In high-temperature industrial processes, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) heating elements are the definitive choice for applications requiring extreme heat in an oxidizing atmosphere. They are used extensively in the production of glass, ceramics, and semiconductors, as well as in metallurgical heat treatments and advanced materials research, where reliable performance above 1600°C is essential.
The decision to use MoSi₂ heating elements is driven by a need for exceptional temperature stability and longevity in oxygen-rich environments. While other elements may produce heat, MoSi₂ elements are engineered to survive and thrive in conditions that would destroy most alternatives.

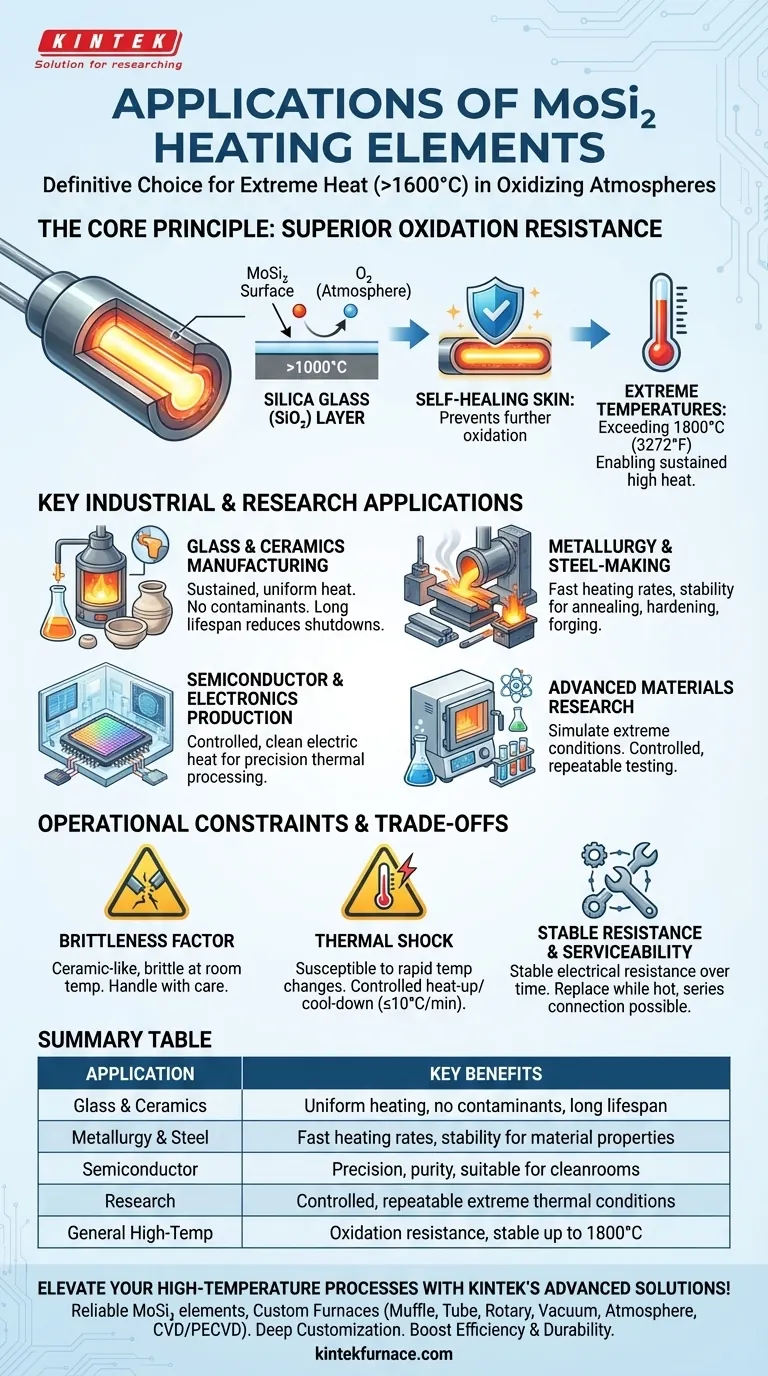
The Core Principle: Superior Oxidation Resistance
The fundamental advantage of a MoSi₂ element is its behavior at high temperatures. Unlike many materials that degrade or burn away, it forms a protective outer layer.
How MoSi₂ Protects Itself
At temperatures above 1000°C, the element's surface reacts with oxygen in the atmosphere to form a thin, non-porous layer of silica glass (SiO₂).
This self-healing "skin" acts as a barrier, preventing further oxidation of the underlying material and allowing the element to operate reliably for extended periods.
Enabling Extreme Process Temperatures
This robust oxidation resistance is what allows MoSi₂ elements to achieve the highest operating temperatures of any metallic-based heating element, often exceeding 1800°C (3272°F).
This capability is not just about reaching a peak temperature; it's about sustaining it consistently, which is critical for industrial production and sensitive research.
Key Industrial and Research Applications
The unique properties of MoSi₂ make it indispensable in several demanding fields. Its use is a direct result of its ability to provide stable, clean, and reliable high-temperature heat.
Glass and Ceramics Manufacturing
The production of high-purity glass and the sintering of advanced ceramics require sustained, uniform heat. MoSi₂ elements provide this without introducing contaminants that could result from gas-fired heating.
Their long lifespan also reduces the frequency of furnace shutdowns for element replacement, improving production efficiency.
Metallurgy and Steel-Making
In metallurgy, MoSi₂ elements are used in high-temperature furnaces for processes like annealing, hardening, and forging. Their fast heating rates and stability are crucial for achieving specific material properties in metals and alloys.
Semiconductor and Electronics Production
The manufacturing of electronic components, from crystals to semiconductor wafers, often involves thermal processing steps that demand precision and purity. MoSi₂ elements provide a controlled, electric heat source suitable for these cleanroom environments.
Advanced Materials Research
For scientists and engineers in laboratory settings, MoSi₂-equipped furnaces are essential tools. They enable the testing and development of new materials by simulating extreme thermal conditions in a controlled, repeatable manner.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Operational Constraints
While powerful, MoSi₂ elements are not universally applicable. Understanding their limitations is critical for successful implementation and avoiding costly failures.
The Brittleness Factor
MoSi₂ elements are ceramic-like at room temperature and are very brittle. Care must be taken during shipping, handling, and installation to avoid fractures.
Managing Thermal Shock
Despite being suitable for thermal cycling, the material is susceptible to thermal shock from excessively rapid temperature changes. A controlled heat-up and cool-down rate, often advised not to exceed 10°C per minute, is crucial to prevent cracking.
Stable Resistance and Serviceability
A key operational advantage is their stable electrical resistance over time. This unique feature allows new elements to be connected in series with older ones without compromising performance, simplifying maintenance.
Furthermore, elements can often be replaced while a furnace is still hot, dramatically reducing process downtime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating element depends entirely on your specific process goals and operational environment.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures in an air furnace: MoSi₂ elements are the industry standard due to their unparalleled oxidation resistance and stability.
- If your primary focus is process uptime and longevity: The long lifespan and ability to replace elements while hot make MoSi₂ a superior choice for minimizing production downtime.
- If your process involves frequent, aggressive temperature shocks or rough handling: You must account for the brittle nature of MoSi₂ by implementing controlled protocols or considering more mechanically robust (but lower-temperature) alternatives.
By understanding both their exceptional capabilities and their specific limitations, you can effectively leverage MoSi₂ elements to achieve your most demanding thermal processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Glass & Ceramics Manufacturing | Uniform heating, no contaminants, long lifespan |
| Metallurgy & Steel-Making | Fast heating rates, stability for material properties |
| Semiconductor Production | Precision, purity, suitable for cleanroom environments |
| Advanced Materials Research | Controlled, repeatable extreme thermal conditions |
| General High-Temp Processes | Oxidation resistance, stable up to 1800°C |
Elevate your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable MoSi2 heating elements and custom high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, boosting efficiency and durability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your industrial or research goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance



















