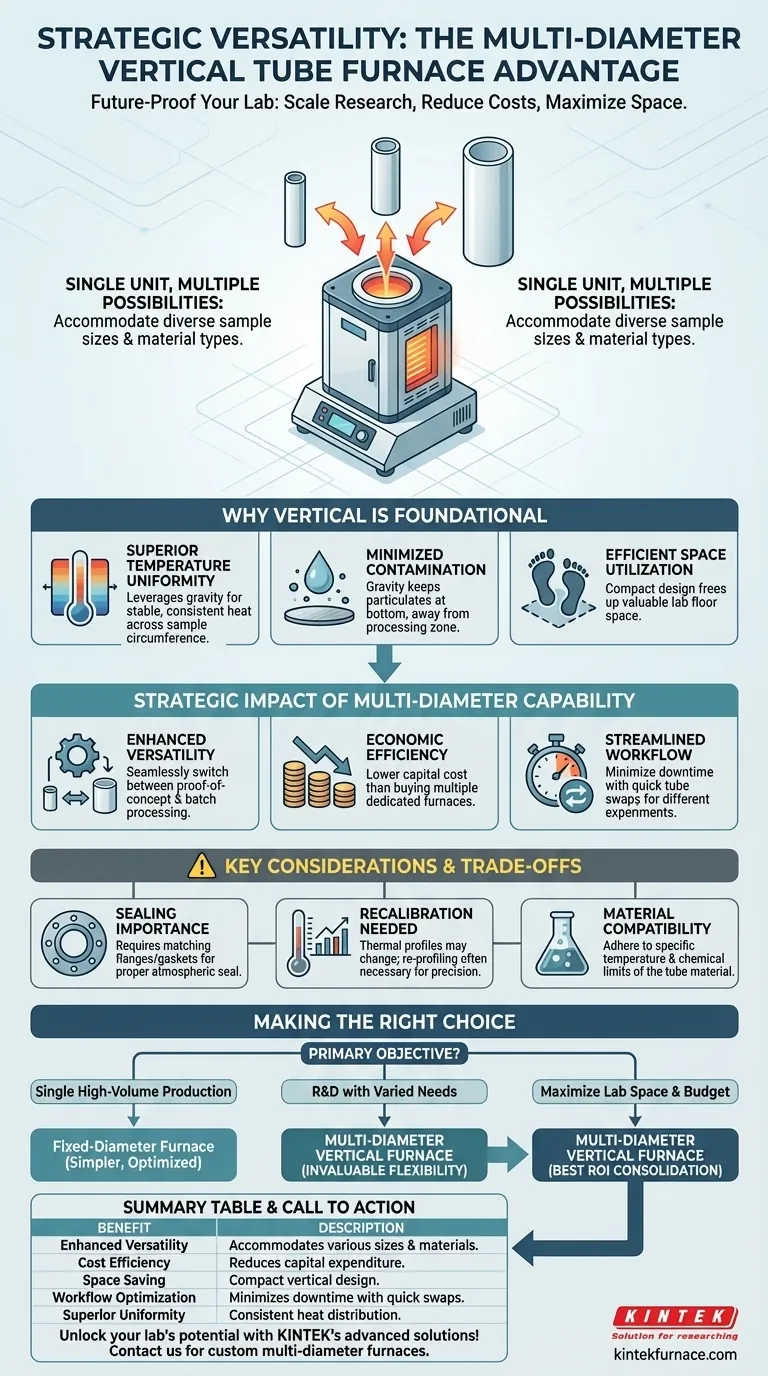
The primary benefit is strategic versatility. Opting for a vertical tube furnace with multiple diameter tube options allows a single unit to accommodate a wide range of sample sizes and material types. This flexibility fundamentally reduces capital costs and saves valuable lab space by removing the need for multiple, dedicated furnaces for different experimental scales.
While the immediate advantage is accommodating different sample sizes, the true value lies in future-proofing your laboratory's capabilities. This feature transforms a specialized instrument into a versatile workhorse, maximizing its long-term utility and return on investment.

Why the Vertical Furnace Design Is Foundational
Before exploring the benefits of multiple tubes, it's crucial to understand why the vertical orientation itself is often the superior choice for high-precision thermal processing. The design inherently solves problems common in older, horizontal systems.
Superior Temperature Uniformity
A vertical setup leverages gravity and natural convection to promote a highly stable and uniform thermal environment. This is critical for processes like crystal growth or wafer processing, where even minor temperature gradients can compromise results.
Unlike horizontal furnaces, where samples can be subject to sagging or uneven gas flow, the vertical orientation ensures consistent heat exposure around the entire circumference of the sample.
Minimized Contamination
The vertical design significantly reduces particle generation and contamination. Gravity helps keep loose particulates at the bottom of the chamber, away from the sample processing zone.
This contrasts with horizontal furnaces, where particles can easily fall onto the surface of wafers or other samples, leading to defects.
Efficient Space Utilization
Vertical tube furnaces have a much smaller footprint than their horizontal counterparts. For laboratories where floor space is a premium, this compact design allows for more efficient use of the available area without sacrificing processing capacity.
The Strategic Impact of Multi-Diameter Capability
Adding interchangeable tubes to a vertical furnace multiplies its intrinsic benefits, turning it from a single-task instrument into a multi-purpose platform.
Enhancing Experimental Versatility
The core advantage is the ability to switch between tube diameters. A researcher can use a small-diameter tube for initial proof-of-concept tests on small material quantities and then scale up to a larger-diameter tube for batch processing, all within the same furnace.
This adaptability supports a dynamic research environment where experimental parameters and material volumes frequently change.
Driving Economic Efficiency
Purchasing a single furnace with multiple tube adapters is far more cost-effective than buying several furnaces of different sizes. This reduces the initial capital expenditure and lowers ongoing operational costs related to power, maintenance, and space.
Streamlining Laboratory Workflow
This feature minimizes downtime between different types of experiments. Instead of moving a process to an entirely different furnace, technicians can simply swap the process tube and its corresponding seals. This simplifies scheduling and maximizes the productivity of both the equipment and personnel.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While highly advantageous, the flexibility of multiple tube diameters requires attention to certain operational details to ensure accuracy and safety.
The Importance of Sealing
Each tube diameter requires a corresponding set of flanges and gaskets to ensure a proper atmospheric seal. Mismatched components can lead to leaks, compromising experiments that require a vacuum or a specific inert gas environment.
Recalibration of Thermal Profiles
The thermal characteristics of the heating chamber can change with different tube sizes. A smaller tube may heat faster or reach a different peak temperature in the same zone compared to a larger tube due to variations in radiative and convective heat transfer.
For high-precision work, it may be necessary to re-profile the temperature for each tube configuration to guarantee process repeatability.
Material Compatibility
The versatility of the furnace does not change the limitations of the tube material itself. Whether using quartz, alumina, or a metal alloy, you must still operate within the material's specific temperature limits and chemical compatibility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if this feature is right for you, consider the primary objective of your thermal processing work.
- If your primary focus is a single, high-volume production process: A fixed-diameter furnace optimized specifically for that task may be more cost-effective and simpler to operate.
- If your primary focus is research and development with varied needs: The flexibility of multiple tube options is invaluable, allowing you to seamlessly transition from small-scale discovery to larger-scale validation.
- If your primary focus is maximizing lab space and budget: A single furnace with interchangeable tubes offers the best return on investment by consolidating the function of several machines into one.
Ultimately, choosing a system with multi-diameter capability is a strategic investment in the adaptability and efficiency of your entire laboratory.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Versatility | Accommodates various sample sizes and materials with interchangeable tubes. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces capital expenditure by eliminating need for multiple furnaces. |
| Space Saving | Compact vertical design maximizes lab space utilization. |
| Workflow Optimization | Minimizes downtime with quick tube swaps for different experiments. |
| Superior Temperature Uniformity | Vertical orientation ensures consistent heat distribution for precise results. |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with versatile options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and ROI. Contact us today to discuss how our multi-diameter vertical tube furnaces can transform your thermal processing workflows!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















