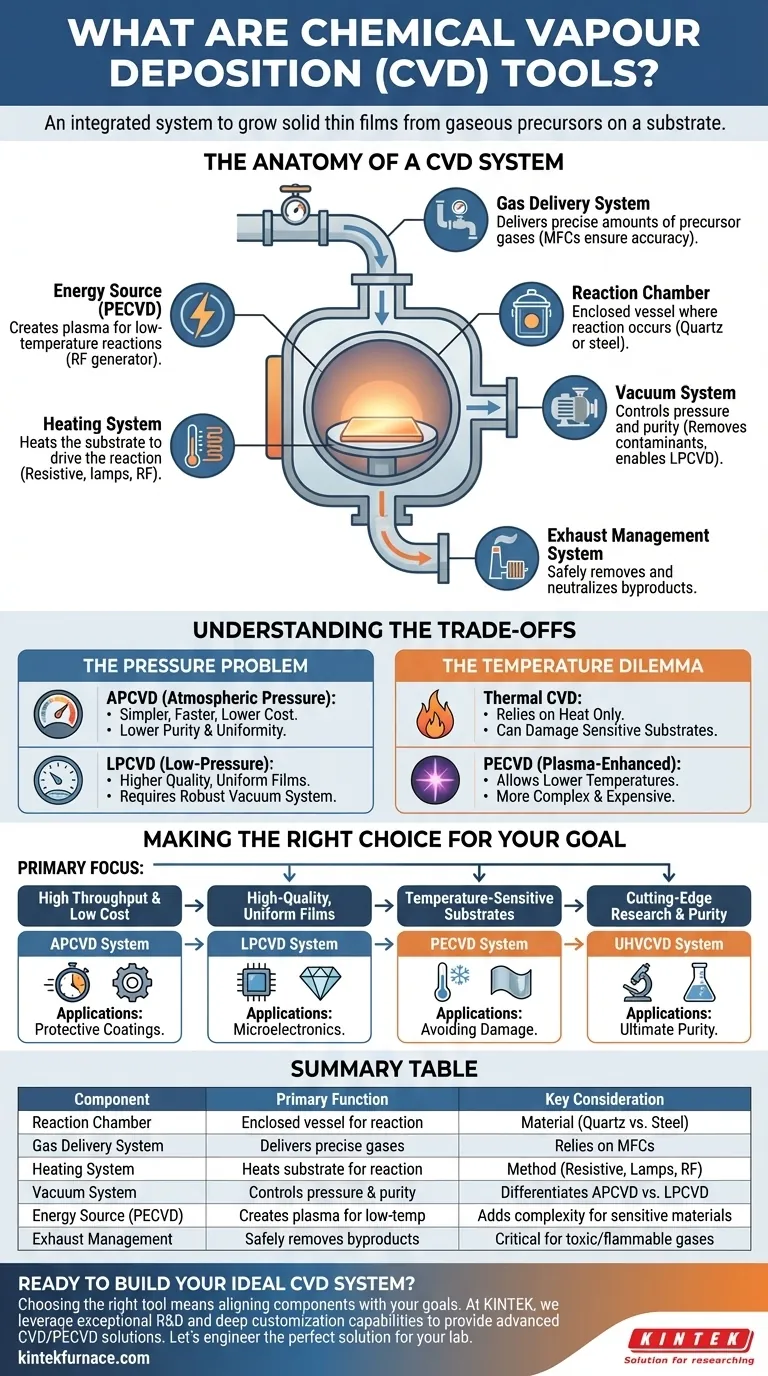
At its core, a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) "tool" is not a single instrument but rather an integrated system designed to grow a solid thin film onto a surface, known as a substrate, from gaseous chemical precursors. The essential components of this system are a reaction chamber, a gas delivery system to supply the chemicals, a heating system to provide energy for the reaction, and a vacuum system to control the environment's pressure and purity.
A CVD system is best understood as a highly controlled chemical reactor. Each component serves a specific purpose: to precisely manage the pressure, temperature, and chemical composition inside a chamber to dictate the properties of the material being created.
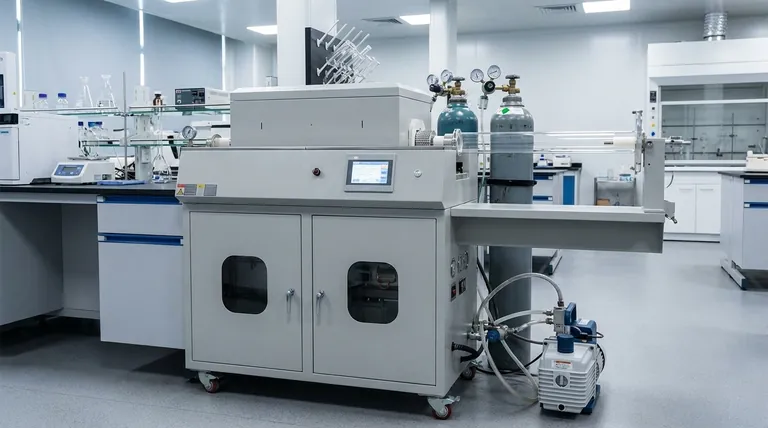

The Anatomy of a CVD System
A CVD system's configuration can vary significantly based on the specific material being deposited and the required film quality. However, nearly all systems are built around the same fundamental components.
The Reaction Chamber
This is the heart of the CVD tool. It is an enclosed vessel where the substrate is placed and the chemical reaction occurs. Chambers are typically made from materials like quartz (for high temperatures and purity) or stainless steel (for durability and vacuum integrity).
Gas Delivery System
This network of pipes, valves, and controllers is responsible for delivering precise amounts of precursor gases into the reaction chamber. The most critical component here is the Mass Flow Controller (MFC), an electronic device that measures and controls the flow rate of a specific gas, ensuring the chemical "recipe" is exact.
Substrate and Heating System
The substrate is the material upon which the thin film is grown (e.g., a silicon wafer). To drive the chemical reaction, the substrate must be heated to a specific temperature, often several hundred degrees Celsius. This is accomplished using resistive heating elements, high-intensity lamps, or RF induction coils that heat the substrate holder (susceptor).
Vacuum System
Most CVD processes are conducted at pressures well below atmospheric levels. A vacuum system, consisting of one or more pumps, removes air and other contaminants from the chamber before deposition begins. This prevents unwanted reactions and allows for precise control over the process pressure, which directly influences film quality.
Energy Source (for Enhanced CVD)
In some advanced CVD techniques, thermal energy alone isn't sufficient or desirable. Systems like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) incorporate an additional energy source, typically a Radio Frequency (RF) generator. This generator creates a plasma (an ionized gas) within the chamber, which provides the energy to break down precursor gases at much lower temperatures.
Exhaust Management System
The process does not consume all precursor gases, and the reaction creates byproducts. An exhaust system, often including a "scrubber," safely removes these unreacted and potentially toxic or flammable gases from the chamber and neutralizes them before they are vented.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice and complexity of a CVD system's components involve critical trade-offs between speed, cost, and the quality of the final film.
The Pressure Problem: APCVD vs. LPCVD
The complexity of the vacuum system is a primary differentiator. Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD) systems are simpler and faster because they don't require expensive vacuum pumps, but films are often less pure and uniform. In contrast, Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) systems produce much higher quality films, making them a standard in the semiconductor industry, but require a robust vacuum system.
The Temperature Dilemma: Thermal vs. Plasma
High temperatures can damage or alter sensitive substrates, such as plastics or previously fabricated device layers. Thermal CVD relies entirely on heat, limiting its use. Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is the solution here; its tools are more complex and expensive due to the RF plasma generation system, but they allow deposition at significantly lower temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "right" CVD tool is determined entirely by the desired outcome. The system's design is a direct reflection of the material properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and low cost: An APCVD system is often sufficient, especially for applications like protective coatings where ultimate purity is not the main concern.
- If your primary focus is high-quality, uniform films for microelectronics: An LPCVD system is the industry standard for creating critical layers like silicon nitride and polysilicon.
- If your primary focus is depositing films on temperature-sensitive substrates: A PECVD system is the necessary choice to avoid damaging the underlying material.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge research and ultimate film purity: Highly specialized systems, like Ultra-High Vacuum CVD (UHVCVD), provide the cleanest possible environment but at the highest cost and complexity.
Ultimately, the components of a CVD tool are the levers you pull to control the atomic-scale assembly of your material.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Reaction Chamber | Enclosed vessel where the chemical reaction occurs | Material (e.g., quartz for purity, steel for durability) |
| Gas Delivery System | Delivers precise amounts of precursor gases | Relies on Mass Flow Controllers (MFCs) for accuracy |
| Heating System | Heats the substrate to drive the reaction | Method (resistive, lamps, RF) depends on temperature needs |
| Vacuum System | Controls chamber pressure and purity | Differentiates APCVD (simple) from LPCVD (high-quality) |
| Energy Source (PECVD) | Creates plasma for low-temperature reactions | Adds complexity but enables deposition on sensitive materials |
| Exhaust Management | Safely removes and neutralizes reaction byproducts | Critical for handling toxic or flammable gases |
Ready to Build Your Ideal CVD System?
Choosing the right CVD tool is about aligning its components with your specific material and performance goals. At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with advanced, high-temperature furnace solutions.
Our expertise in CVD/PECVD Systems is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you need high-throughput APCVD, high-purity LPCVD, or low-temperature PECVD.
Let's engineer the perfect solution for your lab. Contact our experts today to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why are CVD tube furnace sintering systems indispensable for 2D material research and production? Unlock Atomic-Scale Precision
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab



















