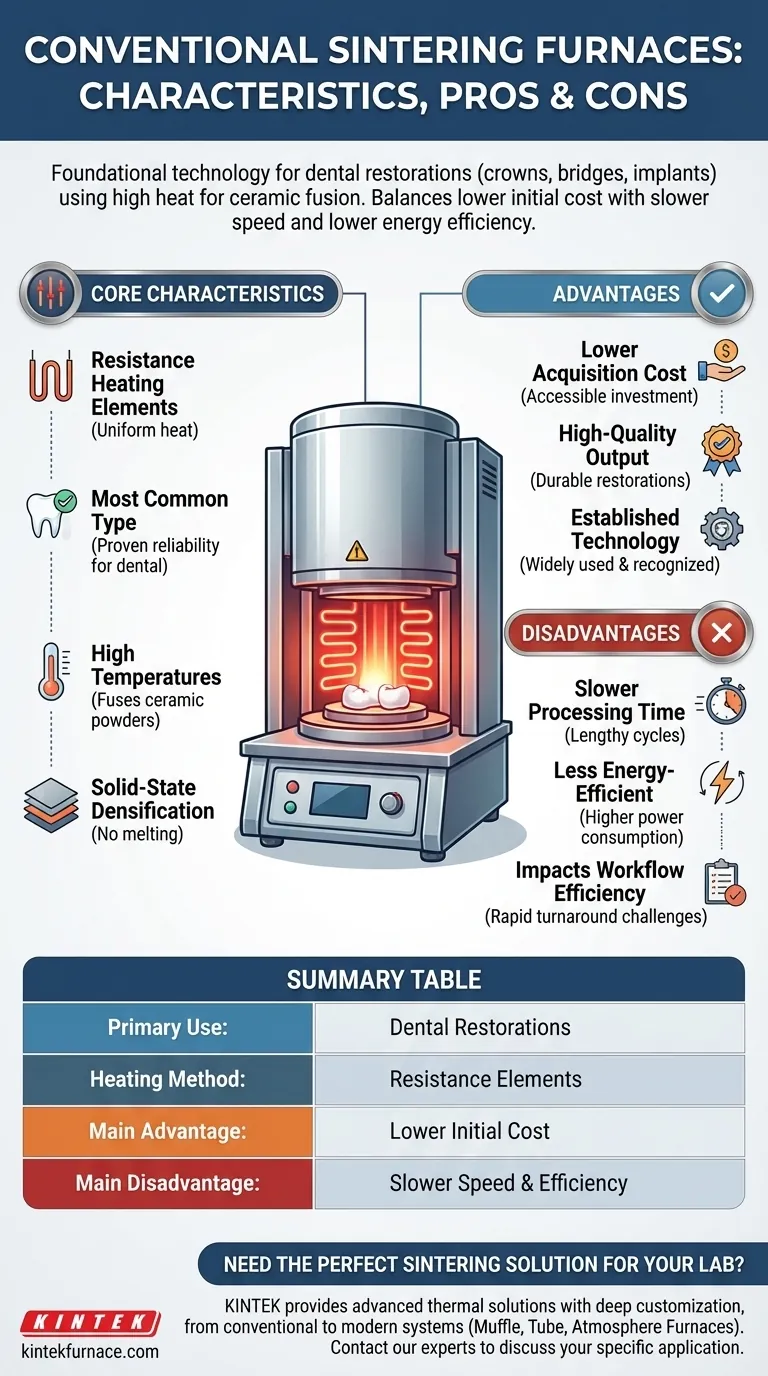
A conventional sintering furnace operates by using a heating element to raise ceramic materials to high temperatures, facilitating fusion and producing high-quality restorations. These furnaces are widely recognized for their ability to create durable dental products like crowns, bridges, and implants. While they serve as a reliable and established technology, their operational characteristics also present certain trade-offs concerning speed and energy consumption.
Conventional sintering furnaces are a foundational technology, particularly in dental applications, offering a cost-effective means to achieve high-quality ceramic fusion. Their primary draw is their lower initial expense, balanced against a slower processing speed and reduced energy efficiency compared to modern alternatives.

Understanding Conventional Sintering Furnaces
Core Characteristics
A conventional sintering furnace relies on resistance heating elements to generate the necessary temperatures. This heating mechanism ensures uniform temperature distribution within the chamber for consistent material fusion.
These furnaces are the most common type for dental restorations, indicating their widespread adoption and proven reliability in this specific field. They are essential for processes requiring high temperatures to fuse ceramic powders into solid, dense objects.
Operational Principle
The furnace works by elevating ceramic material to a high temperature. This intense heat causes the ceramic particles to bond together, or fuse, a process known as sintering.
This process results in the creation of high-quality restorations, such as crowns, bridges, and implants, by densifying the ceramic material without melting it to a liquid phase. The high temperatures are crucial for achieving the desired material properties and structural integrity.
Advantages of Conventional Sintering
Cost-Effectiveness
One of the primary benefits of conventional sintering furnaces is their lower acquisition cost. They are generally less expensive to purchase than more advanced or specialized furnace types.
This makes them an accessible option for many laboratories and practices, allowing for high-quality production without a significant capital investment. The established technology contributes to their affordability.
Disadvantages and Trade-offs
Slower Processing Time
A notable drawback of conventional sintering furnaces is their slower operational speed. The heating and cooling cycles can be lengthy.
This extended processing time can impact workflow efficiency, especially in environments requiring rapid turnaround for dental restorations. Modern alternatives often prioritize faster cycle times.
Energy Efficiency Concerns
Conventional sintering furnaces are typically less energy-efficient. Their design and heating mechanisms may consume more power to achieve and maintain target temperatures.
This can translate to higher operational costs over time, particularly for continuous use. More advanced furnaces often incorporate features designed for optimized energy consumption.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a sintering furnace involves balancing initial investment with long-term operational efficiency and specific production needs.
- If your primary focus is initial budget and proven technology for standard dental restorations: A conventional sintering furnace is a strong, cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput and energy savings, and you have a higher budget: Explore more advanced furnace technologies that offer faster cycles and better energy efficiency.
Ultimately, the best furnace aligns with your specific application requirements, volume needs, and financial constraints.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | High-quality dental restorations (crowns, bridges, implants) |
| Heating Method | Resistance heating elements for uniform temperature |
| Main Advantage | Lower initial acquisition cost |
| Main Disadvantage | Slower processing speed and lower energy efficiency |
Need a sintering furnace that perfectly fits your lab's workflow and budget?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced thermal solutions. Whether you prioritize the proven, cost-effective performance of a conventional furnace or require the speed and efficiency of a modern system, our diverse line—including Muffle, Tube, and Atmosphere Furnaces—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique requirements for dental restorations.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the ideal sintering solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the working principle of a dental furnace? Mastering Precision Sintering & Firing for Crowns
- Why is using a universal setting for all materials in a dental furnace a mistake? Master Precision Sintering for Perfect Restorations
- Why is accurate temperature control important in dental furnaces? Ensure Perfect Restorations Every Time
- How often should dental furnaces be calibrated? Ensure Precision for Perfect Restorations
- What role does temperature range and accuracy play in dental furnace performance? Ensure Precision for Superior Dental Restorations



















