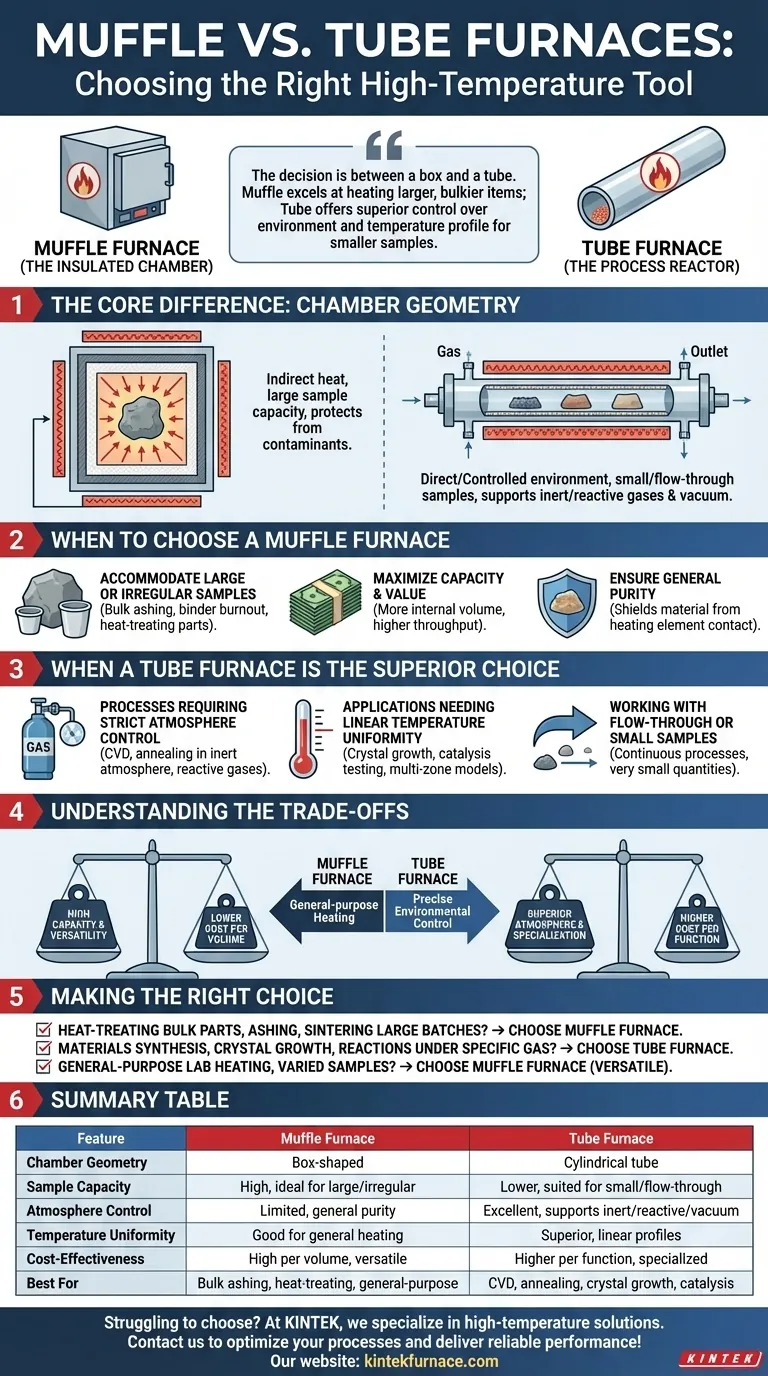
In essence, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven, prized for its larger sample capacity and cost-effectiveness, making it a versatile workhorse for general-purpose heating. In contrast, a tube furnace is a specialized instrument designed for processes requiring precise atmospheric control or specific temperature gradients along a linear path. Choosing between them depends entirely on the geometry and atmospheric requirements of your application.
The decision between a muffle and a tube furnace is a choice between a box and a tube. A muffle furnace's box-like chamber excels at heating larger, bulkier items, while a tube furnace's cylindrical design offers superior control over the gaseous environment and temperature profile for smaller or flowing samples.

The Core Difference: Chamber Geometry
The distinct advantages of each furnace type stem directly from their fundamental design. Understanding this difference is the key to selecting the right tool.
The Muffle Furnace: The Insulated Chamber
A muffle furnace is built around a box-shaped chamber made of a "muffle"—an insulating material that separates the sample from the heating elements.
This design provides indirect heat, protecting samples from any contaminants produced by combustion or direct element radiation. It functions much like a high-performance oven.
The Tube Furnace: The Process Reactor
A tube furnace heats a cylindrical tube, which contains the sample. The heating elements are positioned around the exterior of this tube.
This geometry is ideal for creating a highly controlled environment. The tube can be easily sealed, purged with inert or reactive gases, or even placed under a vacuum, making it a small-scale process reactor.
When to Choose a Muffle Furnace
A muffle furnace is the superior choice for applications where capacity, sample shape, and general-purpose heating are the primary concerns.
Accommodating Large or Irregular Samples
The open, box-like chamber is perfect for heating larger components, multiple crucibles at once, or irregularly shaped objects that would not fit within a narrow tube. This makes it ideal for bulk ashing, binder burnout, or heat-treating parts.
Maximizing Capacity and Value
For a given price point, a muffle furnace will almost always offer significantly more internal volume than a tube furnace. If your goal is simply high-temperature processing of many samples, the muffle furnace provides better throughput and value.
Ensuring General Purity
The muffle's design inherently shields the material from direct contact with the heating elements. This is critical for applications like ashing, where contamination from heating elements could skew analytical results.
When a Tube Furnace is the Superior Choice
A tube furnace excels in specialized laboratory applications where the environment and temperature profile are just as important as the heat itself.
Processes Requiring Strict Atmosphere Control
The ability to seal and purge the work tube is the defining advantage of this furnace. It is essential for materials science applications like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), annealing in an inert atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen), or reactions with specific gases.
Applications Needing Linear Temperature Uniformity
Multi-zone tube furnaces, often with three distinct heating zones, offer exceptional temperature uniformity along the length of the tube. This is critical for processes like crystal growth or catalysis testing, where a consistent temperature profile is required over a specific distance.
Working with Flow-Through or Small Samples
The tubular design is naturally suited for continuous processes where gases flow over a stationary sample or where samples are pushed through the heated zone. It is also ideal for very small sample quantities where controlling the atmosphere is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither furnace is universally better; they are simply different tools for different jobs. The decision involves clear trade-offs.
Capacity vs. Atmosphere
A muffle furnace gives you high capacity at the expense of precise atmospheric control. A tube furnace offers superior atmospheric control but for much smaller sample volumes.
Versatility vs. Specialization
A muffle furnace is a versatile workhorse for a wide range of heating tasks. A tube furnace is a specialized instrument for processes that demand environmental or linear thermal precision.
Cost per Volume vs. Cost per Function
A muffle furnace is less expensive per unit of internal volume. However, if your process absolutely requires atmospheric control, the tube furnace is the only functional choice, making its higher cost-per-volume irrelevant.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct furnace, focus on the non-negotiable requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating bulk parts, ashing, or sintering large batches: Choose a muffle furnace for its superior capacity and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is materials synthesis, crystal growth, or reactions under a specific gas: Choose a tube furnace for its unmatched atmospheric control and linear temperature profile.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab heating with varied sample sizes and shapes: A muffle furnace is often the more versatile and economical starting point.
Ultimately, aligning the furnace's fundamental design—a box or a tube—with your specific process requirements is the key to a successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Chamber Geometry | Box-shaped | Cylindrical tube |
| Sample Capacity | High, ideal for large/irregular samples | Lower, suited for small/flow-through samples |
| Atmosphere Control | Limited, general purity | Excellent, supports inert/reactive gases and vacuum |
| Temperature Uniformity | Good for general heating | Superior, with linear profiles in multi-zone models |
| Cost-Effectiveness | High per volume, versatile | Higher per function, specialized |
| Best For | Bulk ashing, heat-treating, general-purpose | CVD, annealing, crystal growth, catalysis |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-temperature solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer advanced muffle and tube furnaces, vacuum & atmosphere furnaces, and CVD/PECVD systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your processes and deliver reliable performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















