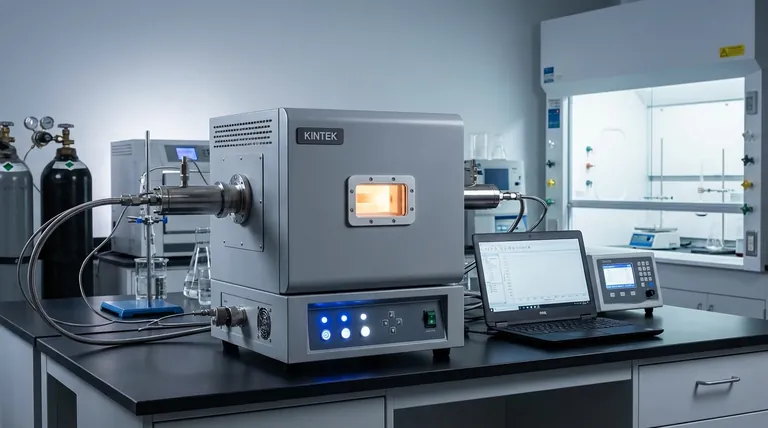
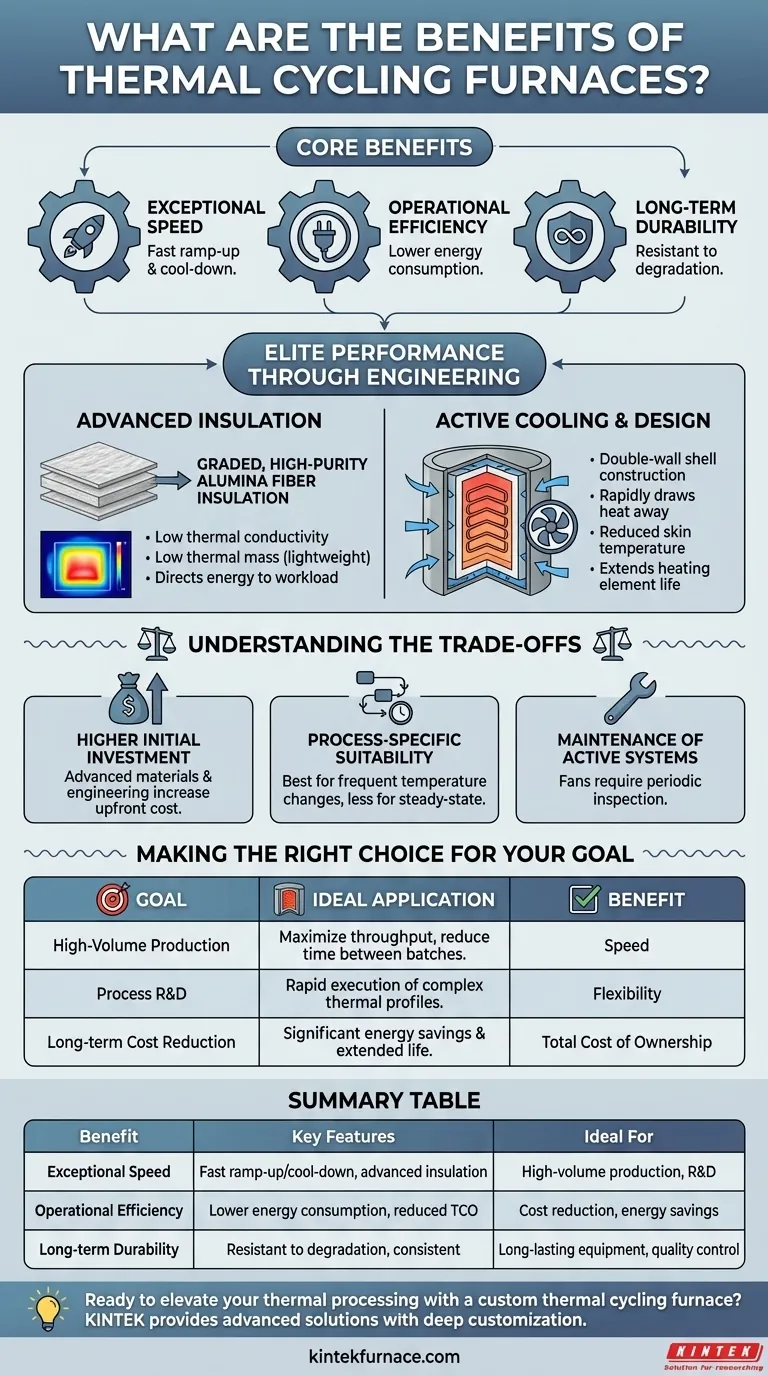
At their core, thermal cycling furnaces provide three primary benefits: exceptional speed, operational efficiency, and long-term durability. They achieve this by combining advanced, lightweight insulation with sophisticated cooling systems, allowing for extraordinarily fast ramp-up and cool-down times compared to traditional furnace designs.
The key advantage of a thermal cycling furnace is not just its speed. It is the integration of rapid processing with lower energy consumption and greater equipment longevity, creating a significant impact on both production throughput and total cost of ownership.

How Thermal Cycling Furnaces Achieve Elite Performance
The unique benefits of these furnaces stem directly from their specialized engineering and material choices. Each component is designed to minimize thermal inertia and maximize control.
The Central Role of Advanced Insulation
The performance of a thermal cycling furnace begins with its insulation package. These furnaces utilize a graded, high-purity alumina fiber insulation.
This material is chosen for two critical properties: low thermal conductivity and low thermal mass (light weight). Low conductivity prevents heat from escaping, while low mass means very little energy is wasted heating the furnace walls themselves. The result is that nearly all energy is directed to the workload, enabling rapid temperature changes.
Engineered for Durability and Consistency
The alumina fiber insulation is also highly resistant to hot spotting and degradation over time. This ensures that the furnace delivers consistent, uniform heating profiles cycle after cycle, which is critical for process repeatability and quality control.
Active Cooling and Structural Design
Rapid heating is only half of the equation. To achieve fast cycling, a furnace must also cool down quickly. These furnaces feature a double-wall shell construction that allows for active fan cooling.
This design forces air between the inner and outer walls, rapidly drawing heat away from the furnace chamber. This not only enables fast cool-down but also keeps the outer shell at a reduced skin temperature, improving operator safety and extending the life of the internal heating elements by preventing overheating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, thermal cycling furnaces are a specialized tool. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Initial Investment
The advanced materials and engineering—such as high-purity fiber insulation and double-wall construction—often result in a higher upfront purchase price compared to standard, single-wall brick or fiber furnaces.
Process-Specific Suitability
The primary benefit is speed. If your process involves very long, steady-state temperature holds with infrequent cycles, the advantages of rapid cycling may be less significant. These furnaces deliver maximum value in applications requiring frequent changes in temperature.
Maintenance of Active Systems
The inclusion of cooling fans introduces an active mechanical system. Like any such component, these fans require periodic inspection and maintenance to ensure reliable operation, adding a step not present in simpler, passively cooled furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace requires aligning its capabilities with your primary operational objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: A thermal cycling furnace is ideal for maximizing throughput by drastically reducing the time between batches.
- If your primary focus is process research and development: The ability to rapidly execute complex, multi-step thermal profiles makes these furnaces exceptionally flexible for testing and material science.
- If your primary focus is long-term cost reduction: The significant energy savings per cycle and extended component life can deliver a lower total cost of ownership that justifies the initial investment.
Ultimately, choosing a thermal cycling furnace is a strategic decision to enhance the speed, efficiency, and control of your thermal processing operations.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Features | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Exceptional Speed | Fast ramp-up and cool-down times, advanced insulation | High-volume production, R&D |
| Operational Efficiency | Lower energy consumption, reduced total cost of ownership | Cost reduction, energy savings |
| Long-term Durability | Resistant to degradation, consistent performance | Long-lasting equipment, quality control |
Ready to elevate your thermal processing with a custom thermal cycling furnace?
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can boost your speed, efficiency, and durability—let's optimize your operations together!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the work process of a quartz tube furnace typically proceed? Master Precision Heating for Advanced Materials
- What is the difference between an alumina tube furnace and a quartz tube furnace? Choose the Right Tube Furnace for Your Lab
- What technical requirements affect the external thermal strength of furnace tubes? Optimize for High-Temp Performance
- What is a quartz tube furnace and what is its primary use? Essential for Controlled High-Temp Processing
- What factors should be considered when purchasing a quartz tube furnace? Ensure Reliable High-Temperature Processing



















