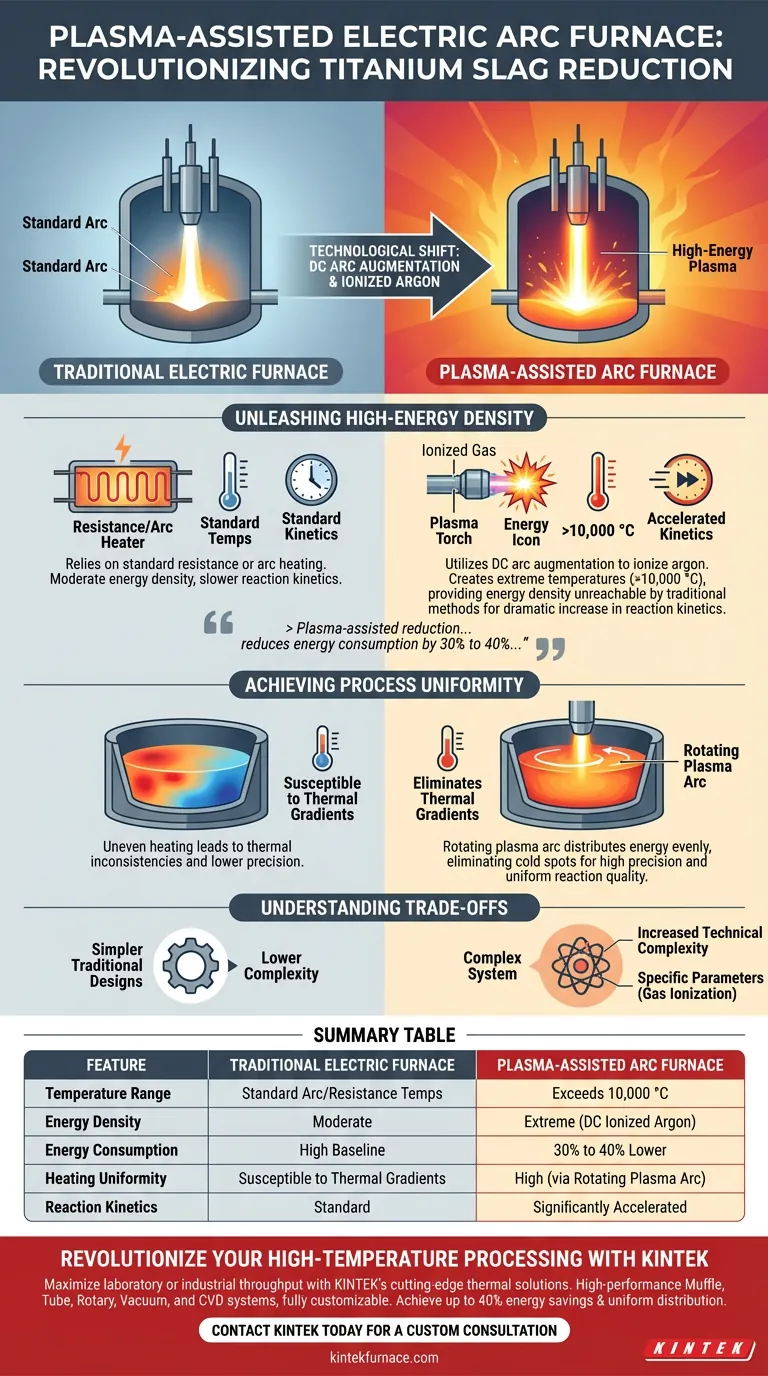
The integration of plasma technology into electric arc furnaces fundamentally transforms the carbothermic reduction process. By utilizing Direct Current (DC) arc augmentation to ionize argon gas, plasma-assisted systems generate temperatures exceeding 10,000 °C with extreme energy density. This technological shift delivers significantly faster reaction kinetics and reduced energy consumption compared to traditional electric furnace setups.
Plasma-assisted reduction represents a shift from simple heating to high-precision energy management, capable of reducing energy consumption by 30% to 40% while eliminating the thermal inconsistencies that plague traditional methods.
Unleashing High-Energy Density
The Role of Ionized Argon
Traditional electric furnaces rely on standard resistance or arc heating. Plasma-assisted units, however, utilize DC arc augmentation to ionize argon gas.
Extreme Temperature Generation
This ionization process creates a high-temperature plasma state. The system reaches temperatures exceeding 10,000 °C, providing an energy density that traditional furnaces cannot achieve.
Accelerated Kinetics
The immediate result of this energy density is a dramatic increase in reaction kinetics. The reduction process for titanium-bearing slag occurs significantly faster, optimizing throughput.
Achieving Process Uniformity
The Rotating Plasma Arc
A common challenge in traditional smelting is uneven heating. Plasma-assisted equipment addresses this by employing a rotating plasma arc mechanism.
Eliminating Thermal Gradients
This rotation ensures the energy is distributed evenly across the melt pool. It effectively eliminates thermal gradients, ensuring the entire batch reaches the necessary reaction temperature simultaneously.
Precision Control
With the elimination of cold spots and thermal variance, operators achieve much higher precision in reaction control. This is critical for maintaining the quality of complex titanium-bearing materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
System Complexity
While the reference highlights performance gains, the technology introduces new variables. Utilizing argon gas and DC arc augmentation increases the technical complexity of the furnace system compared to simpler traditional designs.
Operational Requirements
The shift to plasma-assisted reduction moves the operation away from standard thermal processing. It requires adherence to specific parameters, such as gas ionization management, to maintain the reported efficiency gains.
Assessing the Value for Your Operation
For metallurgists and plant managers evaluating this technology, the decision relies on your specific operational bottlenecks.
- If your primary focus is reducing operational expenditure: The capability to reduce energy consumption by 30% to 40% offers a substantial reduction in long-term utility costs.
- If your primary focus is reaction quality and consistency: The rotating arc's ability to eliminate thermal gradients provides the uniform environment required for high-specification output.
Adopting plasma-assisted reduction allows you to leverage extreme temperatures and precise motion to maximize the efficiency of the carbothermic process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Traditional Electric Furnace | Plasma-Assisted Arc Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Standard Arc/Resistance Temps | Exceeds 10,000 °C |
| Energy Density | Moderate | Extreme (DC Ionized Argon) |
| Energy Consumption | High Baseline | 30% to 40% Lower |
| Heating Uniformity | Susceptible to Thermal Gradients | High (via Rotating Plasma Arc) |
| Reaction Kinetics | Standard | Significantly Accelerated |
Revolutionize Your High-Temperature Processing with KINTEK
Maximize your laboratory or industrial throughput with KINTEK’s cutting-edge thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet the rigorous demands of your carbothermic reduction and material synthesis projects.
Our advanced furnace technology ensures uniform energy distribution and extreme temperature control, helping you achieve up to 40% energy savings while eliminating thermal gradients. Whether you are processing titanium-bearing slag or developing new alloys, our technical team is ready to design a system tailored to your unique specifications.
Ready to upgrade your thermal capabilities? Contact KINTEK today for a custom consultation!
Visual Guide
References
- C. X. Li, Yue Long. Advances in Integrated Extraction of Valuable Components from Ti-Bearing Slag. DOI: 10.3390/met15101080
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of benchtop SPS/FAST for titanium R&D? Accelerate Your Microstructural Engineering
- Why is Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) preferred for Ba0.95La0.05FeO3-δ ceramics? Achieve High Density Fast
- How does Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) offer technical advantages over traditional sintering? Achieve Rapid Densification
- What are the advantages of industrial SPS vs traditional sintering for SiC? Superior Density and Fine-Grain Structure
- How does a Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) system compare to traditional furnaces for Al2O3-TiC ceramics?



















