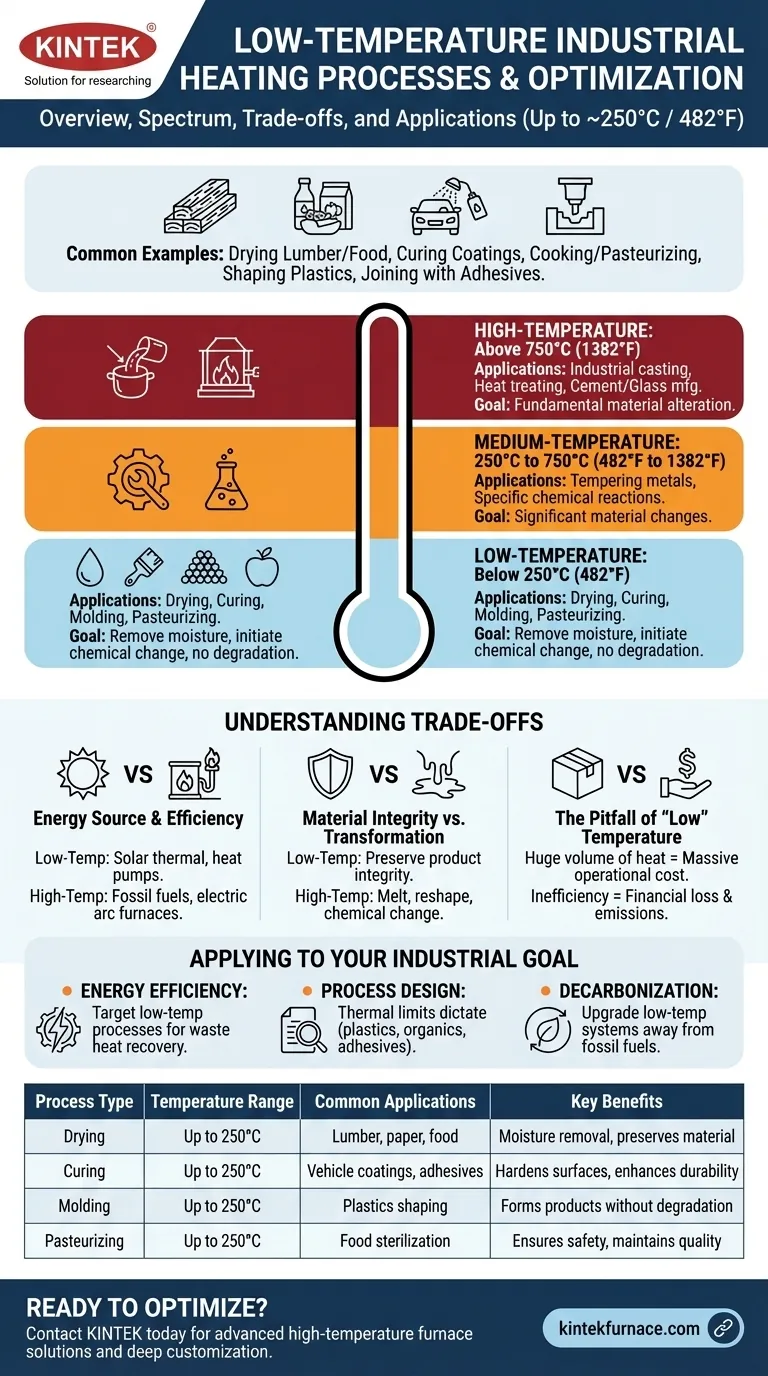
In industrial settings, low-temperature heating processes are those operating up to approximately 250°C (482°F). Common examples include drying lumber or food products, curing coatings on vehicles, cooking and pasteurizing, shaping plastics, and joining materials with adhesives. These processes form the backbone of manufacturing for many consumer and industrial goods.
The distinction between low, medium, and high-temperature heat is not just academic. It fundamentally dictates the required energy sources, the potential for energy efficiency, and the types of materials that can be processed.
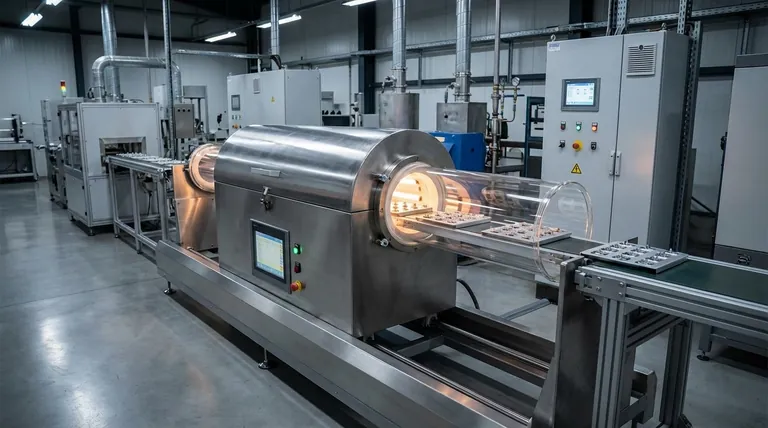

The Industrial Temperature Spectrum
To understand low-temperature applications, it's essential to see where they fit within the broader context of industrial heat. Processes are typically segmented into three distinct tiers.
Low-Temperature: Below 250°C (482°F)
This range is defined by processes that often involve removing moisture or initiating a chemical change without degrading the underlying material.
The primary applications are preparing, finishing, and assembling. This includes drying paper, curing paint, molding plastics, and sterilizing food products.
Medium-Temperature: 250°C to 750°C (482°F to 1382°F)
This intermediate range serves as a bridge between finishing processes and fundamental material transformation.
Applications in this tier often involve more significant changes to materials, such as tempering certain metals or initiating specific chemical reactions that require more energy than low-temperature processes.
High-Temperature: Above 750°C (1382°F)
High-temperature heat is used to fundamentally alter or create materials. The energy intensity here is an order of magnitude greater.
This category includes processes like industrial casting and forging of metals, heat treating steel to achieve specific hardness, and manufacturing materials like cement and glass.
Understanding the Implications and Trade-offs
Choosing a process temperature is rarely arbitrary. It's dictated by material science, energy costs, and desired outcomes, each with critical trade-offs.
Energy Source and Efficiency
Low-temperature heat is unique because it can be supplied by a wider, often more efficient, range of energy sources. This includes solar thermal systems, geothermal heat, and high-efficiency industrial heat pumps.
In contrast, high-temperature processes almost always rely on the direct combustion of fossil fuels or electric arc furnaces, which are far more energy-intensive and costly.
Material Integrity vs. Transformation
The primary goal of low-temperature heat is often to preserve the integrity of the product. For example, food is cooked to be safe and palatable, but not incinerated. A car's paint is cured to be hard and durable, but the underlying metal must not be warped.
High-temperature processes, conversely, are entirely about transformation. The goal is to melt, reshape, or fundamentally change the chemical structure of the raw material itself.
The Pitfall of "Low" Temperature
The term "low temperature" can be misleading. While the temperature per unit is low, the sheer volume of heat required in large-scale manufacturing represents a massive operational cost.
Inefficiency in these systems—through poor insulation or a lack of waste heat recovery—is a significant source of financial loss and carbon emissions for many industries.
Applying This to Your Industrial Goal
Your operational focus will determine how you approach the challenge of industrial heat.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Target your low-temperature processes first, as they present the greatest opportunity for improvement through waste heat recovery and integration with technologies like heat pumps.
- If your primary focus is process design: The thermal limits of your materials will be the deciding factor. Low-temperature processes are required for plastics, organics, and complex assemblies with adhesives.
- If your primary focus is decarbonization: Upgrading low-temperature heating systems away from fossil fuels provides the clearest and most technologically mature pathway to reducing your carbon footprint.
Ultimately, mastering the use of low-temperature heat is central to running an efficient, modern, and sustainable industrial operation.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Temperature Range | Common Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drying | Up to 250°C | Lumber, paper, food products | Moisture removal, preserves material |
| Curing | Up to 250°C | Vehicle coatings, adhesives | Hardens surfaces, enhances durability |
| Molding | Up to 250°C | Plastics shaping | Forms products without degradation |
| Pasteurizing | Up to 250°C | Food sterilization | Ensures safety, maintains quality |
Ready to optimize your low-temperature heating processes? Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our advanced high-temperature furnace solutions can be tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, helping you achieve superior efficiency and sustainability. Get in touch now to elevate your industrial operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
People Also Ask
- What happens to convective and radiative heat transfer effects at high furnace gas temperatures? Radiation Dominates for Superior Heating
- What technical requirements affect the external thermal strength of furnace tubes? Optimize for High-Temp Performance
- What are the key features of a quartz tube furnace? Discover High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- What is the necessity of using vacuum-sealed quartz tubes? Ensuring Integrity in Ti-Cu Alloy Heat Treatment
- What is the difference between an alumina tube furnace and a quartz tube furnace? Choose the Right Tube Furnace for Your Lab



















