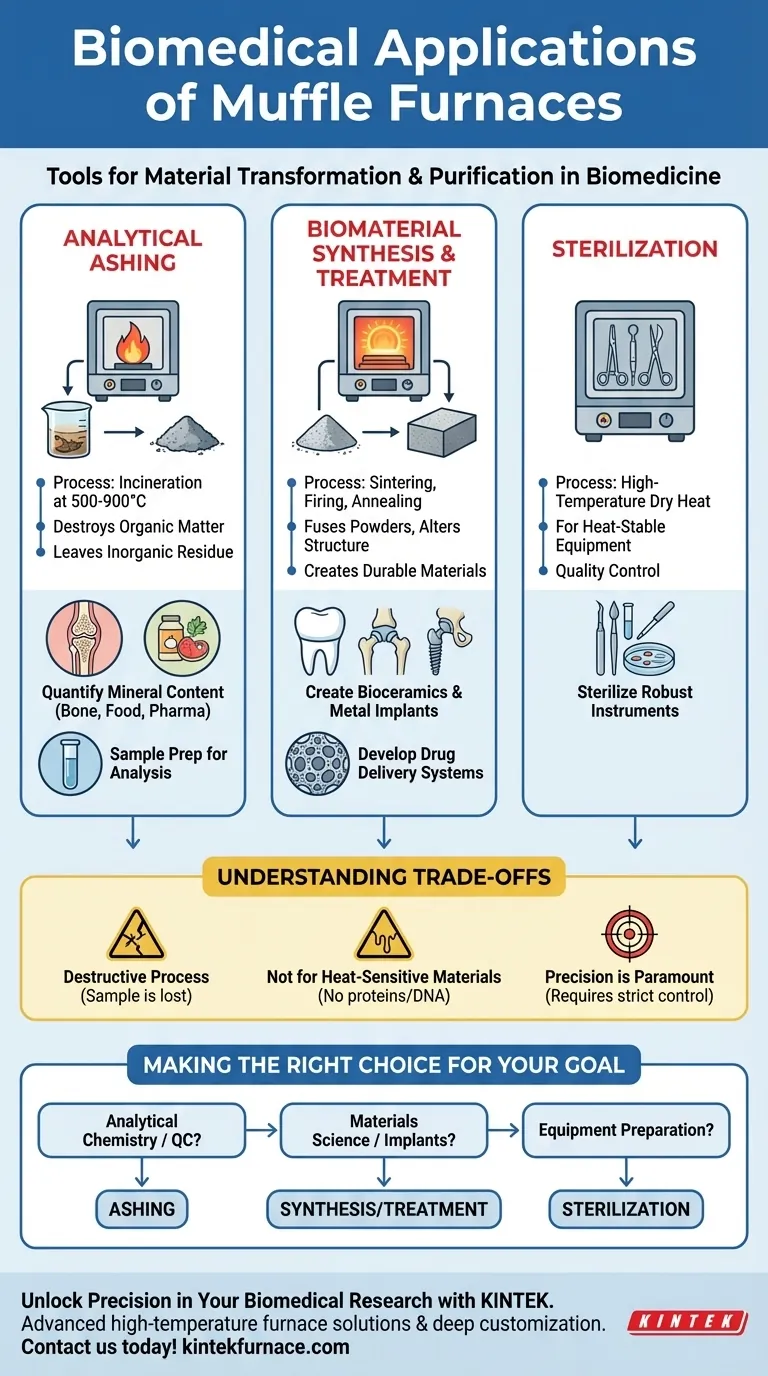
In the biomedical and pharmaceutical fields, muffle furnaces serve three primary functions: analyzing the inorganic composition of a sample through ashing, synthesizing and treating high-temperature biomaterials like ceramics and metal implants, and sterilizing heat-stable equipment. They are essential tools for both quality control and the development of new medical technologies.
A muffle furnace is not simply an oven; it is a tool for material transformation and purification. Its core value in biomedicine is its ability to either strip away organic matter to reveal the inorganic components beneath or to forge new, durable materials under precisely controlled high temperatures.

The Core Principle: Analytical Ashing
A primary biomedical application of the muffle furnace is a process called ashing or incineration. This is a foundational technique in analytical chemistry.
What is Ashing?
Ashing involves heating a biological or organic sample at extremely high temperatures, typically between 500°C and 900°C. This intense heat completely combusts and vaporizes the organic components—like proteins, fats, and carbohydrates—leaving behind only the non-combustible, inorganic residue known as ash.
Application: Quantifying Mineral Content
This resulting ash consists of the minerals and metallic elements that were present in the original sample. By weighing the sample before and after ashing, researchers can precisely determine the total inorganic content.
This is critical for analyzing the mineral composition of bone tissue, testing foods for nutritional value, or checking pharmaceutical products for trace metal contaminants.
Application: Sample Preparation for Analysis
Ashing also serves as a crucial sample preparation step. Once the interfering organic matrix is removed, the remaining ash can be dissolved and analyzed using more sensitive techniques, such as atomic absorption spectroscopy, to identify and quantify specific elements.
Synthesizing and Treating Advanced Biomaterials
Muffle furnaces provide the extreme, controlled heat necessary to create and refine materials used in the human body.
Creating Bioceramics
Processes like sintering and firing use high temperatures to fuse powdered materials into a solid, durable mass. This is fundamental to manufacturing bioceramics for dental crowns, synthetic bone grafts, and prosthetic implants that must be strong and biocompatible.
Heat Treating Metal Implants
Medical implants made from materials like stainless steel or titanium alloys are often heat-treated in a muffle furnace. Processes like annealing alter the metal's internal structure, improving its strength, flexibility, and resistance to fatigue, thereby extending the life of the implant.
Developing Drug Delivery Systems
Researchers use muffle furnaces in a process called calcination to create porous material structures. These structures can be loaded with a drug and designed to release it at a controlled rate within the body, representing an advanced form of drug delivery.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a specialized tool with clear limitations that dictate its proper use.
It Is a Destructive Process
The primary analytical method, ashing, is inherently destructive. The original organic sample is completely destroyed and cannot be recovered for other types of analysis.
Not for Heat-Sensitive Materials
A muffle furnace is only suitable for materials that can withstand extreme temperatures. It cannot be used to sterilize plastics, complex electronics, or biological samples like proteins or DNA that you intend to study afterward. For those, an autoclave is the appropriate tool.
Precision is Paramount
The results of ashing or material synthesis are highly dependent on precise temperature control, ramp rates, and duration. Inconsistent parameters will lead to unreliable and non-repeatable data, making quality control and calibration essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge effectively, align the furnace's capabilities with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is analytical chemistry or quality control: Use the furnace for ashing to determine the mineral content of biological samples or to test for inorganic impurities in pharmaceuticals.
- If your primary focus is materials science or implant development: Use the furnace for sintering, calcination, and annealing to create and strengthen bioceramics and metal alloys.
- If your primary focus is equipment preparation: Use the furnace only for the high-temperature dry-heat sterilization of simple, robust metal instruments.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace provides an essential bridge between the organic and inorganic worlds, enabling you to either analyze what matter is made of or forge it into something new.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Ashing | Incineration at 500-900°C | Quantify inorganic content in samples like bone or pharmaceuticals |
| Biomaterial Synthesis | Sintering, calcination, annealing | Create durable bioceramics, metal implants, and drug delivery systems |
| Sterilization | High-temperature heating | Sterilize heat-stable equipment for quality control |
Unlock Precision in Your Biomedical Research with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements in ashing, biomaterial synthesis, and sterilization. Enhance your lab's efficiency and accuracy—contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can support your biomedical innovations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















